Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2013; 19(12): 1912-1918
Published online Mar 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i12.1912
Published online Mar 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i12.1912
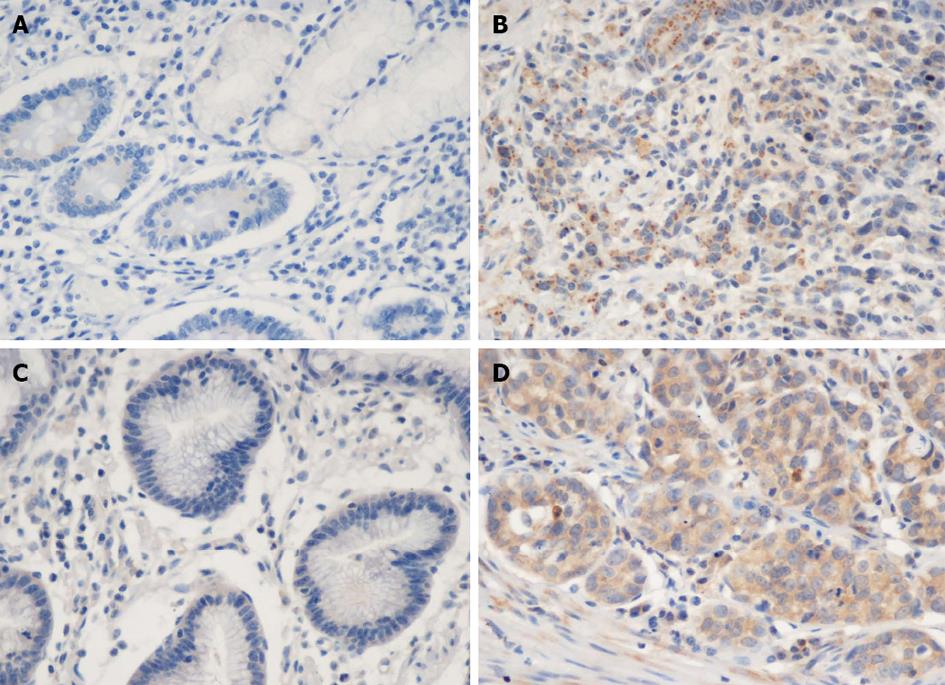
Figure 1 Expression of CD73 and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in gastric carcinoma (immunohistochemical stain, ×400).
A, C: Negative staining for CD73 (A) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) (C) in healthy control gastric mucosa; B, D: Positive staining for CD73 (B) and HIF-1α (D) in gastric carcinoma.
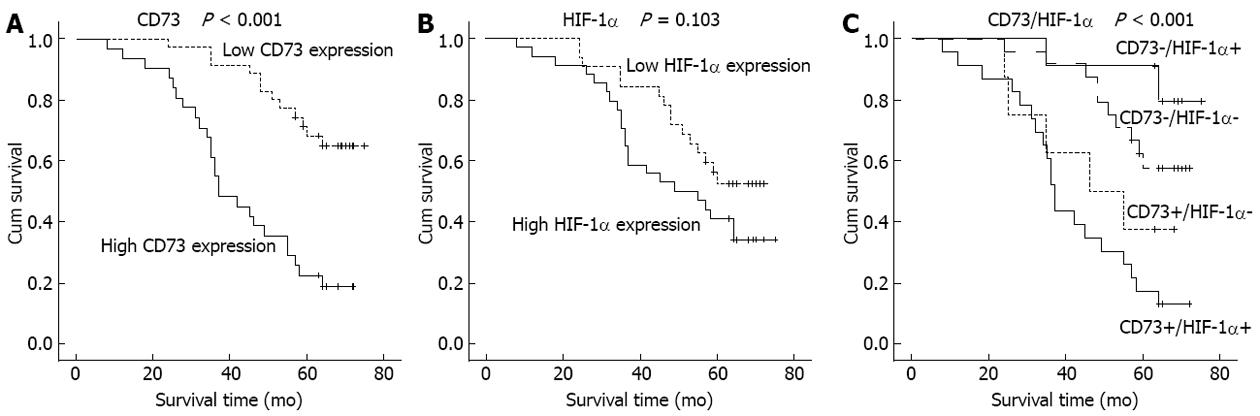
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier curves for postoperative survival.
A: The median survival time of patients with positive CD73 was shorter than that of patients with negative CD73 (log-rank test: P < 0.001); B: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) expression had no correlation with the survival time of patients (log-rank test: P = 0.103); C: There was a significant difference among groups stratified according to CD73/HIF-1α expression (P < 0.001). Patients with CD73+/HIF-1α+ had the worst prognosis.
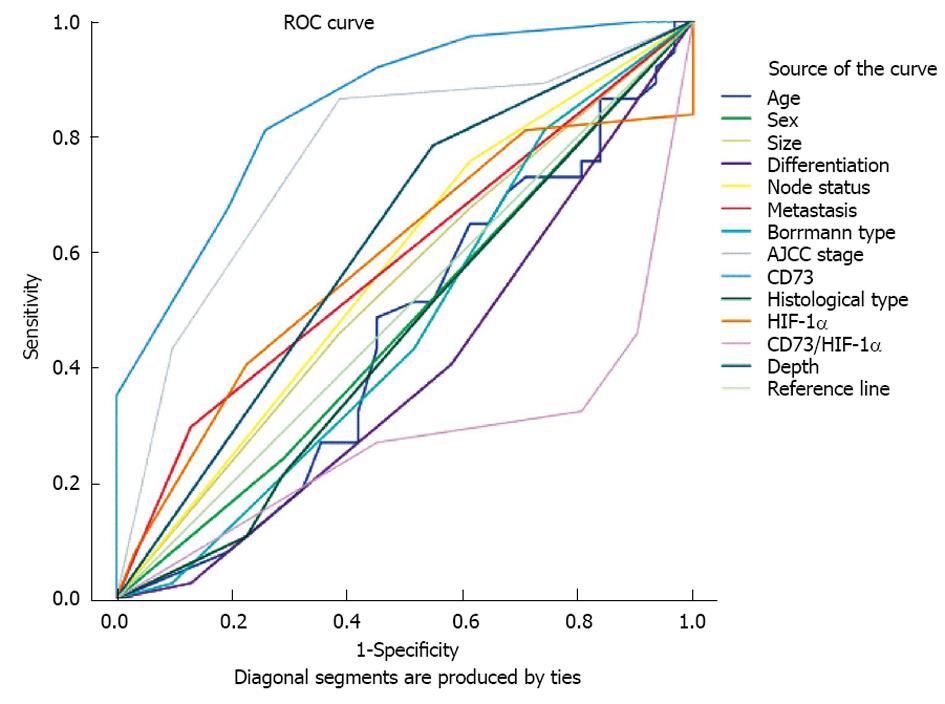
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curves of clinicopathological variables, CD73 expression and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression based on outcomes of gastric carcinoma patients.
CD73 expression (AUC = 0.850; P < 0.001), hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) (AUC = 0.582; P = 0.247), AJCC stage (AUC = 0.765; P < 0.001), CD73/HIF-1α (AUC = 0.275; P = 0.001), Borrmann type (AUC = 0.472; P = 0.689), metastasis (AUC = 0.584; P = 0.235), nodal status (AUC = 0.572; P = 0.310), differentiation (AUC = 0.394; P = 0.135), histopathology (AUC = 0.459; P = 0.559), tumor diameter (AUC = 0.541; P = 0.559), gender (AUC = 0.476; P = 0.740), and age (AUC = 0.456; P = 0.534). ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; AJCC: American Joint Committee on Cancer; AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Lu XX, Chen YT, Feng B, Mao XB, Yu B, Chu XY. Expression and clinical significance of CD73 and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in gastric carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(12): 1912-1918
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i12/1912.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i12.1912