Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2015; 21(29): 8964-8973
Published online Aug 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i29.8964
Published online Aug 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i29.8964
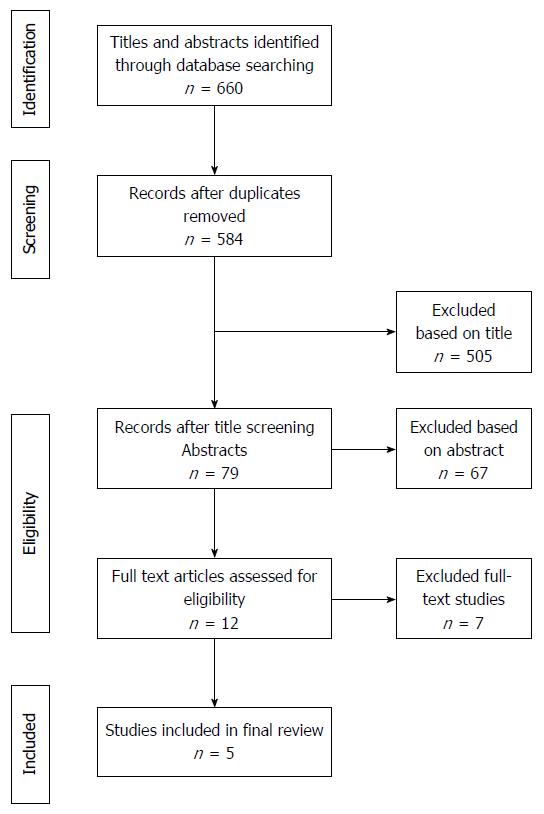
Figure 1 Flowchart of trials.
Flowchart of search string.
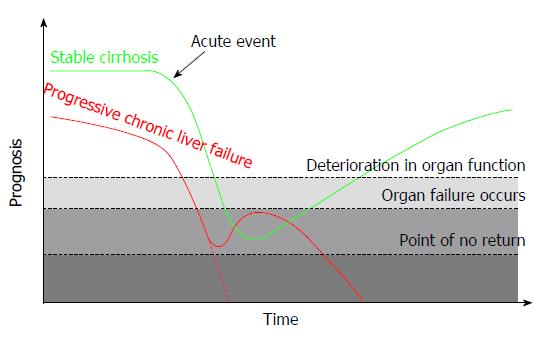
Figure 2 Acute on Chronic Liver Failure.
The green line illustrates a patient with stable cirrhosis (i.e., Child-Pugh class A/B) developing acute on chronic liver failure (ACLF). The red line illustrates a patient with progressive chronic liver failure (i.e., a patients with Child C cirrhosis and refractory ascites) developing ACLF. The Y-axis (Prognosis) is based on Child Pugh score or MELD score and the performance status before ACLF develops and CLIF-SOFA score after ACLF. The threshold “deterioration in organ function” represents a level with i.e. increase in creatinine or oxygen demand without organ failure. The threshold “organ failure” is as defined in the CLIF-SOFA score and “point of no return” is a state of multiorgan failure without reversibility.
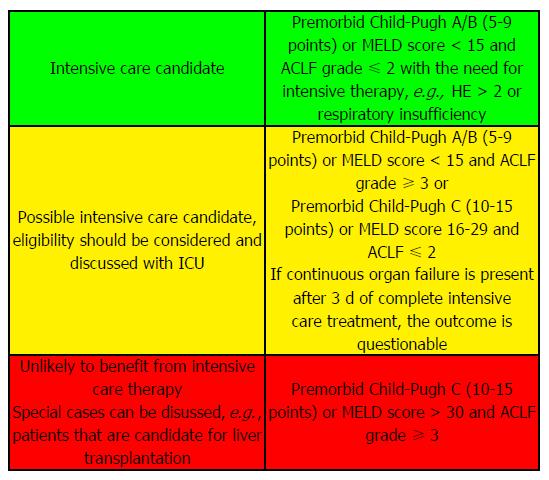
Figure 3 Proposal of a clinical system to identify candidates for intensive care if indicated.
Algorithm based on three scoring systems: Child-Pugh Score, Model of End stage Liver Disease score (MELD) and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score (CLIF-SOFA). ACLF: Acute on chronic liver failure; ICU: Intensive care unit.
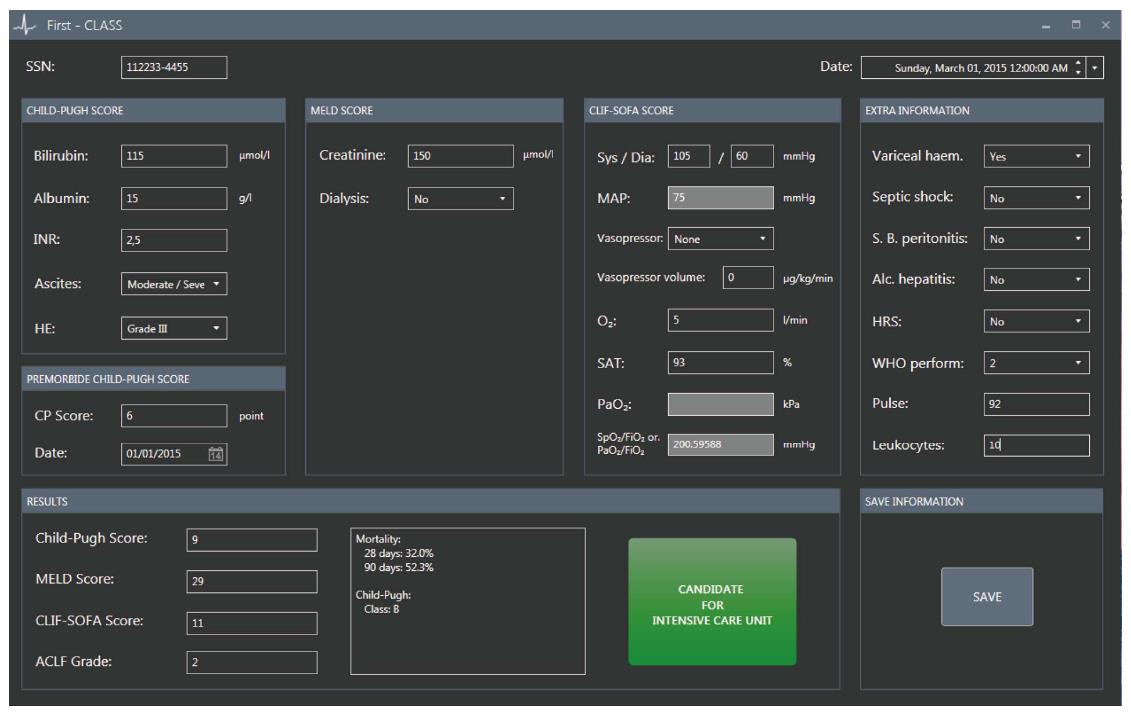
Figure 4 First Chronic Liver Allocation Scoring system.
Danish civil registration number, a unique 10-digit personal identification number assigned to every Danish citizen at birth since 1968. HE: Hepatic encephalopathy; CP Score: Child Pugh Score; MAP: Mean arterial pressure; SAT: Oxygen saturation (%); Varice Haemorr: Variceal haemorrhage; S.B. Peritonitis: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis; Alko. Hepatitis: Alcoholic hepatitis; HRS: Hepato renal syndrome; WHO Perform: WHO performance status; ACLF grade: Acute on chronic liver failure grade; First-CLASS: First Chronic Liver Allocation Scoring System; SSN: Social Security Number.
- Citation: Lindvig KP, Teisner AS, Kjeldsen J, Strøm T, Toft P, Furhmann V, Krag A. Allocation of patients with liver cirrhosis and organ failure to intensive care: Systematic review and a proposal for clinical practice. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(29): 8964-8973
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i29/8964.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i29.8964