Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2015; 21(24): 7598-7603
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7598
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7598
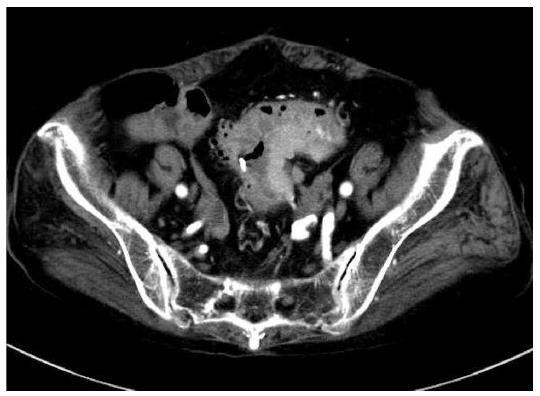
Figure 1 Computed tomography of abdomen.
Computed tomography scan showed a mass measuring 5 cm in diameter, multiple diverticula in the sigmoid colon and enlarged lymph nodes in the sigmoid mesentery.
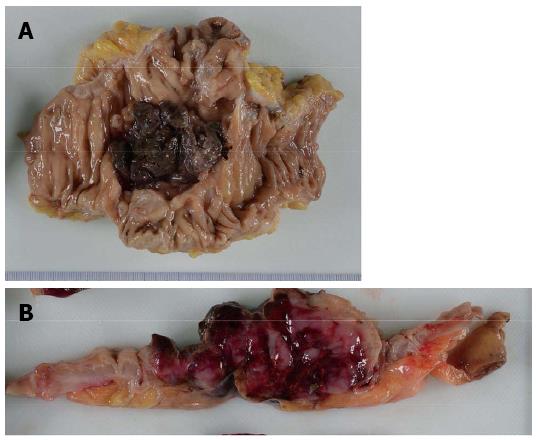
Figure 2 Gross appearance of the primary tumor lesion.
A: A tumor (5 cm in diameter) is present in the sigmoid colon. Coagulation is on the surface; B: The tumor showed hemorrhage on the surface and a white mass within and was soft in consistency.
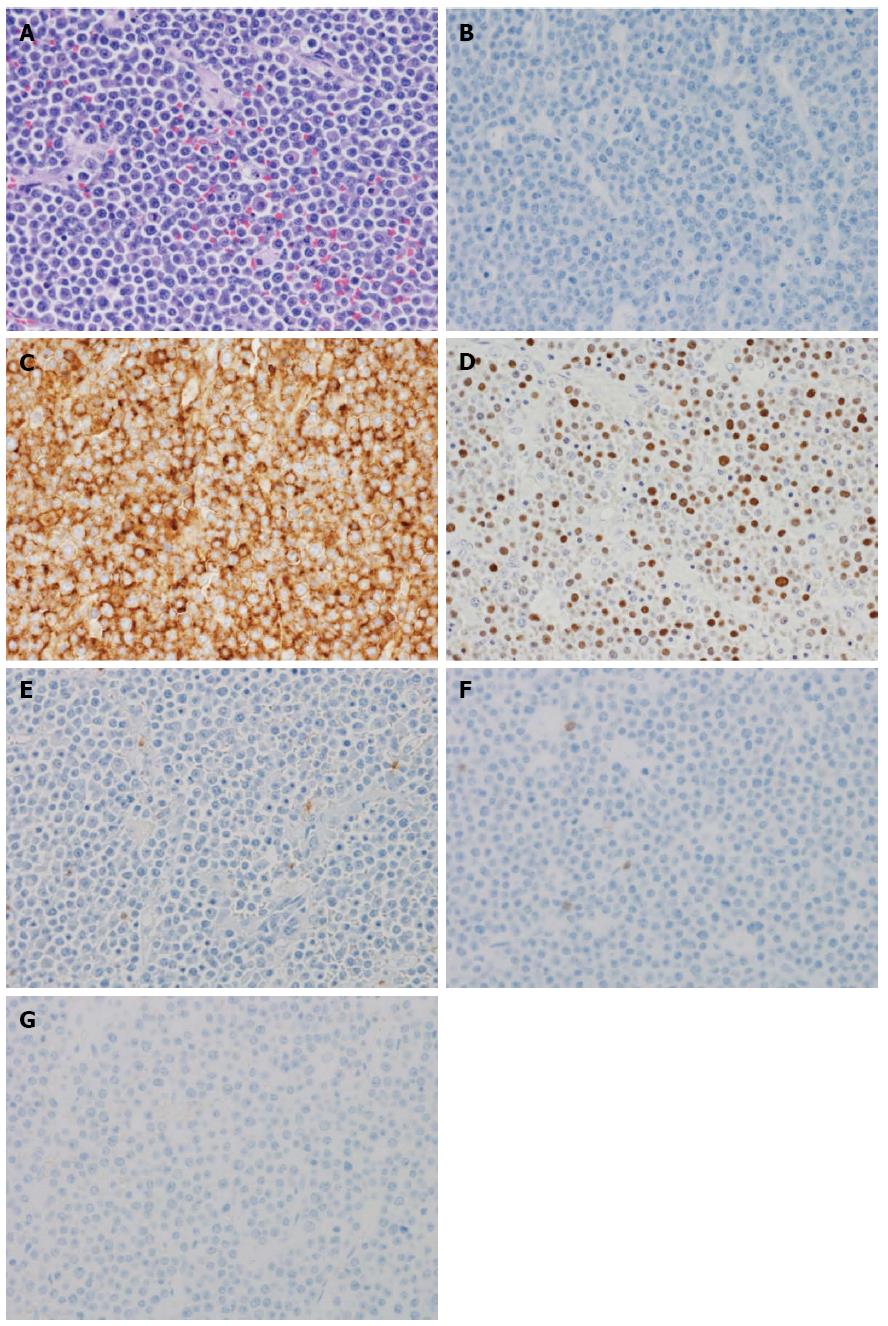
Figure 3 Plasmablastic lymphoma of the sigmoid colon.
A: Tumor cells have large hyperchromatic nuclei with prominent nucleoli. Some tumor cells showed plasmacytic differentiation [hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, original magnification × 400]; B: The atypical cells are negative for the B-cell marker CD20 (original magnification × 400); C: The atypical cells are diffusely positive for the plasma cell marker CD138 (original magnification × 400); D: The nuclei of the atypical cells are positive for EBER, which is Epstein-Barr encoded RNA (original magnification × 400); E: The atypical cells are negative for the leukocyte common antigen CD45RO (UCHL1) (original magnification × 400); F: The atypical cells are negative for the T-cell marker CD3 (original magnification × 400); G: The atypical cells are negative for the pan-B-cell marker CD79a (original magnification × 400).
- Citation: Haramura T, Haraguchi M, Irie J, Ito S, Tokai H, Noda K, Kitajima M, Minami S, Inoue K, Sasaki Y, Oshima K, Eguchi S. Case of plasmablastic lymphoma of the sigmoid colon and literature review. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(24): 7598-7603
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i24/7598.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7598