Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2016; 22(14): 3712-3724
Published online Apr 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3712
Published online Apr 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3712
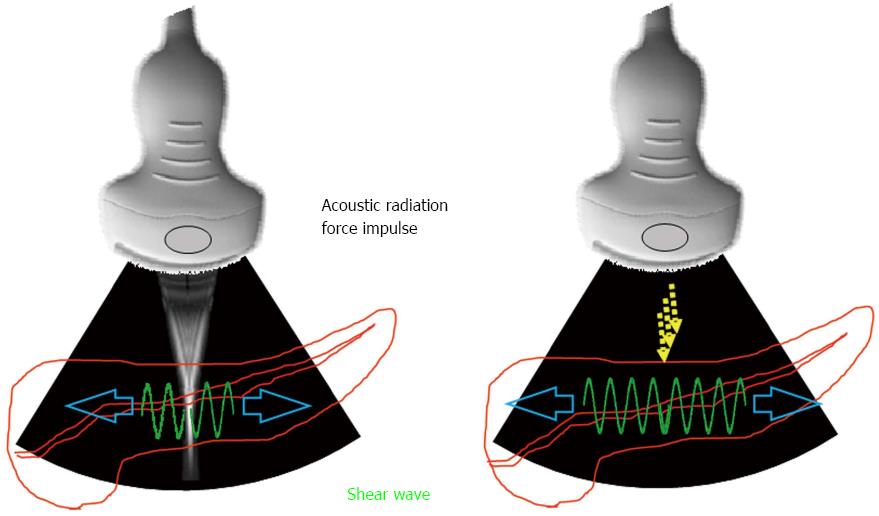
Figure 1 Measurement principle of shear wave elastography.
Acoustic radiation force impulse is emitted from the probe to the target tissue. Accordingly, the transverse wave, so-called shear wave, is generated. The propagation speed of shear wave is measured by the detection pulse transmitted from the probe.
Figure 2 Qualitative diagnosis in US-Real-time Tissue ElastographyTM.
A hypoechoic tumor was seen at the pancreatic tail in B-mode (right). In Real-time Tissue ElastographyTM, blue color is seen on the tumor, green color is seen on non-tumorous area of the pancreas, and red color is seen at ventral side of the pancreas (left).
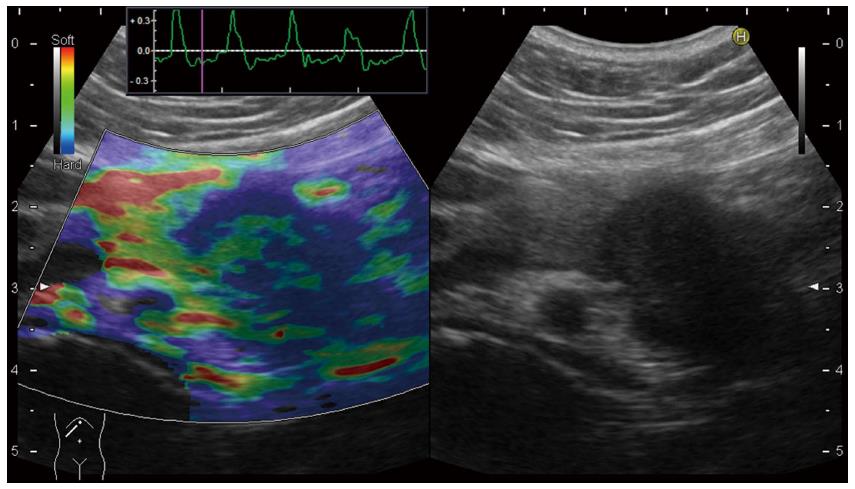
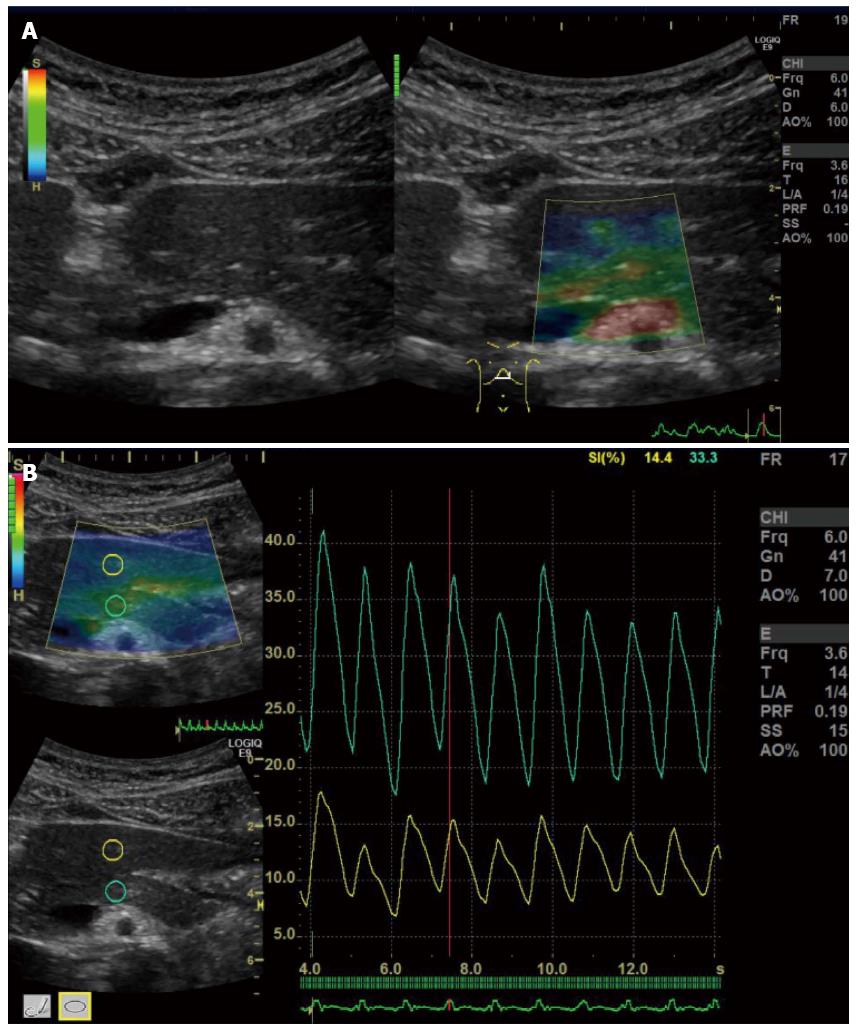
Figure 3 Quantitative diagnosis in US-Real-time Tissue ElastographyTM.
A hypoechoic tumor is seen at the pancreatic tail in B-mode (right). Region of interest (ROI) [A] is set on the tumor, and ROI [B] is set on read area around the pancreas (left). By setting ROI [A] and [B], strain [A], strain [B], and strain ration [B/A] were calculated automatically and displayed at the bottom of the screen (left).
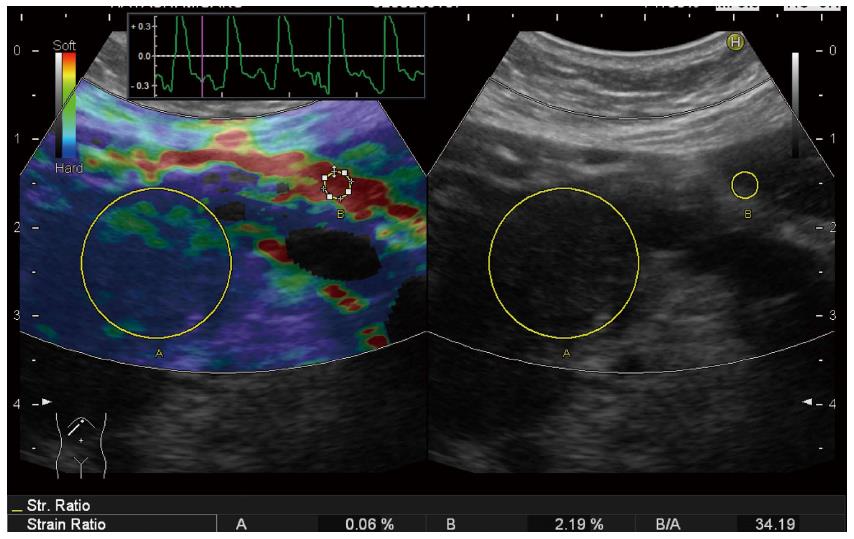
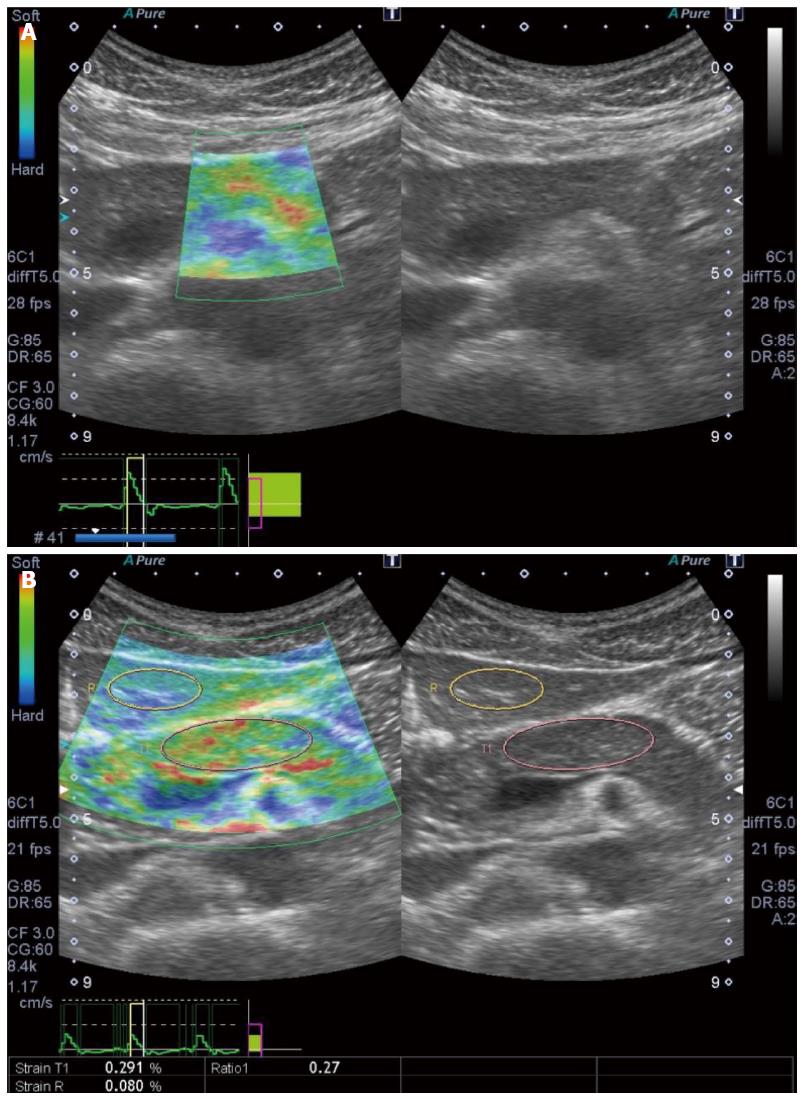
Figure 4 Setting the different reference area in a case of pancreatic tail tumor.
Strain ratio quite differs according to the reference area: When the reference area is set on non-tumorous area of the pancreas, strain ration is calculated as 13.67 (upper). When the reference area was set on read area around the pancreas, strain ration is calculated as 46.62.
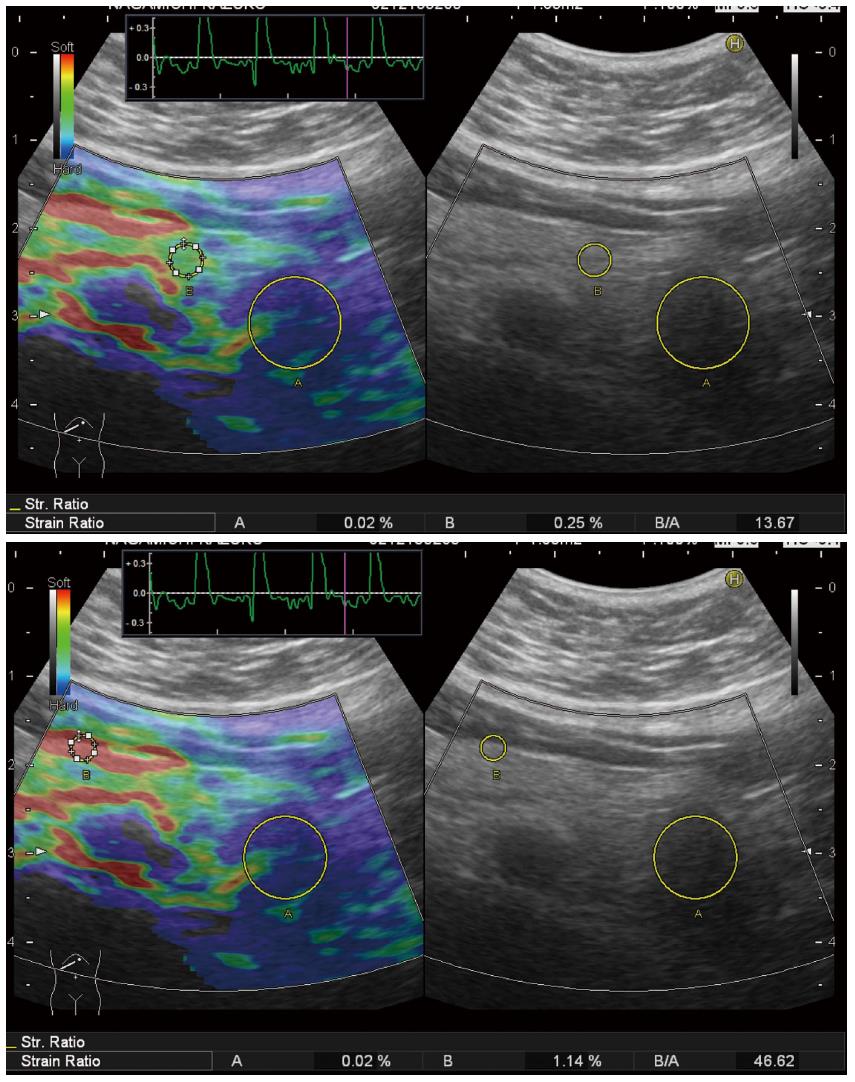
Figure 5 ElastographyTM.
A: Elastography (GE) is performed for a normal pancreas; B: Strain ration can be calculated by setting the reference area.
Figure 6 ElastographyTM (Toshiba).
A: Elastography (Toshiba) is performed for a normal pancreas; B: Strain ration can be calculated by setting the reference area.
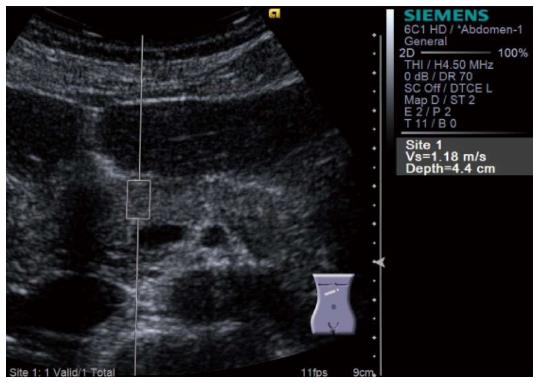
Figure 7 Virtual Touch QuantificationTM (Siemens) performed for the pancreatic head.
Region of interest is set on the pancreatic head. Subsequently, acoustic radiation force impulse is emitted by pressing the button, and shear wave velocity (m/s) is displayed in the right side of the screen in a few seconds.
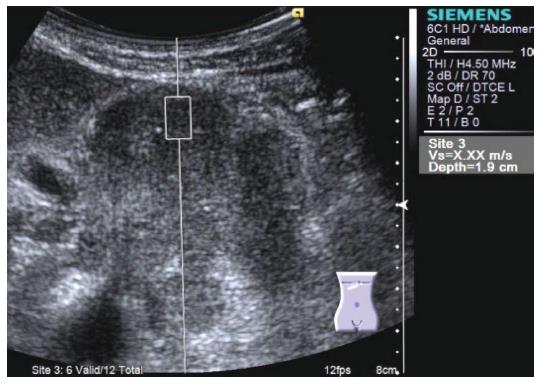
Figure 8 Virtual TouchTM Quantification (Siemens) performed for a large tumor at the pancreatic body.
Shear wave velocity cannot be measured because the tumor is too hard. X,XX m/s is displayed in the right side of the screen instead of digits.
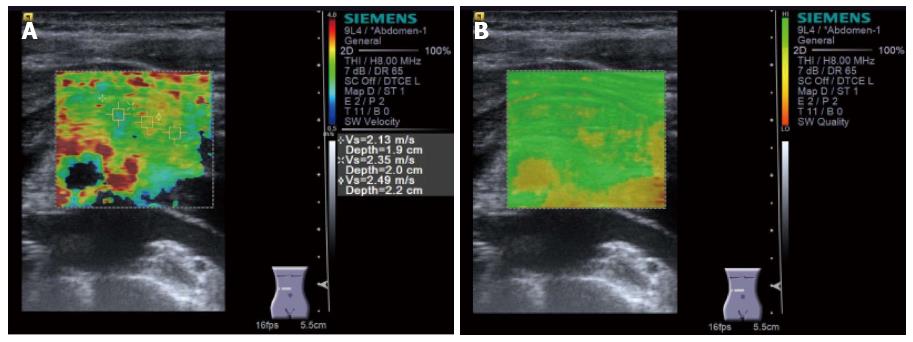
Figure 9 Virtual TouchTM IQ (Siemens) performed for a pancreatic body tumor.
Because only linear probe can be used, Virtual TouchTM IQ (VTIQ) cannot be performed for the case in which the pancreas locates deep from the body surface. Shear wave velocity can be measured post hoc at the point wherever desired (upper). In quality mode, the degree of confidence in measurement is seen for each point (lower). Green color shows the point where shear wave velocity is measured with high confidence.
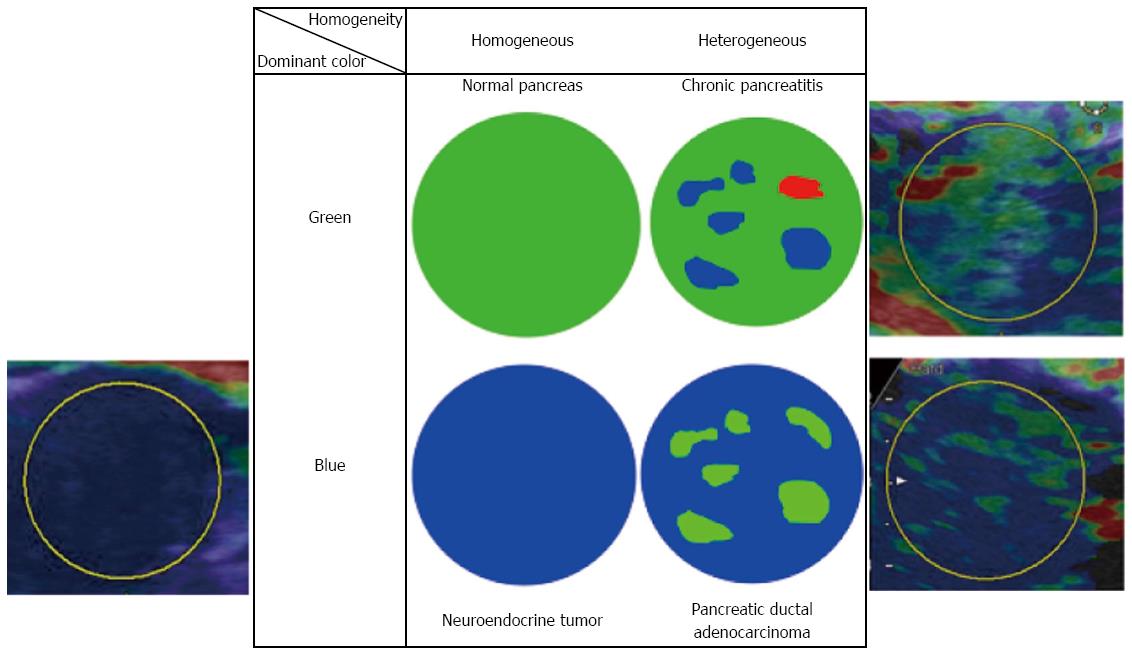
Figure 10 A representative qualitative diagnostic criteria in Real-time Tissue ElastographyTM (Hitachi-Aloka).
Dominant color and homogeneity of color are evaluated in most reports. The representative histology estimated by each combination of color and homogeneity are shown.
- Citation: Kawada N, Tanaka S. Elastography for the pancreas: Current status and future perspective. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(14): 3712-3724
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i14/3712.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3712