Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2014; 20(1): 1-5
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.1
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.1
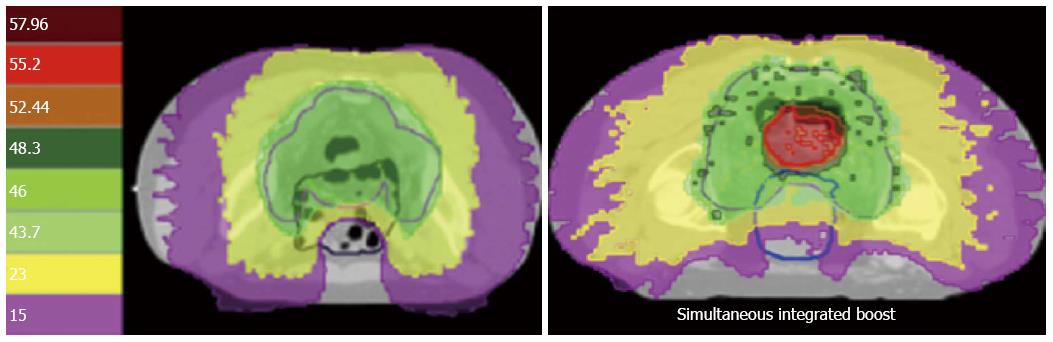
Figure 1 Dose distribution of helical tomotherapy.
The left image shows a classic treatment of 46 Gy in daily fractions of 2 Gy. Note the horseshoe shaped distribution of the dose to spare the small bowel. On the right image a simultaneous integrated boost till 55.2 Gy is prescribed on the tumor.
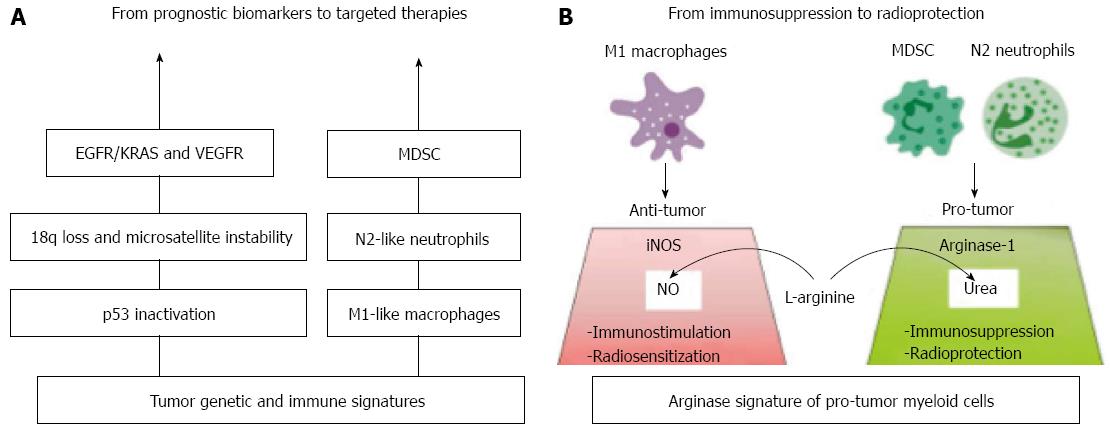
Figure 2 The genetic/immune landscape of colorectal cancer and therapeutic implications.
The concept of personalized treatments in colorectal cancer should be based on integral knowledge of both tumor and immune cell signatures that would ideally provide therapeutic targets as well. A: As a result of genome profiling, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) have been identified as promising targets for personalized therapies, while other biomarkers, like p53 mutations, 18q loss and microsatellite instability, lack prognostic/predictive value. The immune profile of colorectal cancer is rather unique with regard to macrophages (and Tregs), which unexpectedly point to favourable prognosis, yet being immunosuppressive in the most tumor types. Hence, the monocyte lineage of myeloid cells may reveal antitumor M1-like polarization within the compartment of tumor-associated macrophages. The granulocyte lineage of myeloid cells, comprising undifferentiated myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), feature clear protumor N2-like polarization and contribute to poor prognosis. Those cells overexpress Arg that causes L-arginine depletion and thereby suppresses antitumor T-cell immunity; B: We hypothesize that Arg+ neutrophils and MDSC may also display radioprotective properties, as L-arginine deficiency would neutralize the radiosensitizing potential of M1 macrophages. Indeed, classically activated M1 macrophages are known to produce the radiosensitizing molecule nitric oxide (NO) through the iNOS/L-arginine pathway. Therefore, Arg+ neutrofils and MDSC emerge as promising biomarkers and candidates for future targeted therapies, aiming at reversing impaired immune and radiation responses.
- Citation: Sermeus A, Leonard W, Engels B, De Ridder M. Advances in radiotherapy and targeted therapies for rectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(1): 1-5
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.1