Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2015; 21(24): 7400-7411
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7400
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7400
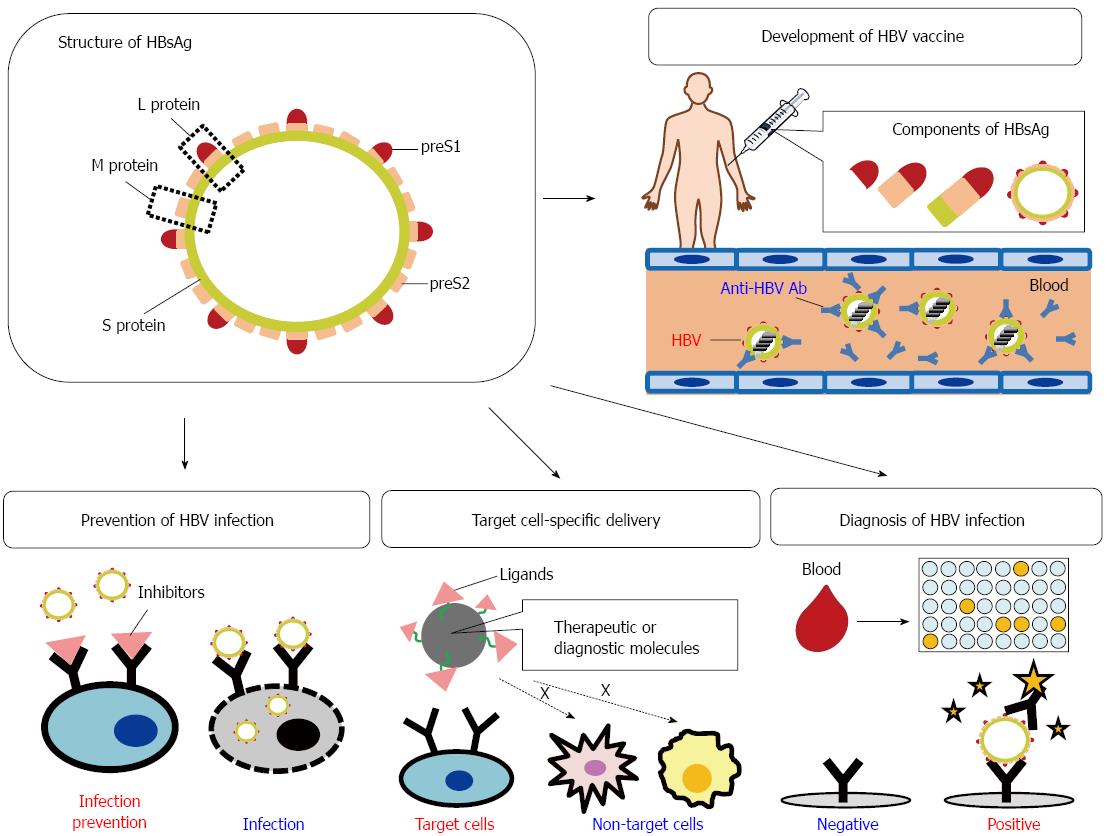
Figure 1 Hepatitis B surface antigen consists of the S protein, M protein (S and preS2 proteins), and L protein (S, preS1, and preS2 proteins).
In hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), the preS domain (preS1 + preS2) plays a key role in the human hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection of hepatocytic cells by facilitating HBV attachment and entry, and contains several immunogenic T- and B-cell epitopes. Therefore, the preS domain containing HBV-binding sites and immunogenic epitopes is a diagnostic and therapeutic target or material. In fact, several diagnostic and therapeutic materials and systems based on preS have been developed, including inhibitors of HBV infection, HBV vaccines, diagnostic tools for HBV infection, and hepatocyte-targeting delivery systems for diagnostic and therapeutic molecules.
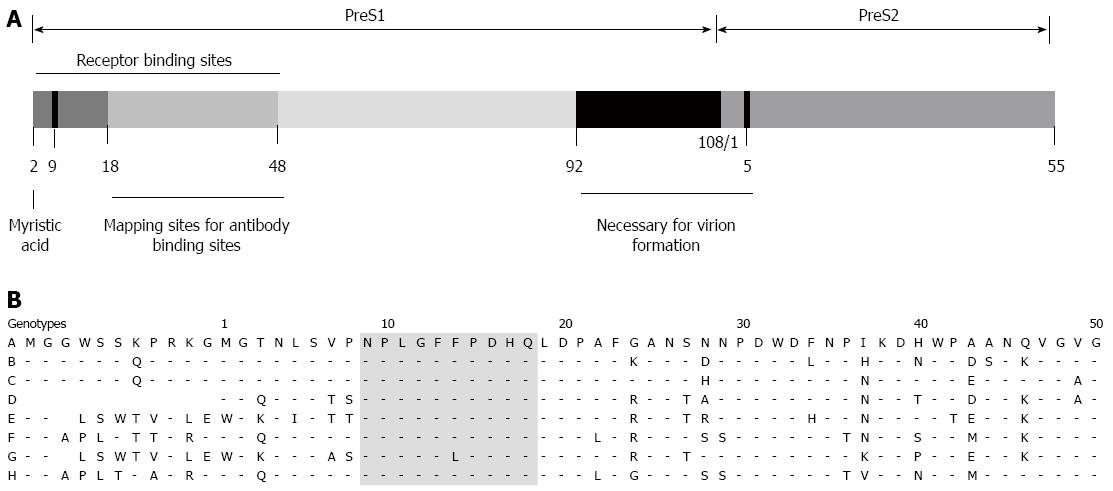
Figure 2 Scheme of the preS domain (preS1 + preS2) and PreS1 sequence.
A: Schematic representation of the preS domain containing HBV attachment sites, antibody-binding sites, and sites for virion formation (modified from Ref.[7]). The receptor-binding sites are important in hepatitis B virus (HBV) attachment and entry, and the antibody-binding sites for developing preS1-specific antibodies and HBV vaccines; B: PreS1 sequence (aa 1-50) in different HBV genotypes (A-H), obtained from ref.[12]. The essential residues for receptor binding (aa 9-18) are very similar in genotypes A-H (gray).
- Citation: Toita R, Kawano T, Kang JH, Murata M. Applications of human hepatitis B virus preS domain in bio- and nanotechnology. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(24): 7400-7411
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i24/7400.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7400