Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2015; 21(8): 2367-2373
Published online Feb 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2367
Published online Feb 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2367
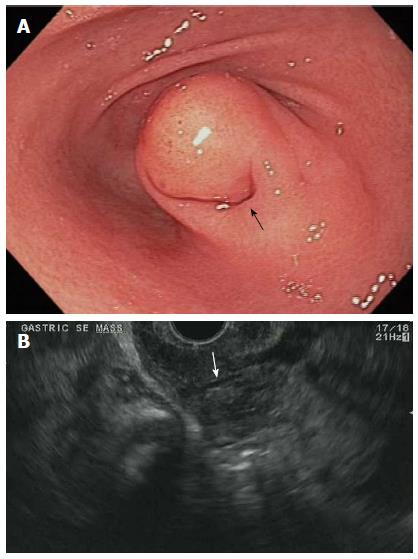
Figure 1 Esophagogastroduodenoscopy and endoscopic ultrasound evaluation of gastric ectopic pancreas.
A: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy image showing subepithelial lesions (SEL) in the antrum with overlying dimple (arrow); B: Endoscopic ultrasound image showing gastric SEL with intra-lesional duct (arrow).
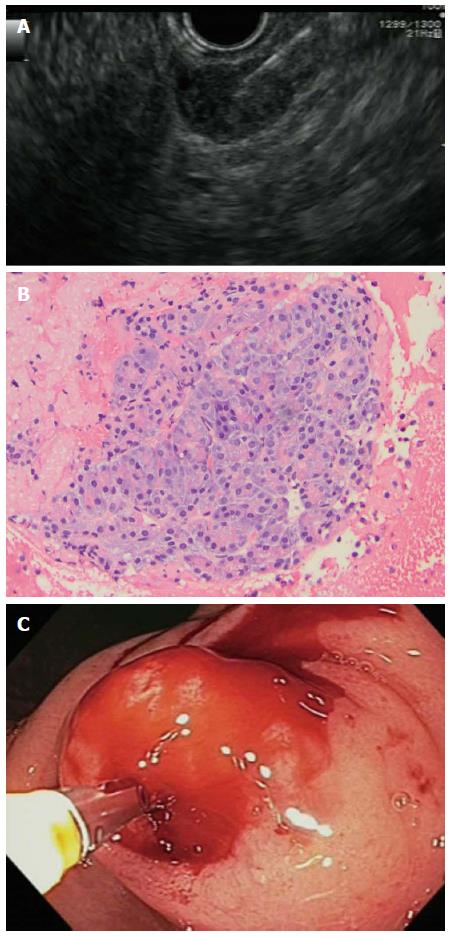
Figure 2 Endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisitions for ectopic pancreas.
A: Endoscopic ultrasound-fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) of gastric ectopic pancreas (EP) lesion; B: Cell block cytology image showing classic cytologic features of EP including pancreatic acini, magnification × 20; C: Endoscopic deep biopsy of EP lesion.
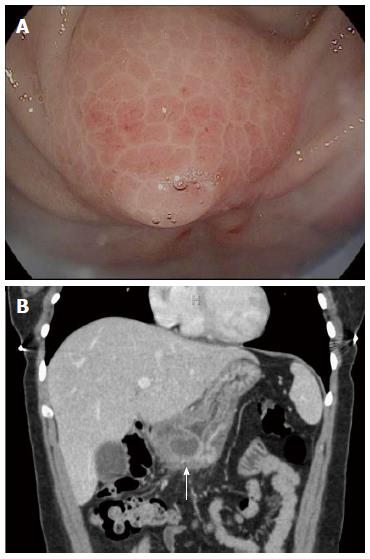
Figure 3 Exam findings consistent with acute ectopic pancreatitis in a 26 year-old female with recurrent epigastric pain.
A: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy image showing subepithelial lesions (SEL) in antrum with overlying erythema and edema; B: Computed tomography scan image showing SEL in antrum of stomach with localized inflammatory reaction (arrow).
- Citation: Attwell A, Sams S, Fukami N. Diagnosis of ectopic pancreas by endoscopic ultrasound with fine-needle aspiration. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(8): 2367-2373
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i8/2367.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2367