Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2015; 21(9): 2746-2753
Published online Mar 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2746
Published online Mar 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2746
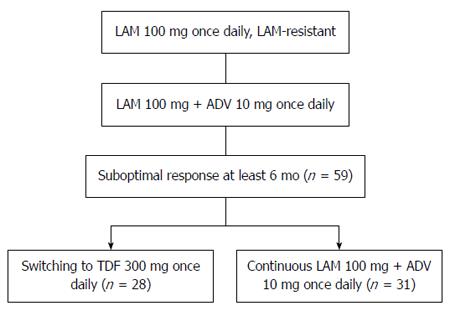
Figure 1 Flow diagram comparing switching to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate monotherapy and continued lamivudine plus adefovir in lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B patients with a suboptimal response to lamivudine plus adefovir.
LAM: Lamivudine; ADV: Adefovir; TDF: Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
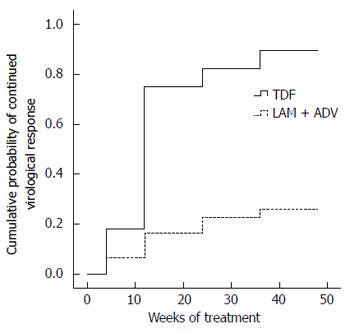
Figure 2 Comparison of cumulative probability of complete virological response in patients undergoing therapy with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate or lamivudine plus adefovir.
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) alone is represented by the medium weight line; lamivudine plus adefovir (LAM plus ADV) combination is shown by the dotted line; and both arms by the dashed line (P < 0.001). Baseline serum HBV DNA level showed no difference (P = 0. 639). LAM: Lamivudine; ADV: Adefovir; HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
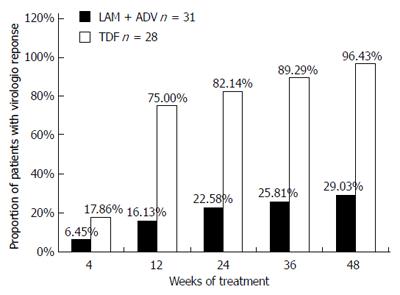
Figure 3 Proportions of patients exhibiting virological response (serum Hepatitis B virus DNA concentration < 103 copies/mL) in the tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and lamivudine plus adefovir treatment groups.
No significant difference was noted at 4 wk between the two groups (P > 0.05). The rate of undetectability was significantly greater in the tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) group than in the lamivudine plus adefovir (LAM plus ADV) group at 12, 24, 36, and 48 wk (P < 0.001). LAM: Lamivudine; ADV: Adefovir.
- Citation: Yang DH, Xie YJ, Zhao NF, Pan HY, Li MW, Huang HJ. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is superior to lamivudine plus adefovir in lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B patients. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(9): 2746-2753
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i9/2746.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2746