Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2013; 19(19): 2941-2949
Published online May 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2941
Published online May 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2941
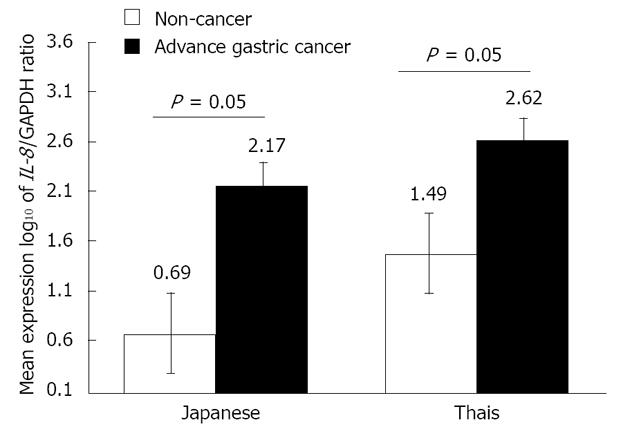
Figure 1 Mean interleukine-8 mRNA expression level measurement of relative quantitation by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction study in gastric cancer comparing with non-cancer population both Japanese and Thais.
In Japanese and Thais, gastric mucosal interleukine-8 (IL-8) mRNA expression in cancer is higher than in non-cancer with P = 0.05. The mean level of IL-8 mRNA expressions in Thai cancer and Japanese cancer were 9615.65 (log10 = 2.62) and 1509.11 (log10 = 2.17), respectively, P = 0.014. The mean level of IL-8 mRNA expression in non-cancer Thais is 2262 (log10 = 1.49) while that in non-cancer Japanese is 10.79 (log10 = 0.69), P < 0.001.
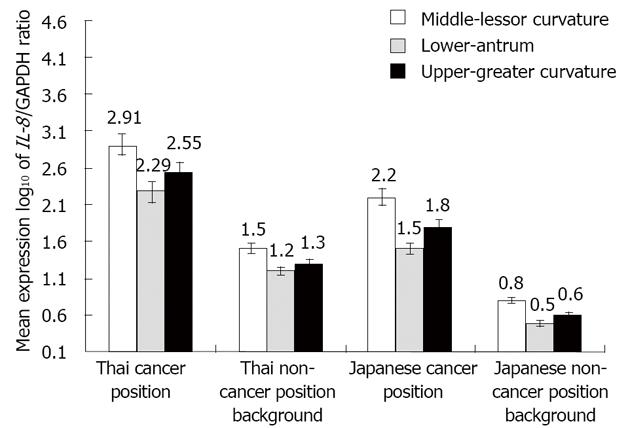
Figure 2 The mean interleukine-8 mRNA expression in Thais divided by histology and cancer position.
Middle is the lessor curvature and non-cancer position, lower is the antrum, and Upper is the greater curvature. IL-8: Interleukine-8.
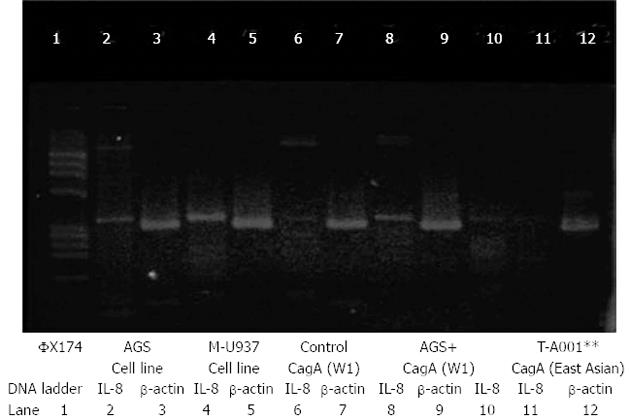
Figure 3 Basic experiment result on real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction of interleukine-8 mRNA expression with AGS, macrophage cell line, normal gastric mucosal cell, AGS cancer cell line co-culture with two strains of cagA Helicobacter pylori, and positive cagA, Thai non-cancer samples sequences showed on 12 lanes.
M: Marker.
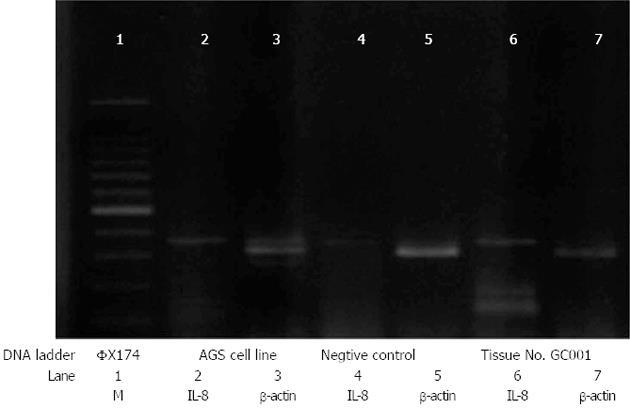
Figure 4 Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction result of interleukine-8 mRNA expression from AGS, negative control, and Thai gastric cancer mucosal tissues.
The positive results of interleukine-8 (IL-8) mRNA expression appeared at 320 bp band comparing with 300 bp band of marker (M) in lane 1.
-
Citation: Yamada S, Kato S, Matsuhisa T, Makonkawkeyoon L, Yoshida M, Chakrabandhu T, Lertprasertsuk N, Suttharat P, Chakrabandhu B, Nishiumi S, Chongraksut W, Azuma T. Predominant mucosal
IL-8 mRNA expression in non-cagA Thais is risk for gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(19): 2941-2949 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i19/2941.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2941