Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2016; 22(41): 9247-9250
Published online Nov 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9247
Published online Nov 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9247
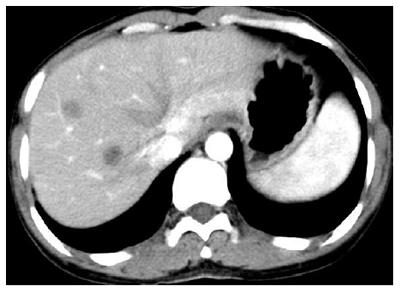
Figure 1 Abdominal contrast-enhanced computerized tomography findings.
Abdominal contrast-enhanced computerized tomography (CT) revealed multiple low density nodular lesions scattered in the liver parenchyma, involving the right lobe and left medial segment, with inhomogeneous enhancement.
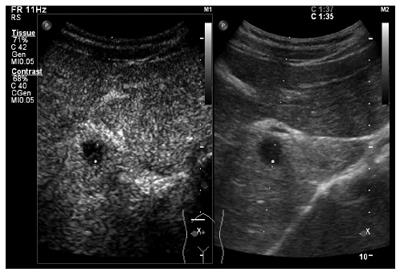
Figure 2 Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography findings.
Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography indicated multiple hypoechoic nodules with peripheral hyper-enhancement during the arterial phase and hypo-enhancement during the portal phase.
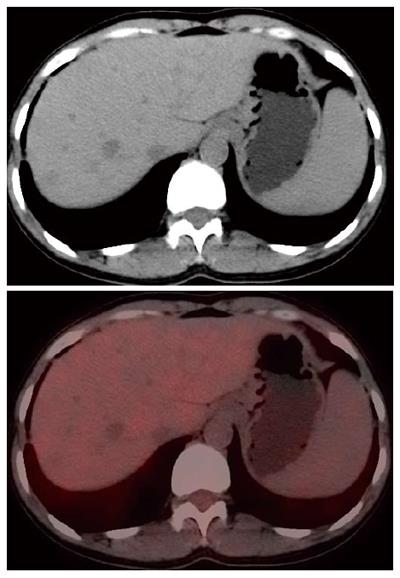
Figure 3 PET-CT findings.
PET-CT showed that the hepatic masses had low glycometabolism.
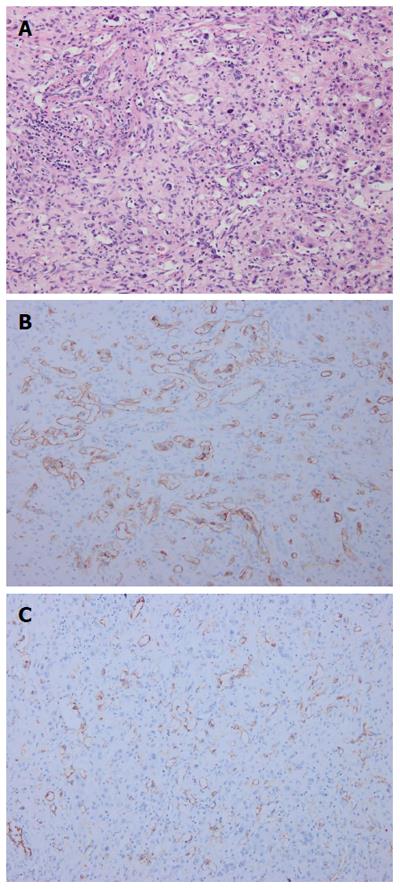
Figure 4 Pathological findings.
Pathological investigations identified hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A: Hematoxylin-eosin staining revealed abnormal hyperplasia of fibrous tissue combined with vessel-like formations, with scattered neoplastic epithelioid cells; B: Immunohistochemistry showed that the tumor was positive for CD34; C: Immunohistochemistry showed that the tumor was positive for CD31.
- Citation: Hu HJ, Jin YW, Jing QY, Shrestha A, Cheng NS, Li FY. Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: Dilemma and challenges in the preoperative diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(41): 9247-9250
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i41/9247.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9247