Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2013; 19(48): 9490-9494
Published online Dec 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9490
Published online Dec 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9490
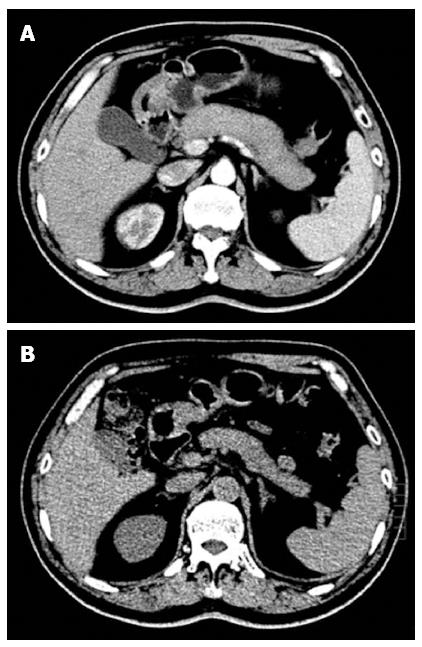
Figure 1 Typical imaging features of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis.
Computed tomography (CT) scan showing diffuse swelling of the pancreas with loss of lobulation (A), and a dramatic decrease in swelling of the pancreas after 3 wk of steroid treatment (B).
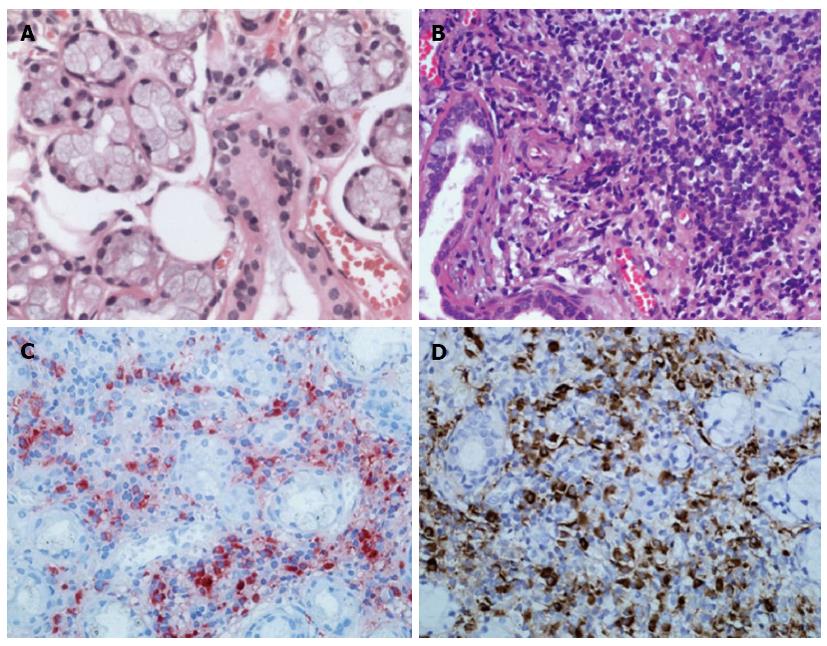
Figure 2 Histological findings of labial salivary gland specimens.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin stain showing normal labial gland; B: Diffuse infiltration of lymphoplasma cells from the patient; C, D: Immunohistochemical staining for IgG4 (C) or IgG (D) in plasma cells from the patient, consistent with Mikulicz’s disease. Original magnification, × 400.
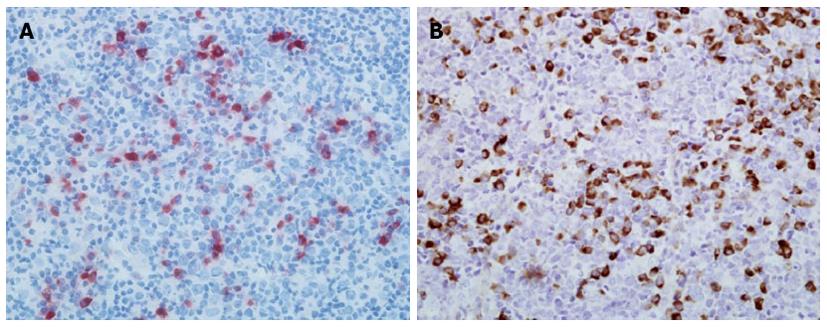
Figure 3 Histological findings of submandibular lymph node specimen.
Immunohistochemical staining showing IgG4-positive plasma cells (A) and IgG-positive plasma cells (B) in lymph node sections of the patient. Original magnification, × 400.
- Citation: Qu LM, Liu YH, Brigstock DR, Wen XY, Liu YF, Li YJ, Gao RP. IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis overlapping with Mikulicz’s disease and lymphadenitis: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(48): 9490-9494
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i48/9490.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9490