Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2013; 19(36): 6035-6043
Published online Sep 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.6035
Published online Sep 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.6035
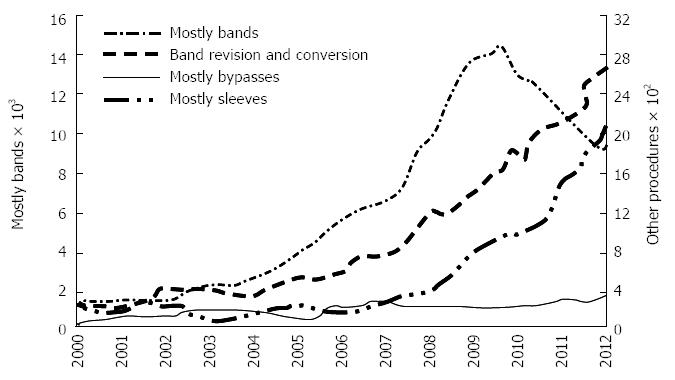
Figure 1 Comparison of changes in the performance of different type of bariatric procedures over a 10-year period in Australia based on medical benefit schedule item number.
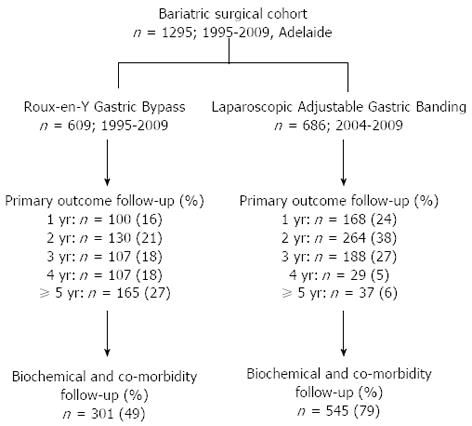
Figure 2 Flow chart of studied cohort in relation to clinical outcomes.
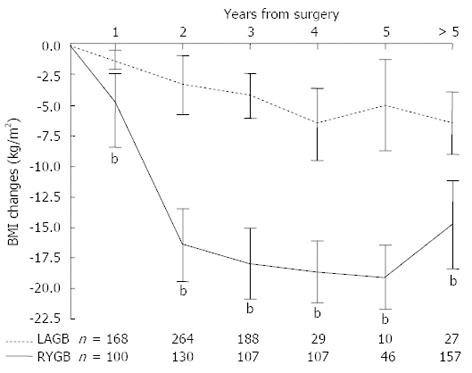
Figure 3 Changes in body mass index in patients who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic adjustable gastric band up to 5 years post-surgery.
bP < 0.001 vs laparoscopic adjustable gastric band (LAGB). RYGB: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
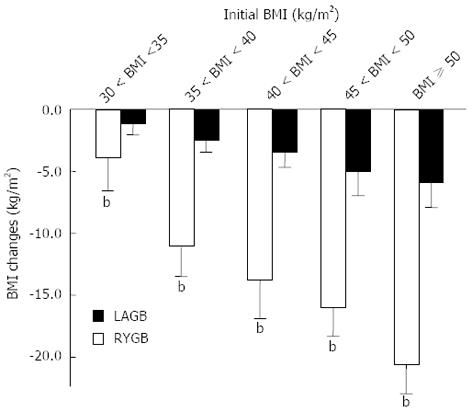
Figure 4 Relationship between the degree of weight loss and presenting body mass index induce by Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic adjustable gastric band procedure.
bP < 0.001 vs laparoscopic adjustable gastric band (LAGB). RYGB: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; BMI: Body mass index.
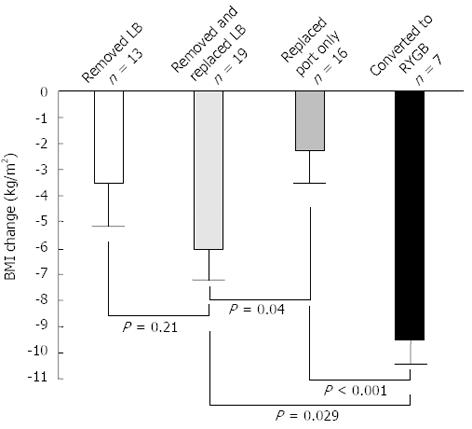
Figure 5 Outcomes of patients who had complications with laparoscopic adjustable gastric band requiring further interventions, including removal of band, removal and placement of band, replacement of port only and conversion to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
RYGB: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; LB: Lap-band; BMI: Body mass index.
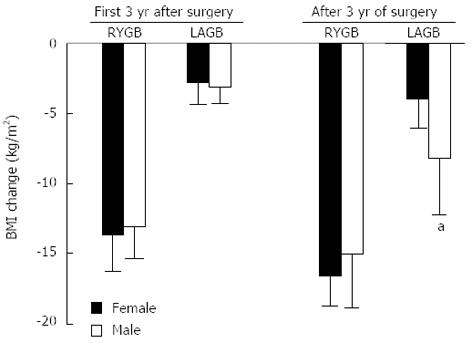
Figure 6 Body mass index changes after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic adjustable gastric band in male and female 3 years post-surgery.
aP = 0.02 vs female. RYGB: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; LAGB: Laparoscopic adjustable gastric band.
- Citation: Nguyen NQ, Game P, Bessell J, Debreceni TL, Neo M, Burgstad CM, Taylor P, Wittert GA. Outcomes of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(36): 6035-6043
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i36/6035.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.6035