Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2013; 19(48): 9189-9197
Published online Dec 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9189
Published online Dec 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9189
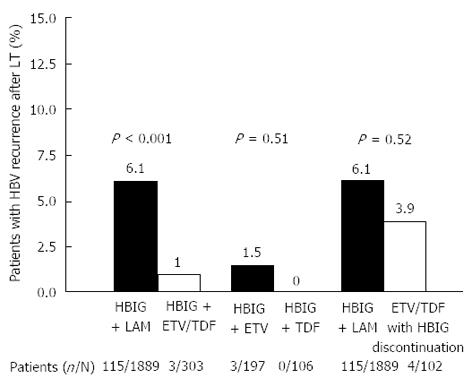
Figure 1 Risk of recurrence of hepatitis B virus infection after liver transplantation in relation to the type of post-transplant hepatitis B virus prophylaxis[64].
HBIG: Hepatitis B immunoglobulin; LAM: Lamivudine; ETV: Entecavir; TDF: Tenofovir; LT: Liver transplantation.
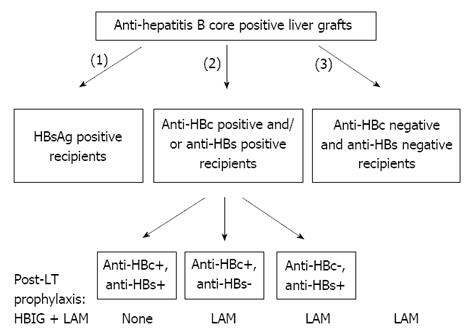
Figure 2 Proposed algorithm for allocation and management of anti-hepatitis B core positive liver grafts.
Such grafts should be first offered to hepatitis B surface antigen positive, then to anti-hepatitis B core (HBc) and/or anti-hepatitis B surface (HBs) positive and lastly to hepatitis B virus naive (both anti-HBc and anti-HBs negative) recipients[79]. LT: Liver transplantation; HBIG: Hepatitis B immunoglobulin; LAM: Lamivudine.
- Citation: Cholongitas E, Papatheodoridis GV. Review of the pharmacological management of hepatitis B viral infection before and after liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(48): 9189-9197
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i48/9189.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9189