Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2014; 20(8): 2091-2097
Published online Feb 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.2091
Published online Feb 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.2091
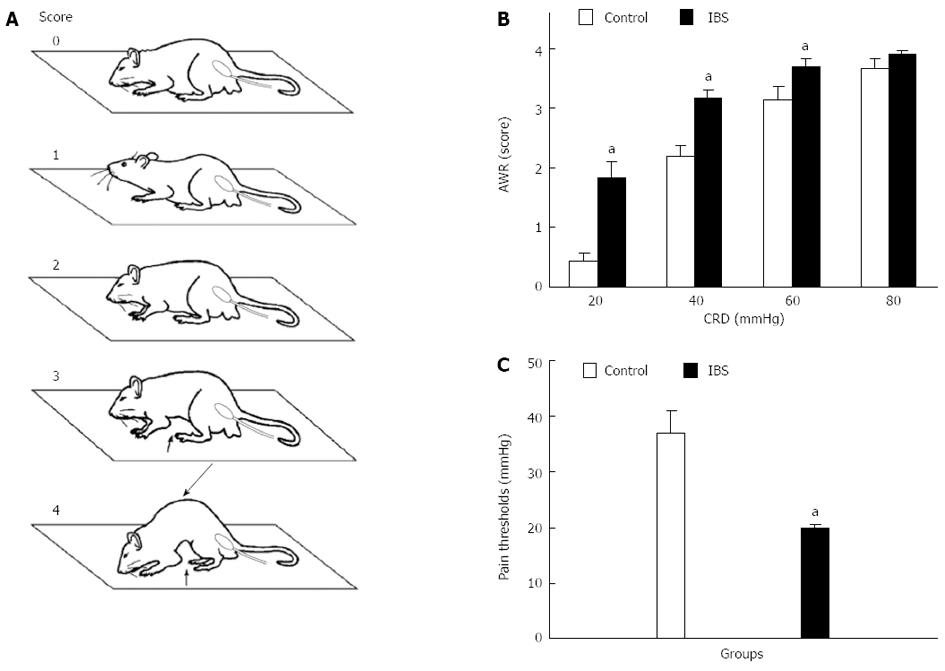
Figure 1 Behavioral evaluation of visceral pain.
A: Schematic drawings illustrating the visually based behavioral scale of the abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) in response to graded colorectal distension (CRD). AWR scores are 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4; B: AWR scores of control and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)-like rats; C: Pain thresholds measured by AWR in rats. The AWR threshold indicates CRD intensity when the AWR score is 3. aP < 0.05 compared with control rats.
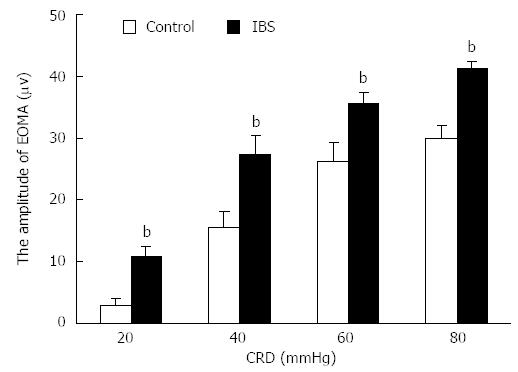
Figure 2 Electromyographic responses to colorectal distension in rats.
The average responses to graded colorectal distension (CRD) were significantly increased in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)-like rats compared with control rats. bP < 0.01, compared with control rats at the same CRD intensity. EOMA: External oblique muscle of the abdomen.
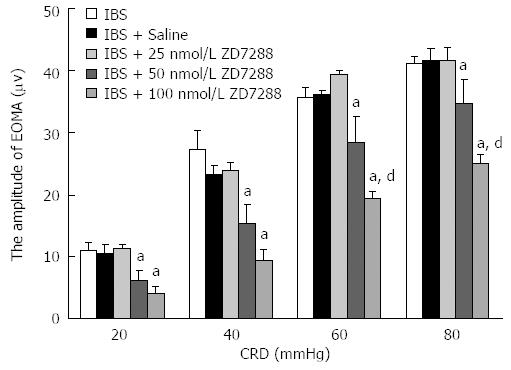
Figure 3 Inhibitory effects of ZD 7288 on amplitudes of external oblique muscle of the abdomen in irritable bowel syndrome-like rats.
aP < 0.05, compared with saline-treated irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)-like rats; dP < 0.01, compared with IBS-like rats receiving 50 nmol/L ZD 7288. EOMA: External oblique muscle of the abdomen; CRD: colorectal distension.
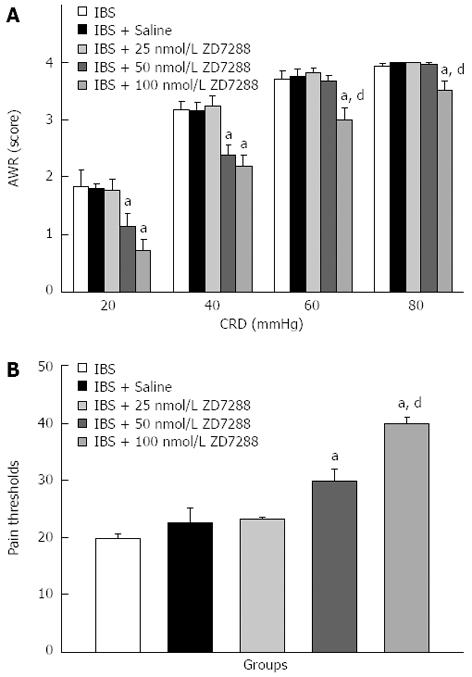
Figure 4 Inhibitory effects of ZD 7288 on abdominal withdrawal reflex scores (A) and pain thresholds (B) of irritable bowel syndrome-like rats.
aP < 0.05, compared with saline-treated IBS-like rats; dP < 0.01, compared with IBS-like rats receiving 50 nmol/L ZD 7288. CRD: Colorectal distension; AWR: Abdominal withdrawal reflex.
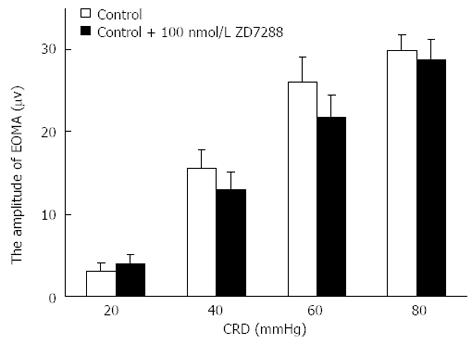
Figure 5 Effects of ZD 7288 on amplitudes of external oblique muscle of the abdomen in control rats.
EOMA: External oblique muscle of the abdomen; CRD: Colorectal distension.
- Citation: Chen Y, Lin C, Tang Y, Chen AQ, Liu CY, Lu DL. ZD 7288, an HCN channel blocker, attenuates chronic visceral pain in irritable bowel syndrome-like rats. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(8): 2091-2097
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i8/2091.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.2091