Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2016; 22(33): 7613-7624
Published online Sep 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i33.7613
Published online Sep 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i33.7613
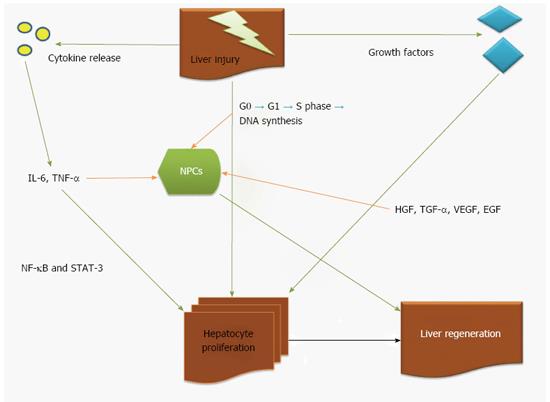
Figure 1 Mechanisms of liver regeneration after liver injury.
Green arrow indicates strong induction, orange arrow indicates secondary induction. NPCs: Non-parenchymal cells; IL-6: Interleukin-6; HGF: Hepatic growth factor; TGF-α: Tumor growth factor-alpha; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; VEGF: Vascular-endothelial growth factor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; STAT-3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription.
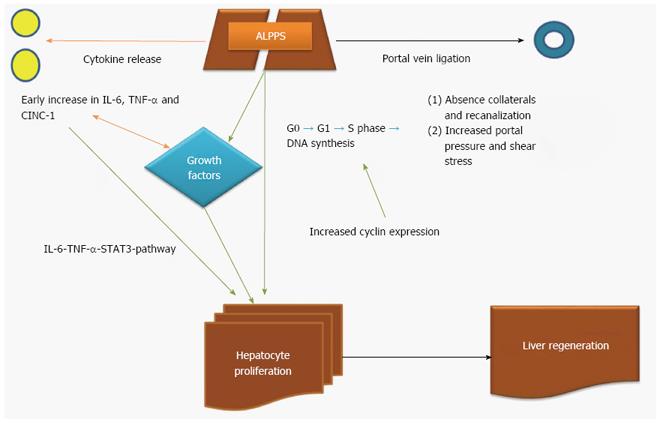
Figure 2 Mechanisms of liver regeneration after associating liver partition with portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy.
Green arrow indicates strong induction, orange arrow indicates secondary induction. IL-6: Interleukin-6; TGF-α: Tumor growth factor-alpha; STAT-3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; CINC-1: Cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant-1; ALPPS: Associating liver partition with portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy.
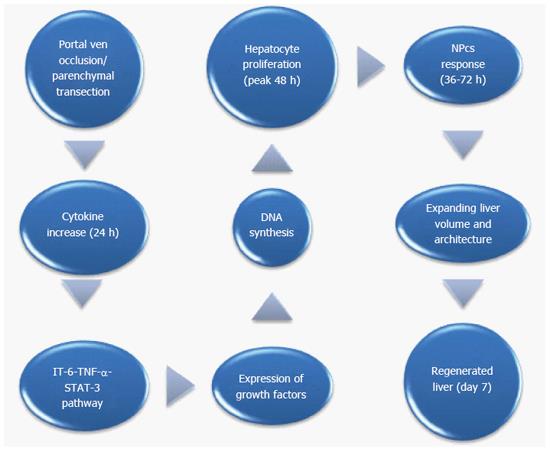
Figure 3 Cascade of mechanisms involved in liver regeneration after associating liver partition with portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy.
STAT-3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; NPCs: Non-parenchymal cells; IL-6: Interleukin-6.
- Citation: Moris D, Vernadakis S, Papalampros A, Vailas M, Dimitrokallis N, Petrou A, Dimitroulis D. Mechanistic insights of rapid liver regeneration after associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for stage hepatectomy. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(33): 7613-7624
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i33/7613.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i33.7613