Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2015; 21(10): 2918-2925
Published online Mar 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2918
Published online Mar 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2918
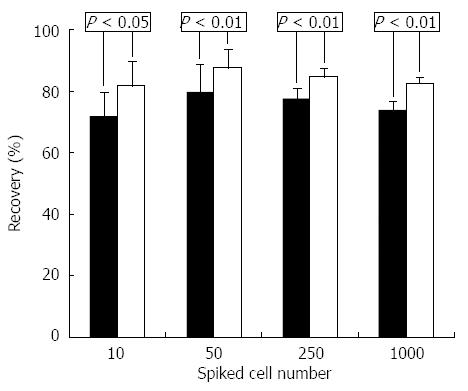
Figure 1 Flow cytometric analysis.
Recovery of spiked HepG2 human liver cancer cells from blood samples using depletion of CD45+ leukocytes (white bars) and asialoglycoprotein receptor-positive selection (black bars).
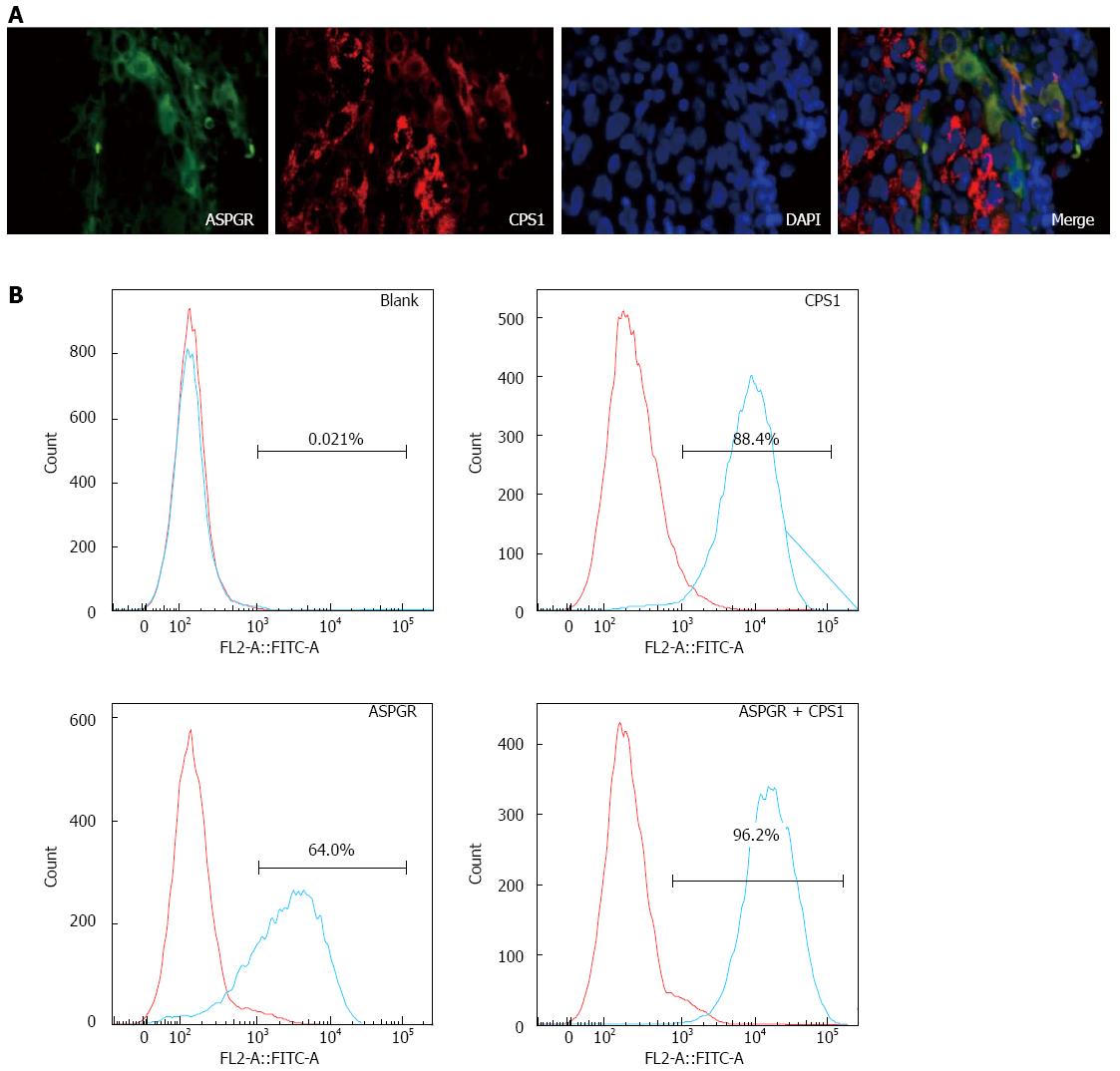
Figure 2 Immunofluorescence with hepatic antibody cocktail.
A: Immunofluorescence staining of human hepatocellular carcinoma tissue with anti-asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASPGR; green) and anti-carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1; red) antibodies and costained with DAPI (blue) (magnification × 400); B: ASGPR+ and CPS1+ cells were analyzed by flow cytometry of Hep3B human liver cancer cells.
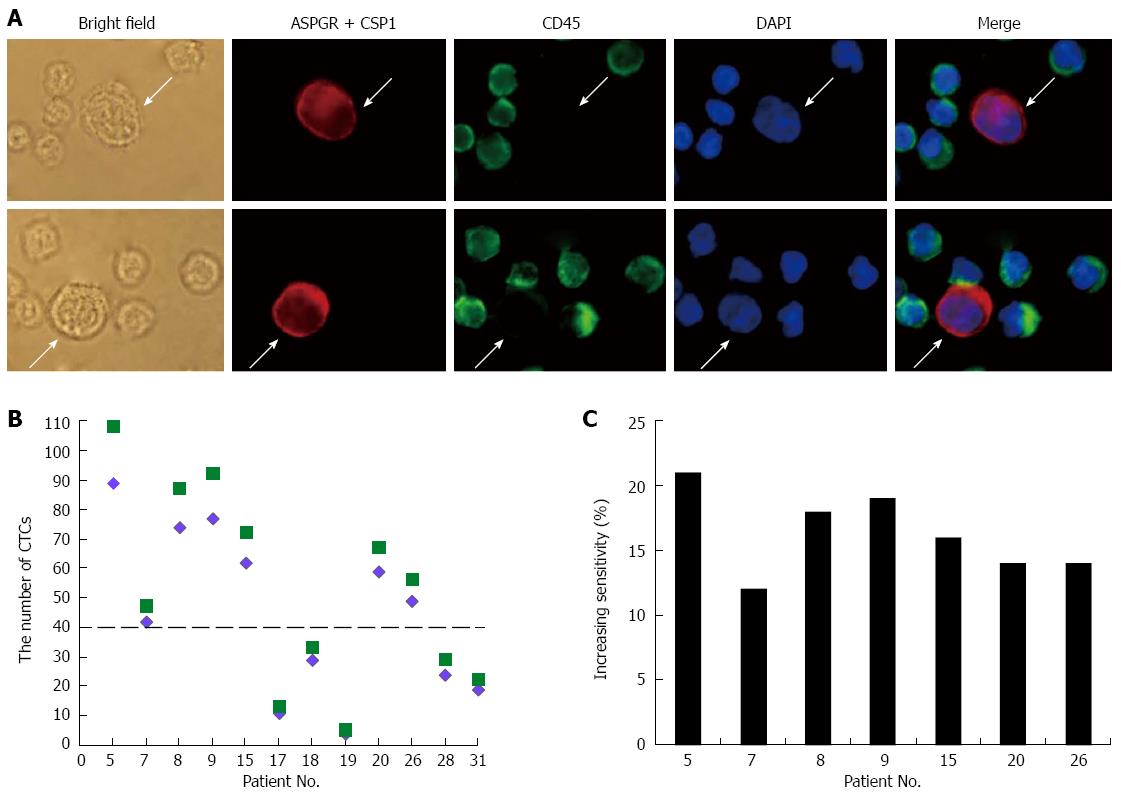
Figure 3 Improved circulating tumor cell detection sensitivity.
A: Immunofluorescence staining of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) (arrow) detected in blood from hepatocellular carcinoma patients with antibodies against asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASPGR) and/or carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CSP1) (red), and CD45 (green) with nuclear DAPI staining (blue) (magnification × 400); B: CTC numbers detected in the same HCC patients using the currently described method of CD45+ depletion and ASPGR+/CSP1+ immunostaining (green squares) and a previously described method with ASPGR+ selection followed by staining with cytokeratin and CSP1 antibodies (purple diamonds); C: The current method showed higher detection sensitivity in all patients with > 40 CTCs.
- Citation: Liu HY, Qian HH, Zhang XF, Li J, Yang X, Sun B, Ma JY, Chen L, Yin ZF. Improved method increases sensitivity for circulating hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(10): 2918-2925
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i10/2918.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2918