Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2013; 19(43): 7788-7794
Published online Nov 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7788
Published online Nov 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7788
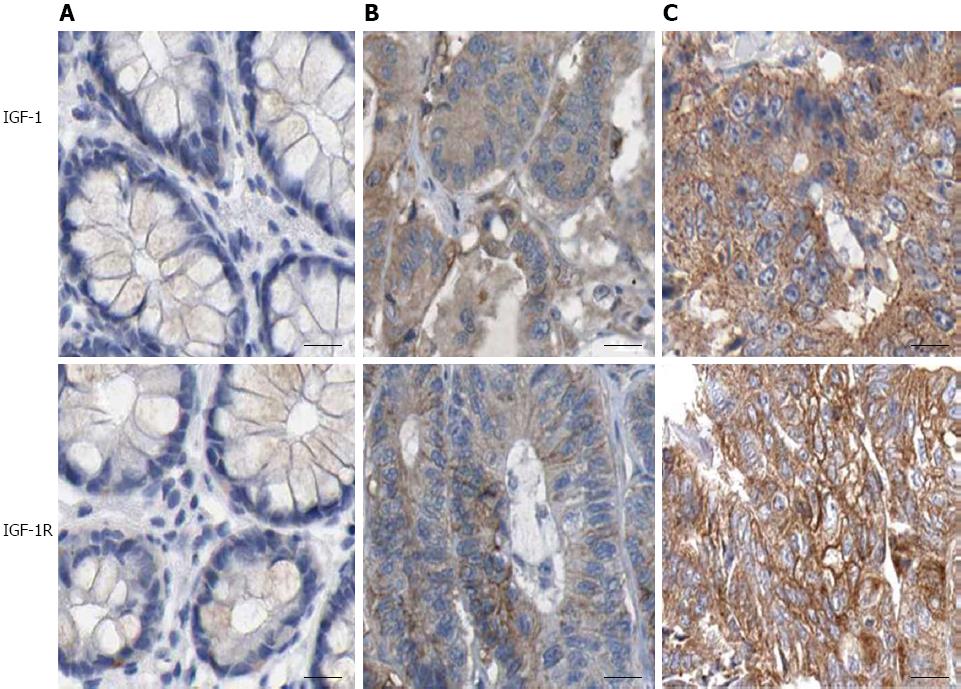
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical staining of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in colorectal cancer tissues.
A: Tumor-adjacent normal tissues; B: Moderately differentiated CRC and C, poorly differentiated CRC (× 200). IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor-1. IGF-I R: Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; CRC: Colorectal cancer.
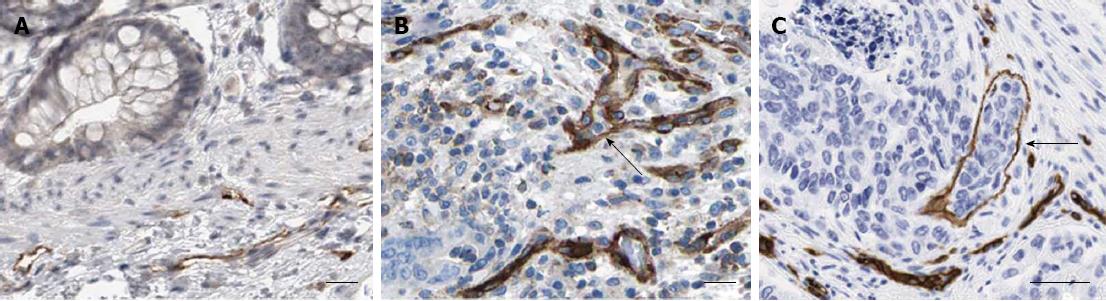
Figure 2 Morphological features of D2-40 positive lymphatic vessels in colorectal cancer.
A: Tumor-adjacent normal tissues; B and C: Colorectal cancer tissues (× 200). Lymphatic vessel invasion of tumor cells was also detected in B and C (black arrow). IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor-1.
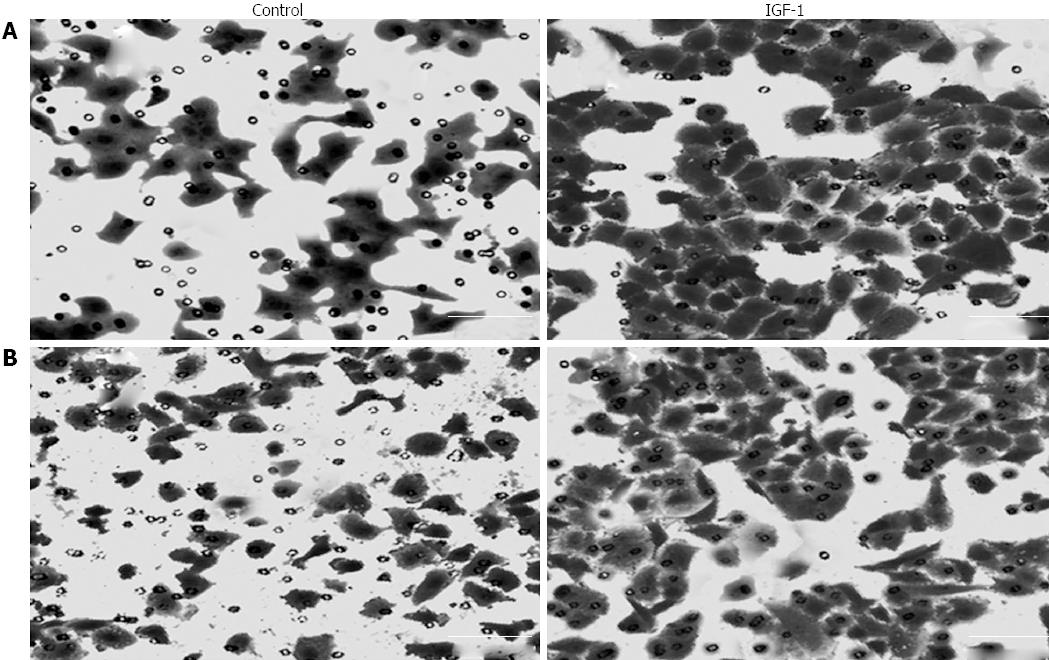
Figure 3 Effect of insulin-like growth factor-1 on the migration and invasion of LoVo cells after 48 h treatment.
A: Cell migration; B: Cell invasion (× 200). IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor-1.
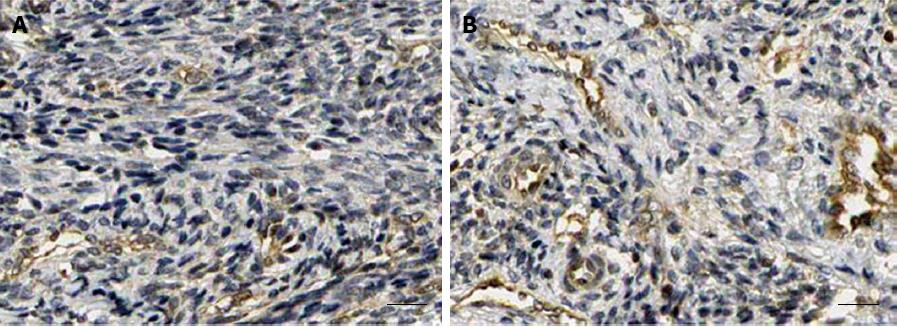
Figure 4 Effect of insulin-like growth factor-1 on lymphatic vessel density in LoVo cell xenografts in nude mice after treatment with insulin-like growth factor-1.
A: Control group; B: 50 μg/kg IGF-1 group (× 200). IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor-1; IGF-I R: Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor.
- Citation: Li ZJ, Ying XJ, Chen HL, Ye PJ, Chen ZL, Li G, Jiang HF, Liu J, Zhou SZ. Insulin-like growth factor-1 induces lymphangiogenesis and facilitates lymphatic metastasis in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(43): 7788-7794
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i43/7788.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7788