Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2013; 19(38): 6319-6328
Published online Oct 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i38.6319
Published online Oct 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i38.6319
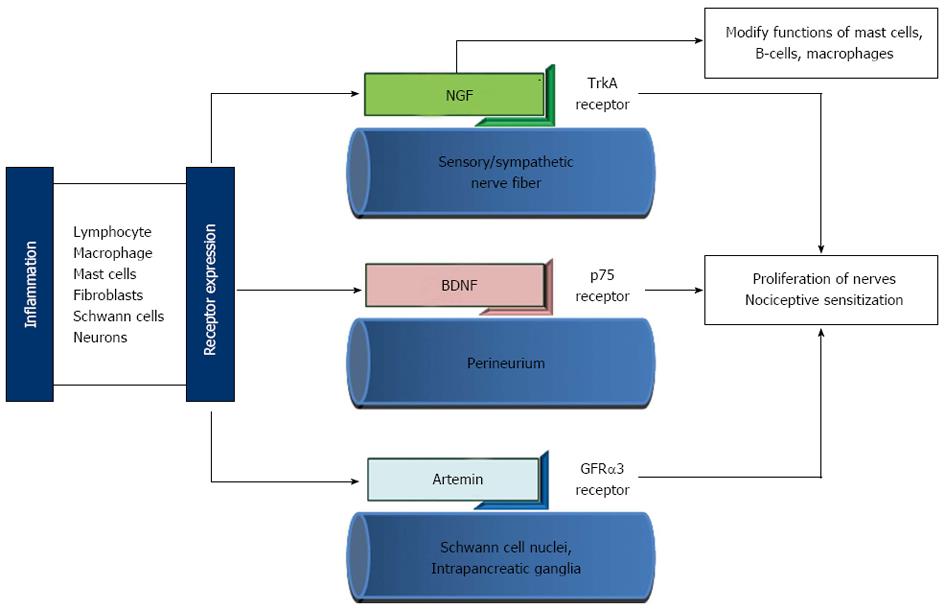
Figure 1 Schematic diagram representing neuroimmune mechanisms of pain in patients with chronic pancreatitis.
The TrkA receptors (for nerve growth factor, NGF) are expressed on the sensory and sympathetic nerve fibres, p75 (for brain derived neurotropic factor, BDNF) on the perineurium and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor receptor α3 (GFRα3) (for Artemin) on the Schwann cell nuclei and intrapancreatic ganglia. The receptor expression is mediated by inflammation involving inflammatory cells and neural elements.
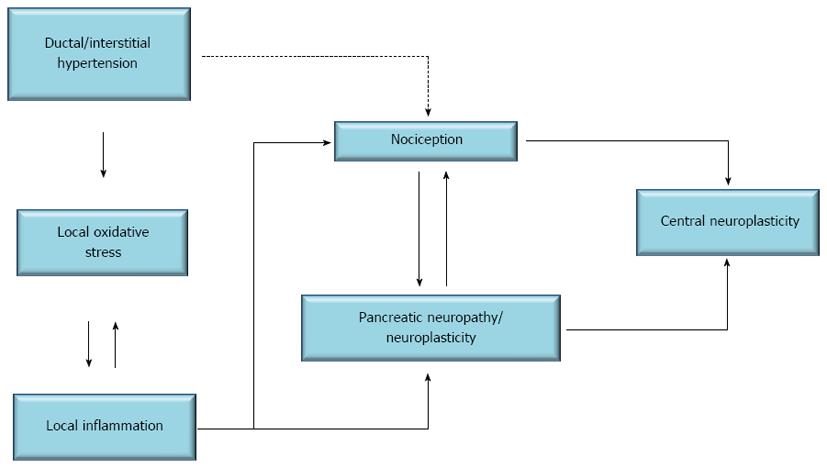
Figure 2 Schematic representation of the conceptual framework of pain mechanisms in chronic pancreatitis.
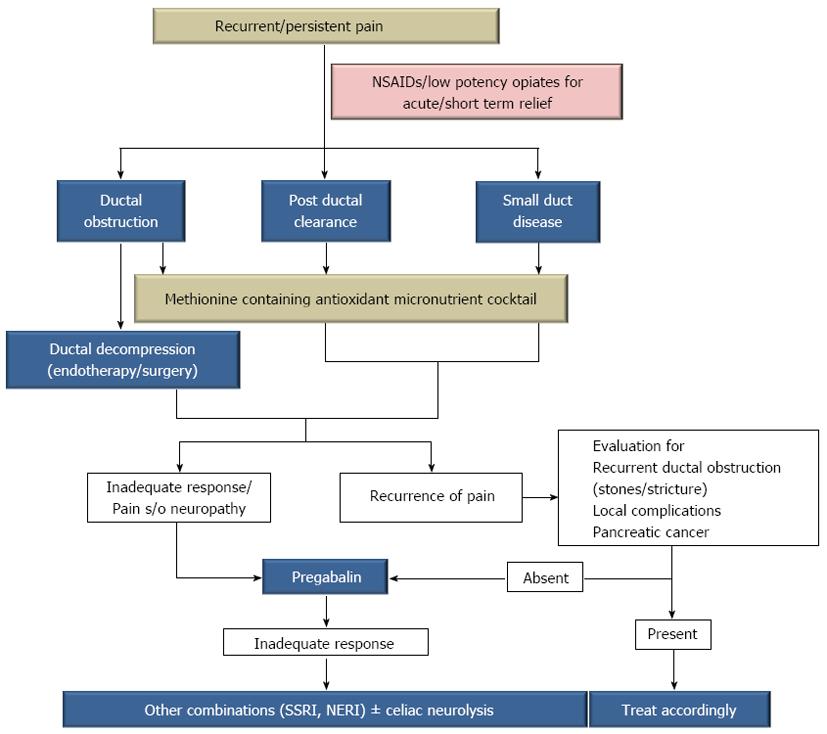
Figure 3 Management approach for recurrent and/or persistent pain in patients with chronic pancreatitis at the Asian Institute of Gastroenterology.
SSRIs: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; NERI: Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Citation: Talukdar R, Reddy DN. Pain in chronic pancreatitis: Managing beyond the pancreatic duct. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(38): 6319-6328
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i38/6319.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i38.6319