Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2014; 20(8): 1972-1985
Published online Feb 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.1972
Published online Feb 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.1972
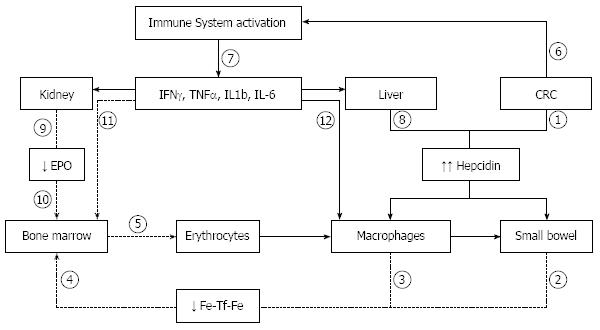
Figure 1 Pathophysiological mechanisms of anemia of inflammation in colorectal cancer.
1: Hepcidin release by colorectal cancer cells (CRC); 2,3: Decreased release of iron via ferroportin: leading to decreased transferrin-bound iron; 4: Decreased iron availability; 5: Reduced erythrocyte production; 6: Activation of immune system by CRC; 7: Release of immune and inflammatory cytokines; 8: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) induced hepcidin release; 9: Decreased erythropoietin (EPO) production; 10: Decreased erythropoietic stimulation; 11: Inhibition of erythroid cell proliferation; 12: Augmented erythrofagocytosis. IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
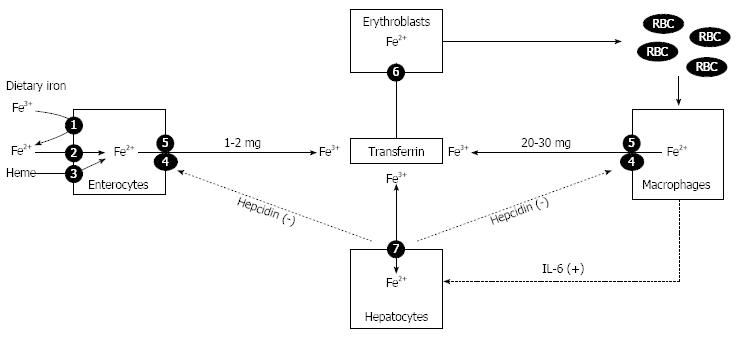
Figure 2 A simplified scheme of main pathways of iron metabolism.
1: Ferrireductase; 2: Divalent metal transporter (DMT1); 3: Heme protein carrier 1; 4: Ferroportin; 5: Hephastin/ceruloplasmin; 6: Transferrin receptor-1 (TfR1); 7: Several mechanisms; IL-6: Interleukin 6; RBC: Red blood cell.
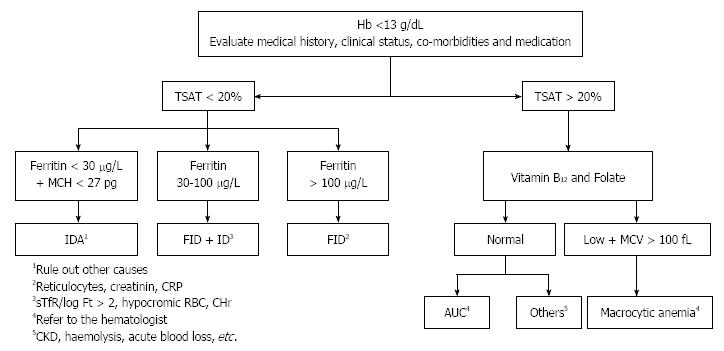
Figure 3 An algorithm for anemia diagnosis.
Modified from Muñoz et al[20]. ACD: Anemia of chronic disease; AUC: Anemia of unknown cause; CHr: Reticulocyte hemoglobin; CKD: Chronic kidney disease; CRP: C-reactive protein; Ft: Ferritin; Hb: Hemoglobin; ID: iron deficiency; IDA: Iron deficiency anemia; MCH: Mean corpuscular hemoglobin; MCV: Mean corpuscular volume; sTfR: Serum transferrin receptor; TSAT: Transferrin saturation; FID: Functional iron deficiency.
Figure 4 An algorithm for iron replacement.
Modified from Muñoz et al[31]. FCM: Ferric caboxymaltose; Hb: Hemoglobin; LMWID: Low molecular weight iron dextran; MNF: Iron isomaltoside-1000; s: Session; TID: Total iron deficiency; CRP: C-reactive protein.
- Citation: Muñoz M, Gómez-Ramírez S, Martín-Montañez E, Auerbach M. Perioperative anemia management in colorectal cancer patients: A pragmatic approach. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(8): 1972-1985
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i8/1972.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.1972