Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2014; 20(2): 593-597
Published online Jan 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.593
Published online Jan 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.593
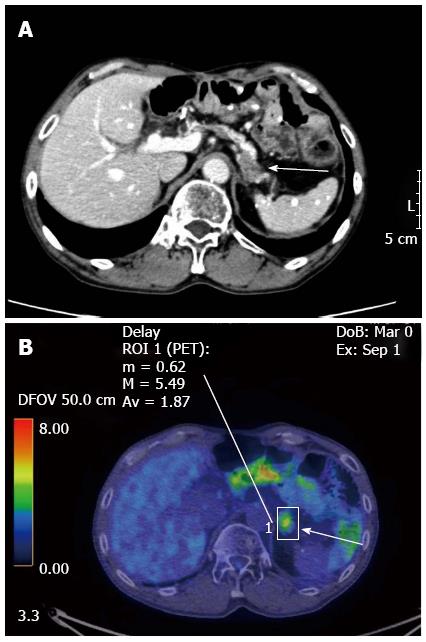
Figure 1 Enhanced computed tomography (A) and 18F-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron-emission tomography (B) showed a tumor of the pancreatic body (arrows).
The major axis of the tumor was 15 mm. Maximum standardized uptake value of the lesion was 5.49.
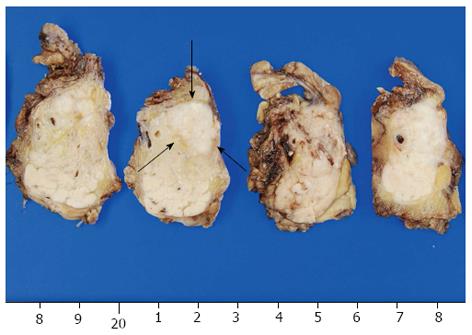
Figure 2 Macroscopic findings of the specimen revealed a 15 mm × 11 mm tumor in the pancreatic body (arrows).
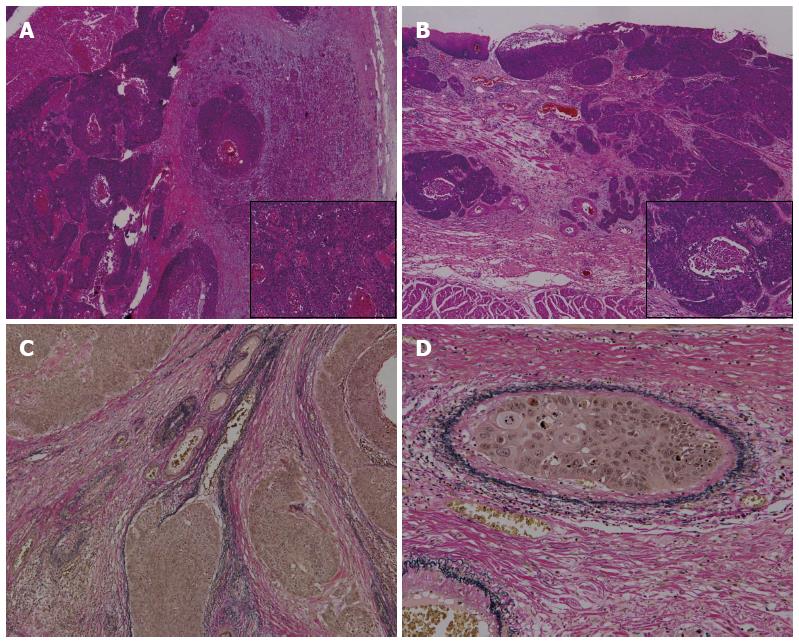
Figure 3 Pathological examination revealed squamous cell carcinoma.
A: Squamous cell carcinoma in the pancreas; B: Squamous cell carcinoma in the esophagus resected previously (hematoxylin-eosin staining, A: × 40; B: × 400); C: Vascular invasion in the pancreatic metastasis; D: Esophageal carcinoma (elastica van gieson staining, C: × 100, D: × 400).
- Citation: Okamoto H, Hara Y, Chin M, Hagiwara M, Onodera Y, Horii S, Shirahata Y, Kamei T, Hashizume E, Ohuchi N. An extremely rare case of pancreatic metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(2): 593-597
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i2/593.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.593