Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2014; 20(34): 12161-12170
Published online Sep 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12161
Published online Sep 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12161
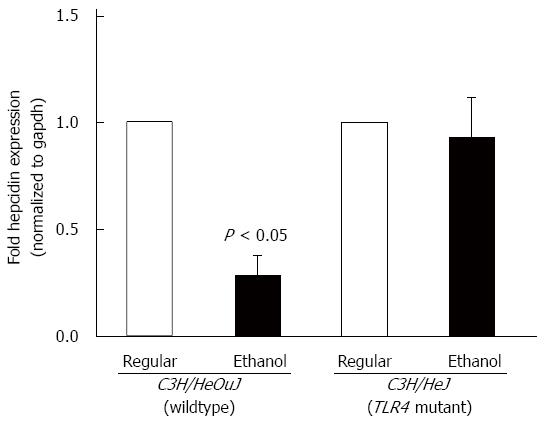
Figure 1 Hepcidin mRNA expression.
cDNA, synthesized from RNA isolated from the livers of toll-like receptor 4 mutant (C3H/HeJ) and wildtype (C3H/HeOuJ) mice pair-fed with regular and ethanol-containing diets, was employed in real-time polymerase chain reaction to measure hepcidin mRNA expression, as described in Methods. Hepcidin expression in ethanol-fed mice was expressed as fold expression of that in the respective mice pair-fed with the regular diet (mean ± SE; n = 10 per group).
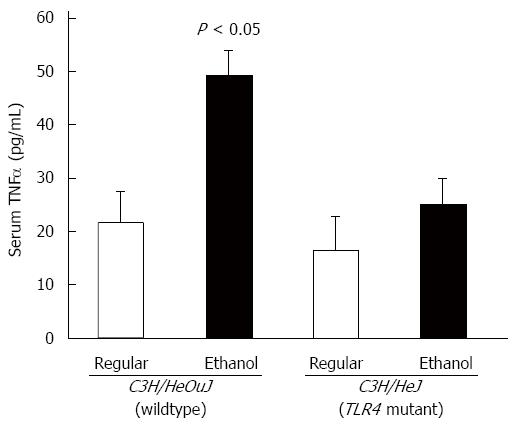
Figure 2 Tumor necrosis factor α expression.
The level of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)α in sera of toll-like receptor 4 mutant (C3H/HeJ) and wildtype control (C3H/HeOuJ) mice, pair-fed with regular and ethanol-containing diets was determined by ELISA assays, using a commercial kit (BioLegend), according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and expressed as picogram cytokine per ml of serum (mean ± SE; n = 10 per group).
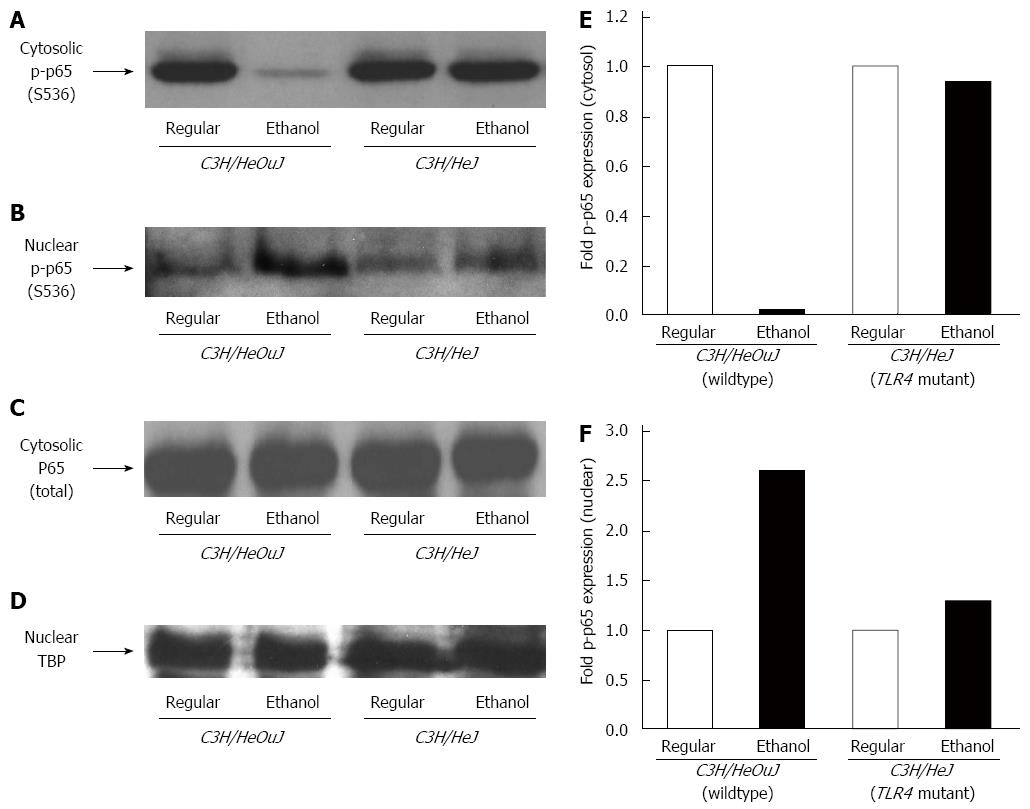
Figure 3 Nuclear factor-κB phosphorylation.
Cytosolic (A, C) and nuclear (B, D) protein fractions isolated from the livers of C3H/HeJ and C3H/HeOuJ mice pair-fed with regular and ethanol-containing diets were used for western blots to detect phosphorylated (serine 536) p65 (p-p65) expression. Anti-total p65 (p65) (C) and anti-TATA-binding protein (TBP) (D) antibodies were used as controls. Cytosolic (E) and nuclear (F) p-p65 expression was quantified by densitometric analysis and normalized to total p65 or TBP protein expression, respectively. Normalized p-p65 expression in ethanol-fed mice was expressed as fold expression of that in the respective mice pair-fed with the regular diet (mean; n = 3 per group).
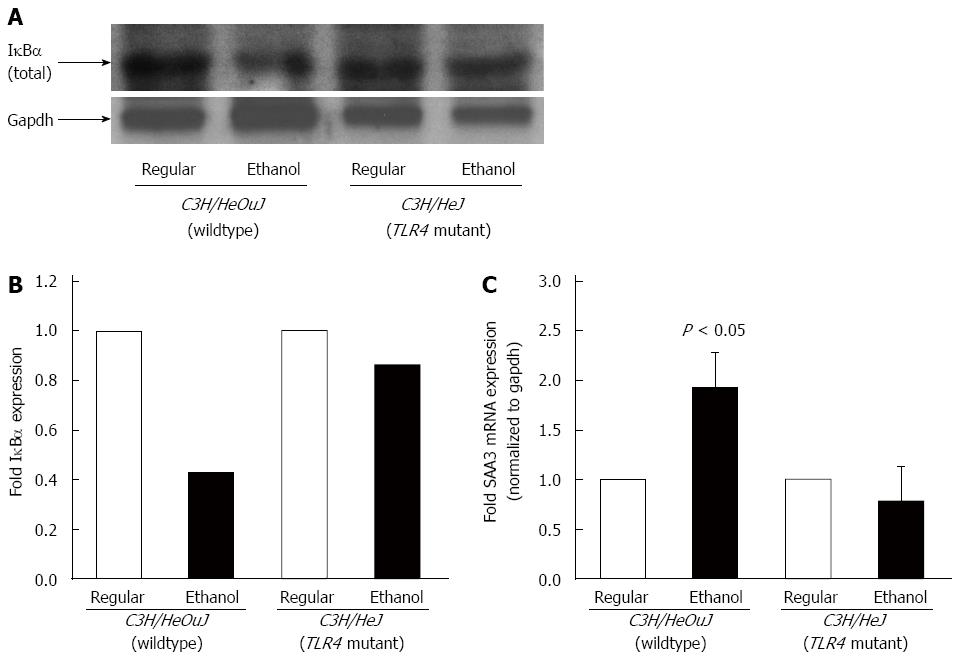
Figure 4 IκBα expression and SAA3 expression.
A: Cytosolic protein fractions isolated from the livers of C3H/HeOuJ and C3H/HeJ mice pair-fed with regular and ethanol-containing diets were used for western blots to detect IκBα expression. An anti-gapdh antibody was used as control; B: IκBα expression was quantified by densitometric analysis and normalized to gapdh expression. Normalized IκBα expression in ethanol-fed mice was expressed as fold expression of that in the respective mice pair-fed with the regular diet (mean; n = 3 per group); C: cDNA, synthesized from RNA isolated from the livers of these mice, was employed in real-time polymerase chain reaction to measure SAA3 mRNA expression. SAA3 expression in ethanol-fed mice was expressed as fold expression of that in the respective mice pair-fed with the regular diet (mean ± SE; n = 10 per group).
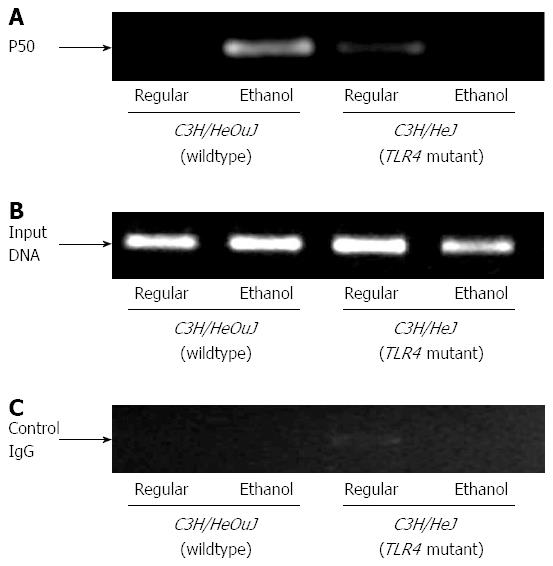
Figure 5 Nuclear factor-κB binding to hepcidin gene promoter.
Chromatin isolated from the livers of control or ethanol-fed C3H/HeJ and C3H/HeOuJ mice was immunoprecipitated with an anti-p50 nuclear factor-κB antibody (A) or control IgG (C). Immunoprecipitated DNAs (A, C) and input DNA control (B) were subjected to polymerase chain reaction, as described in Methods.
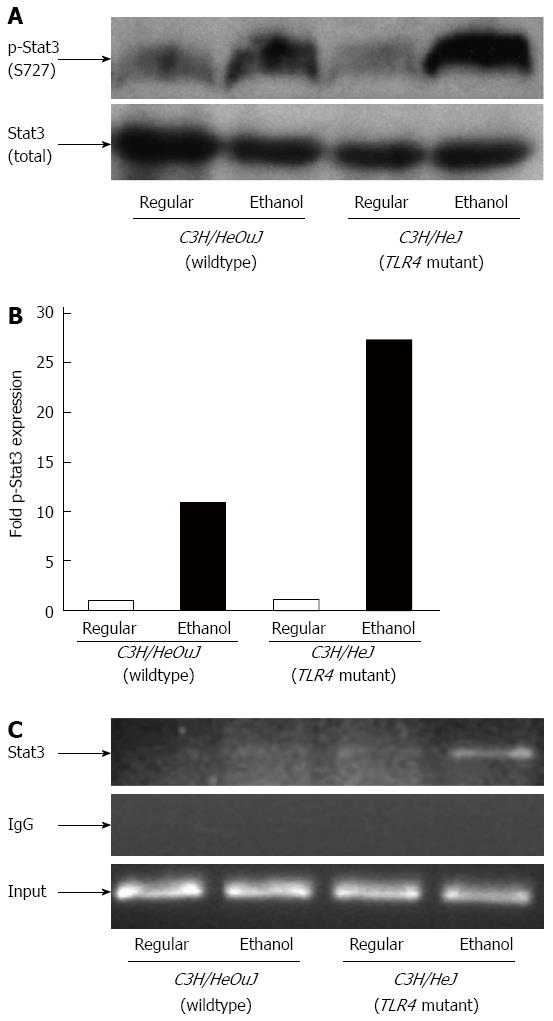
Figure 6 Stat3 activation and binding to hepcidin gene promoter.
A: Phospho-(p-Stat3) and total Stat3 protein expression in whole liver cell lysates isolated from C3H/HeJ and C3H/HeOuJ mice pair-fed with regular and ethanol-containing diets was detected by western blotting; B: p-Stat3 expression in each sample was quantified by densitometric analysis and normalized to total Stat3 protein expression. Normalized p-Stat3 expression in ethanol-fed mice was expressed as fold expression of that in the respective mice pair-fed with the regular diet (mean; n = 3 per group); C: Chromatin isolated from the livers of control or ethanol-fed C3H/HeJ and C3H/HeOuJ mice was immunoprecipitated with an anti-Stat3 antibody or control IgG. Immunoprecipitated DNAs and input DNA control were subjected to polymerase chain reaction, as described in Methods.
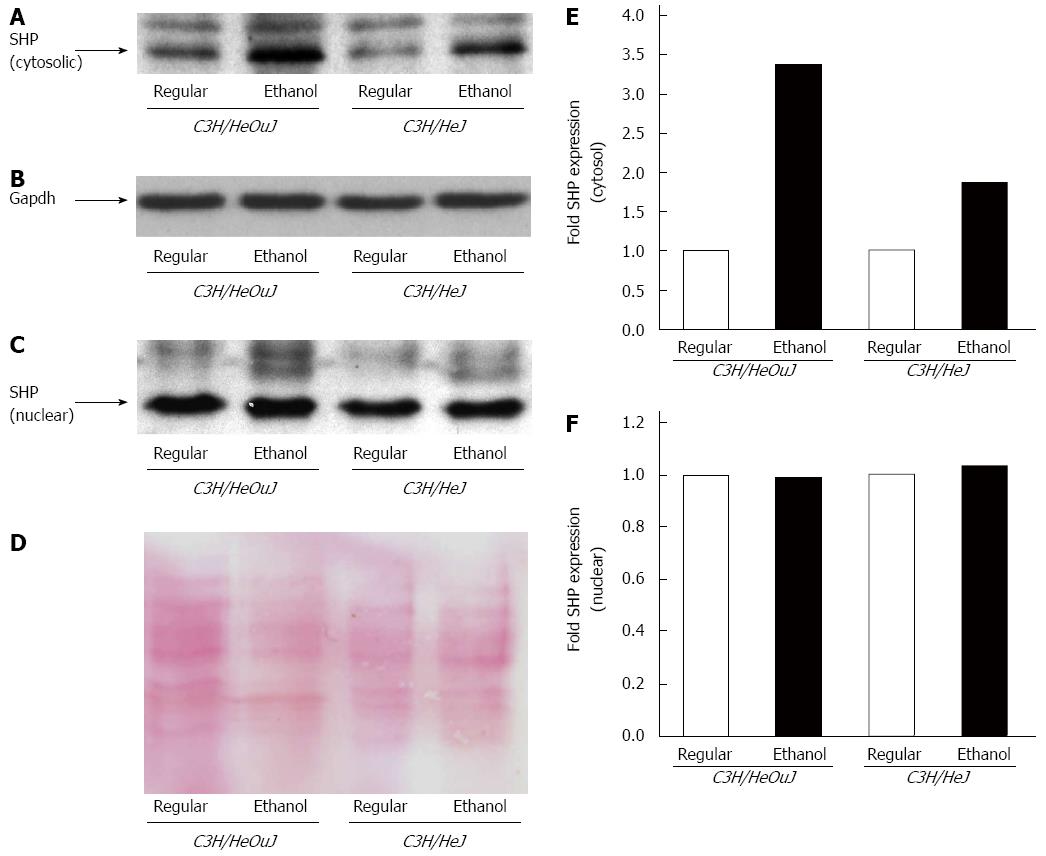
Figure 7 Small heterodimer partner protein expression.
Small heterodimer partner (SHP) protein expression was detected by western blots using cytosolic (A, B) and nuclear (C, D) fractions isolated from the livers of C3H/HeJ and C3H/HeOuJ mice pair-fed with regular and ethanol-containing diets. An anti-gapdh antibody (B) was used as a cytosolic protein loading control; D: Nuclear proteins on PVDF blotting membranes were visualized by Ponceau S staining to evaluate equal protein loading. Cytosolic (E) and nuclear (F) SHP expression was quantified by densitometric analysis and normalized to control protein expression. Normalized SHP expression in ethanol-fed mice was expressed as fold expression of that in the respective mice pair-fed with the regular diet (mean; n = 3 per group).
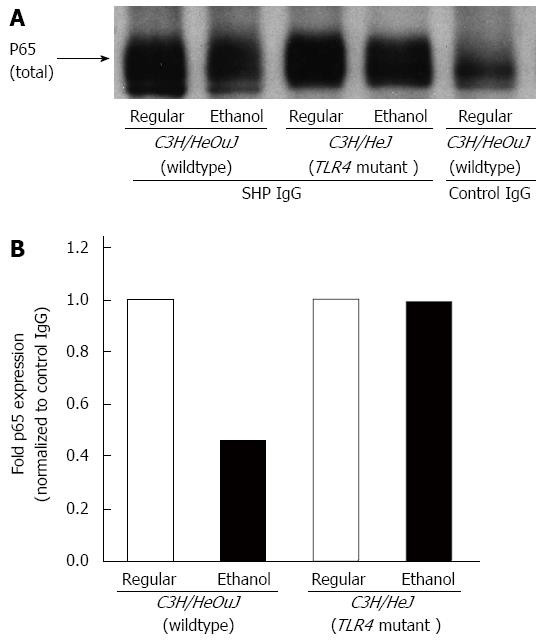
Figure 8 Effect of alcohol on small heterodimer partner and nuclear factor-κB interaction.
A: Whole cell lysates isolated from the livers of C3H/HeJ and C3H/HeOuJ mice pair-fed with regular and ethanol-containing diets were immunoprecipitated with an anti-small heterodimer partner (SHP) antibody or anti-rabbit IgG, as control. The expression of nuclear factor-κB in the immune complexes was determined by western blotting using an anti-p65 antibody, as described in Methods; B: p65 protein expression in SHP immune complexes was quantified by densitometric analysis and normalized to control IgG immune complexes. Normalized p65 expression in ethanol-fed mice was expressed as fold expression of that in the respective mice pair-fed with the regular diet (mean; n = 3 per group).
- Citation: Zmijewski E, Lu S, Harrison-Findik DD. TLR4 signaling and the inhibition of liver hepcidin expression by alcohol. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(34): 12161-12170
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i34/12161.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12161