Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2015; 21(20): 6157-6166
Published online May 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6157
Published online May 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6157
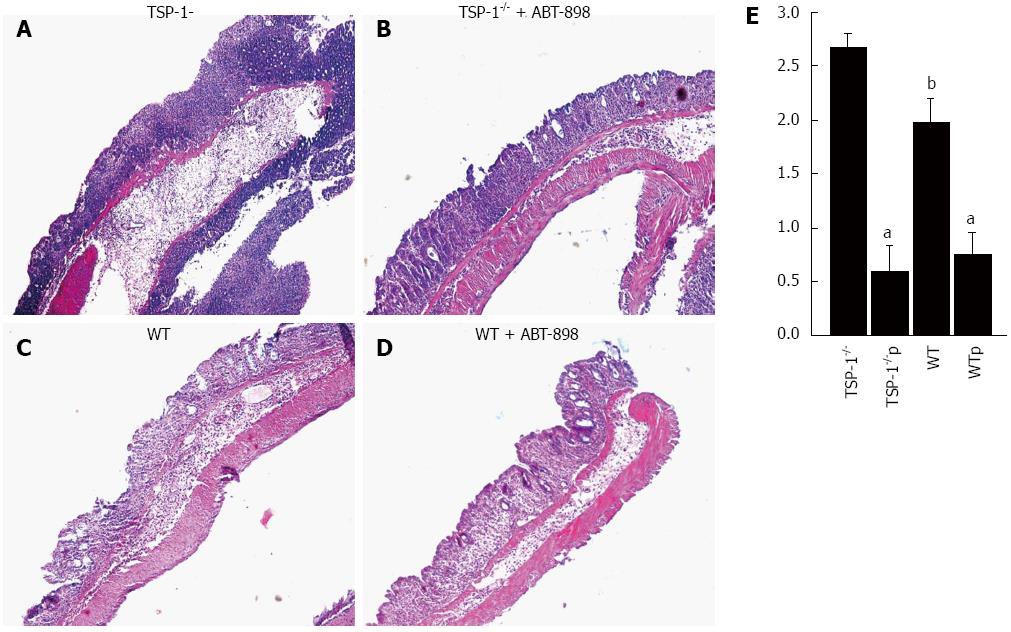
Figure 1 Effects of the TSP-1 mimetic peptide ABT-898 in inflammation.
Inflammation was graded by evaluating hematoxylin-eosin stained sections in a blindly fashion (A-D). Sections from colons of TSP-1-/- mice with DSS and treated with 5% glucose (A), sections from colons of TSP-1-/- mice treated with ABT-898 (B), colonic sections from WT mice treated with 5% glucose (C) and with the peptide ABT-898 only (D). The peptide ABT-898 significantly reduced the leukocytic infiltration in both, WT and TSP-1-/- colitic lesions when compared with their controls (E). TSP-1-/- mice controls (A) displayed more inflammation that WT controls (C). aP < 0.0001 and bP < 0.05 vs control. TSP-1-/-: TSP-1-/- controls; TSP-1-/-p: TSP-1-/-treated with the ABT-898 peptide; WT: WT control; WTp: WT treated with the ABT-898 peptide.
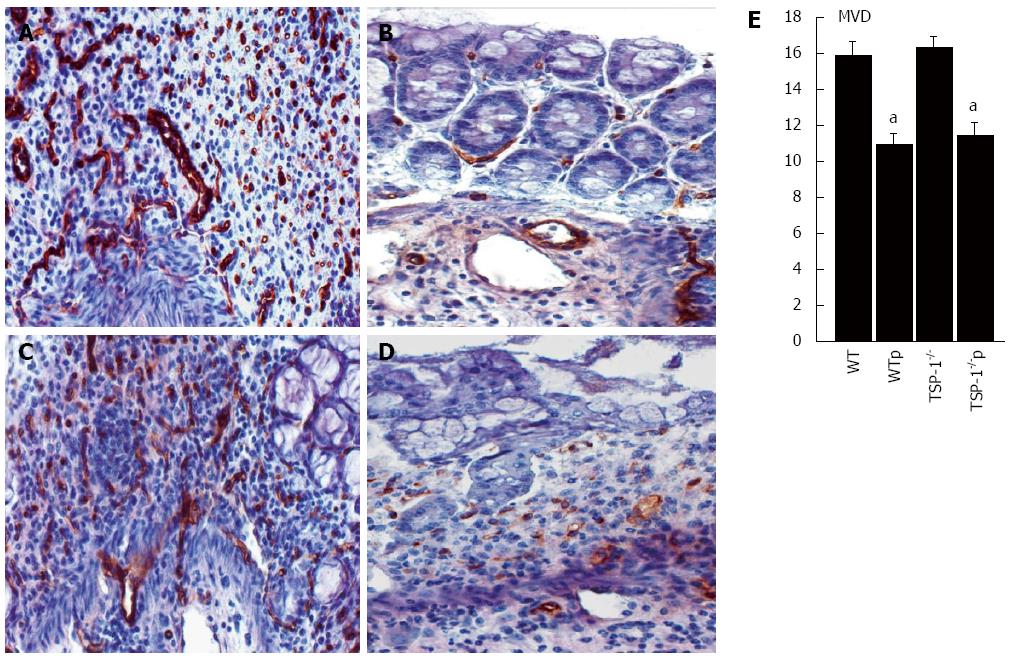
Figure 2 Effects of the TSP-1 mimetic peptide ABT-898 on microvascular density in colons with dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis.
Combined immunohistochemistry against the endothelial markers CD31 and MECA 34 (brown staining) was performed to analyze the vascular density in colitic lesions (A-D). Evaluation of vascular density in TSP-1-/- colonic sections from mice treated with 5% glucose (A), and ABT-898 (B), WT mice controls (C), and the ABT-898 peptide (D). Sections from mice receiving the ABT-898 peptide showed a significant decrease in microvascular density (MVD) vs controls (E) (P < 0.0001 for TSP-1-/- colons and P = 0.0048 for WT). aP < 0.0001 vs control. TSP-1-/-: TSP-1-/- controls; TSP-1-/-p: TSP-1-/- treated with ABT898; WT: WT control; WTp: WT treated with ABT-898 peptide.
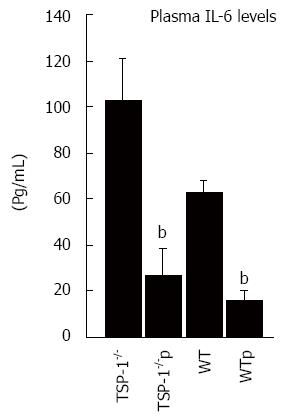
Figure 3 Interleukin-6 protein levels in plasma of mice under dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis.
Interleukin (IL)-6 levels were analyzed using sandwich-based ELISA. Elevated levels of IL-6 were detected in WT and TSP-1-/- plasma samples of mice treated with DSS for 7 d receiving saline injections (P = 0.0114). IL-6 was significantly diminished in plasma of TSP-1-/- treated with the peptide (P = 0.0002) and WT samples under the same treatment (P = 0.0148). bP < 0.05 vs control. Error bars represent SEM. The results shown are representative of three or more independent experiments. TSP-1-/-: TSP-1-/- controls; TSP-1-/-p; TSP-1-/- with ABT-898 peptide; WT: WT control; WTp: WT treated with ABT-898 peptide.
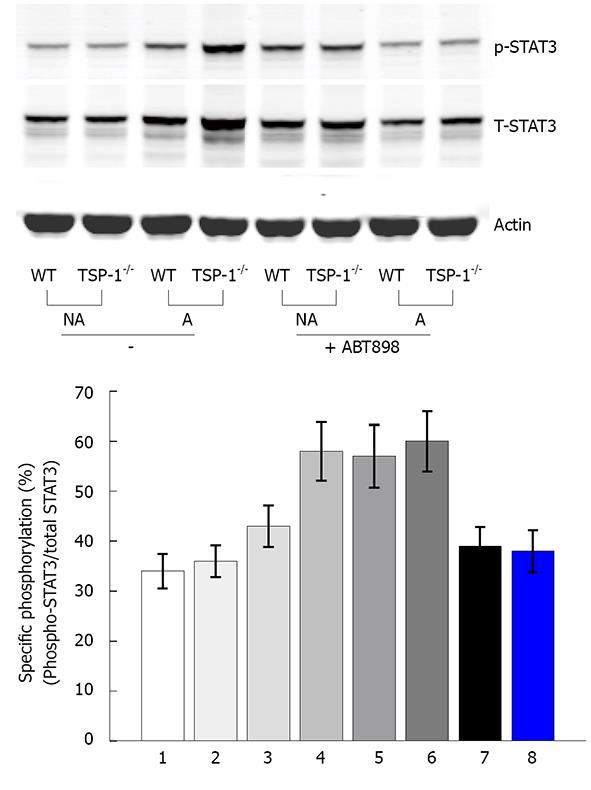
Figure 4 Activation of STAT3 by Western blotting.
Tissue lysates were prepared as described in “MATERIALS AND METHODS”, equal amounts of protein (80 μg) were resolved by 4%-12% SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blot with antibodies against STAT3, phosphorylated STAT3 (pSTAT3) (Ser727) and actin, respectively (bottom panel). STAT3 activation under acute colitis induced by DSS and the effects of the ABT-898 peptide on STAT3 activation during DSS-induced acute colitis; Top panel shows the specific phosphorylation of STAT3 from three repeated Western blots as represented by the bottom panel. The average values with standard deviations are showed. NA: Not affected colon tissue (no DSS); A: DSS induced colon tissue; TSP-1-/-: TSP-1-/- controls; TSP-1-/-p: TSP-1-/- treated with ABT-898 peptide; WT: WT control.
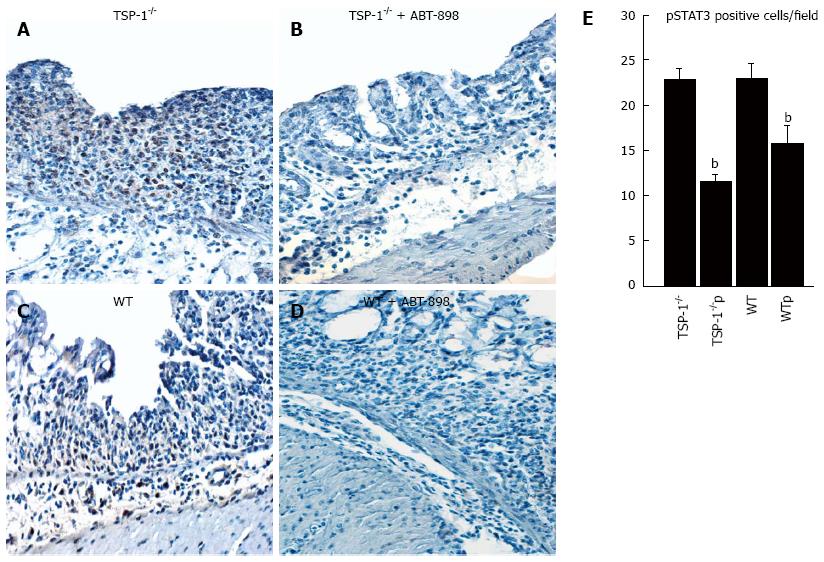
Figure 5 Activation of STAT3 by immunohistochemistry.
Immunohistochemistry for pSTAT3, in colitic tissues of TSP-1-/- controls (A), TSP-1-/- colonic tissues treated with ABT-898 (B), colons from WT mice (C) and from WT mice treated with the ABT-898 peptide (D), pSTAT3 positive brown staining was detected in the nucleus of epithelial cells and infiltrating leukocytes. Quantification of pSTAT3 positive cells was performed in colonic sections (E). Colons from WT and TSP-1-/- mice used as control showed higher numbers of positive cells when compared to mice treated with ABT-898. bP < 0.05 vs control. NS: Not significant; TSP-1-/-: TSP-1-/- controls; TSP-1-/-p: TSP-1-/- treated with ABT-898 peptide; WT: WT control; WTp: WT treated with ABT-898 peptide.
- Citation: Gutierrez LS, Ling J, Nye D, Papathomas K, Dickinson C. Thrombospondin peptide ABT-898 inhibits inflammation and angiogenesis in a colitis model. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(20): 6157-6166
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i20/6157.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6157