Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2013; 19(2): 290-298
Published online Jan 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i2.290
Published online Jan 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i2.290
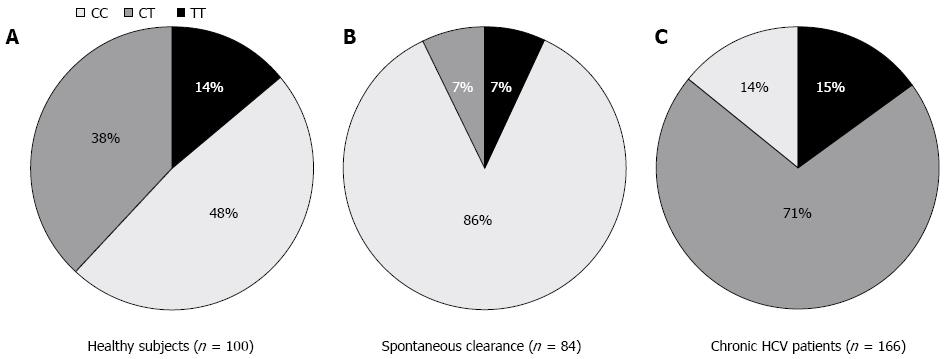
Figure 1 Distribution of LI28B rs12979860 single nucleotide polymorphism alleles among a healthy Egyptian population, spontaneous clearance and chronic hepatitis C patients.
A: A hundred healthy subjects representing ethnic backgrounds of the Egyptian population were typed for IL28B single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs 12979860. The distribution of different allele frequencies is depicted as a pie chart; B: Eighty four patients with spontaneous clearance from hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection were typed for IL28B SNP rs 12979860. The distribution of different allele frequencies is depicted as a pie chart; C: A hundred and sixty six chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients with low F scores (F0-F2) were typed for IL28B SNP rs 12979860. The distribution of different allele frequencies is depicted as a pie chart.
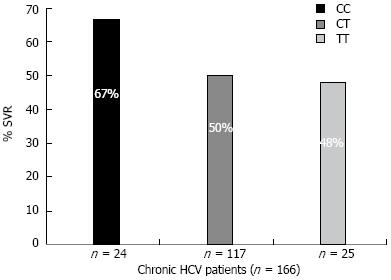
Figure 2 Rate of sustained viral response in IL28B variants.
Among 166 chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients treated with combined interferon (IFN) and ribavirin therapy, 80 patients did not achieve a sustained viral response (SVR) while 86 patients achieved a SVR. Among the 14% (24) of CHC patients bearing the C/C allele, 67% (16 patients) achieved a SVR, while the other two genotypes C/T and TT were associated with lower SVR rates; 50% and 48%, respectively. Genotype CC was associated with response to IFN (P = 0.025). HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
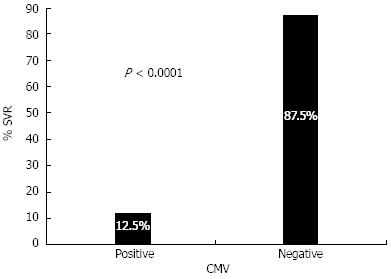
Figure 3 Association of cytomegalovirus reactivation with sustained viral response rates in C/C patients.
The data shown clearly demonstrate that cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation has dramatically reduced the sustained viral response (SVR) rates in C/C genotypes as represented by a 12.5% SVR rate in CMV-positive patients compared with 87.5% in CMV-negative patients (P < 0.0001).
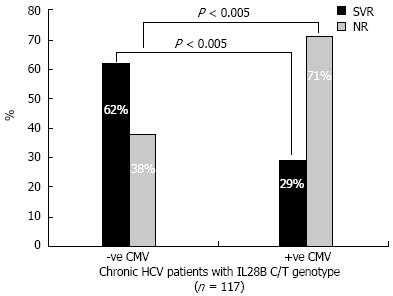
Figure 4 Sorting of C/T genotype according to association with cytomegalovirus infection.
The sustained viral response (SVR) rates among C/T carriers, is reduced to < 50% of its value in cases where patients had cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation. On the other hand, the non-response rate is increased 2-fold in cases of CMV reactivation. HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
- Citation: El Awady MK, Bader El Din NG, Tabll A, El Hosary Y, Abdel Aziz AO, El Khayat H, Salama M, Abdelhafez TH. IL28B polymorphism and cytomegalovirus predict response to treatment in Egyptian HCV type 4 patients. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(2): 290-298
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i2/290.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i2.290