Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2013; 19(10): 1582-1592
Published online Mar 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i10.1582
Published online Mar 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i10.1582
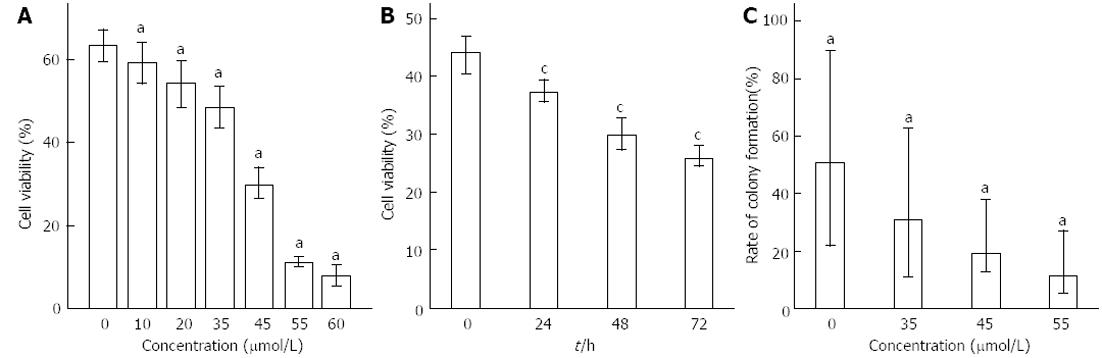
Figure 1 Effect of Rh2 on viability of Bxpc-3 cells.
A and B: Methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium assay showed that the inhibitory effects of Rh2 on the viability of BxPc-3 cells were observed in both a dose- and time-dependent manner; C: A colony formation assay was used to examine the growth of BxPc-3 cells, aP < 0.05 vs 0 μmol /L group; cP < 0.05 vs 0 h group.
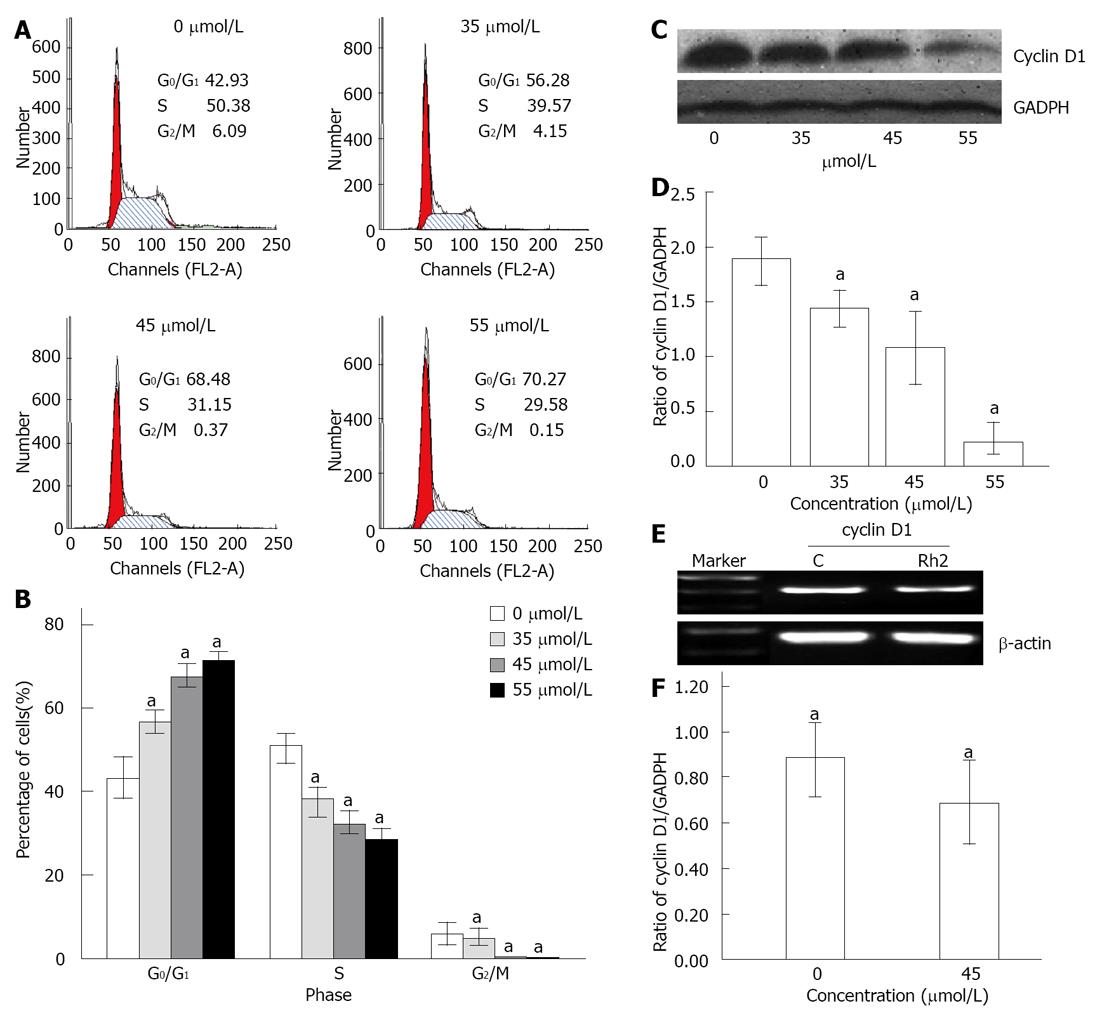
Figure 2 Rh2 induces G0/G1 arrest in Bxpc-3 cells treated for 48 h.
A, B: Cell cycle distribution was assessed by flow cytometry. The results showed that the cell cycle was arrested at the G0/G1 phase when treated with Rh2; C, D: Western blotting was used to examine protein expression of cyclin D1; E, F: Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction was used to examine the expression of cyclin D1 mRNA. The results indicated that Rh2 downregulated protein and mRNA expression of cyclin D1 in Bxpc-3 cells. aP < 0.05 vs 0 μmol /L group. GADPH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
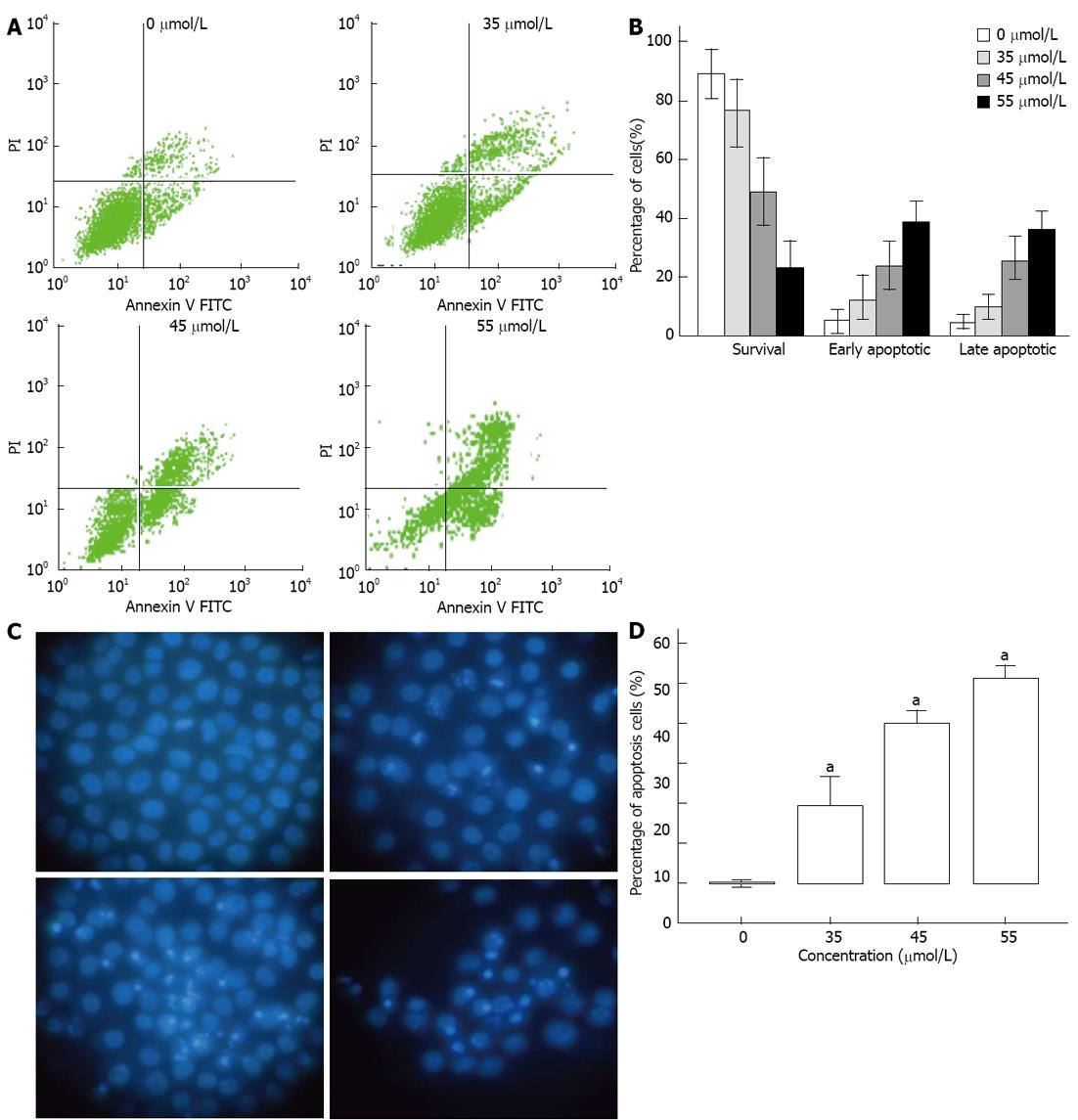
Figure 3 Rh2 induces Bxpc-3 cells apoptosis.
A, B: An apoptosis assay was carried out using flow cytometry after Annexin V-FITC/PI staining. Viable cells are in the lower left quadrant, early apoptotic cells are in the lower right quadrant, late apoptotic or necrotic cells are in the upper right quadrant, and nonviable necrotic cells are in the upper left quadrant. The data showed that Rh2 increased the percentages of early and late apoptotic cells; C, D: An apoptosis assay was also carried out using Hoechst 33 258 staining. Nuclei were stained weak homogeneous blue in the normal cells, and bright chromatin condensation and nuclear fragmentation were found in the apoptosis cells. The percentages of apoptosis cells treated with Rh2 were increased, aP < 0.05 vs 0 μmol /L group.
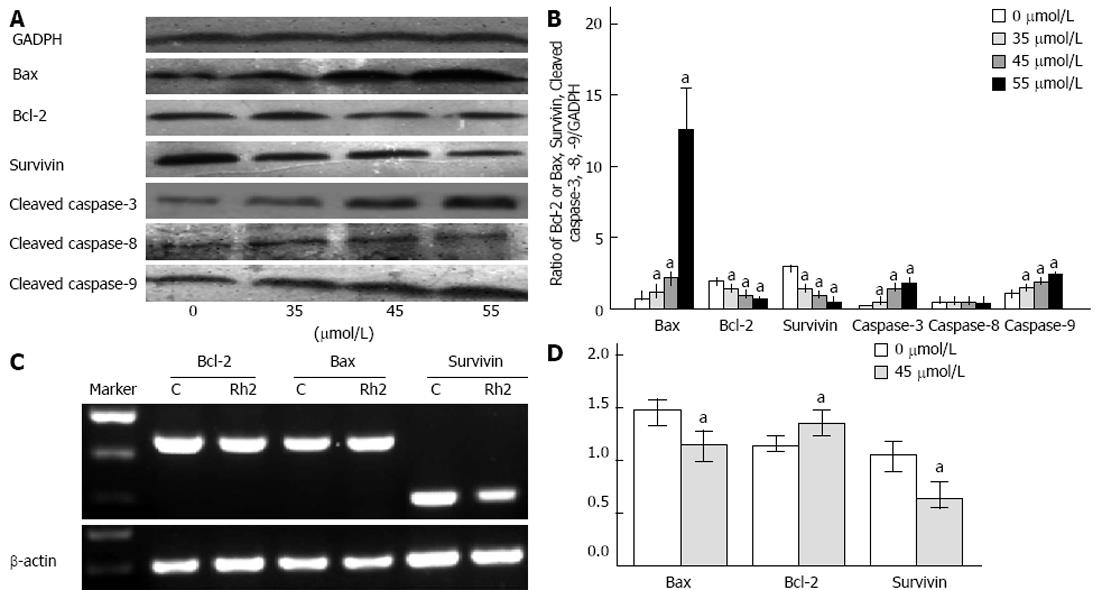
Figure 4 Effects of Rh2 on proteins and mRNA expression of Bax, Bcl-2, survivin, cleaved caspase-3, caspase-8, caspase-9 in Bxpc-3 cells.
A, B: Western blotting was used to examine protein expression of Bax, Bcl-2, survivin, cleaved caspase-3, caspase-8 and caspase-9. Rh2 upregulated protein expression of Bax, cleaved caspase-3 and caspase-9 in a dose-dependent manner and downregulated protein expression of Bcl-2 and survivin in a dose-dependent manner. However, Rh2 had no effect on protein expression of cleaved caspase-8; C, D: Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction was used to examine the expression of Bax, Bcl-2 and survivin mRNA. Rh2 (45 μmol/L) upregulated mRNA expression of Bax, and downregulated mRNA expression of Bcl-2 and survivin, aP < 0.05 vs 0 μmol /L group.
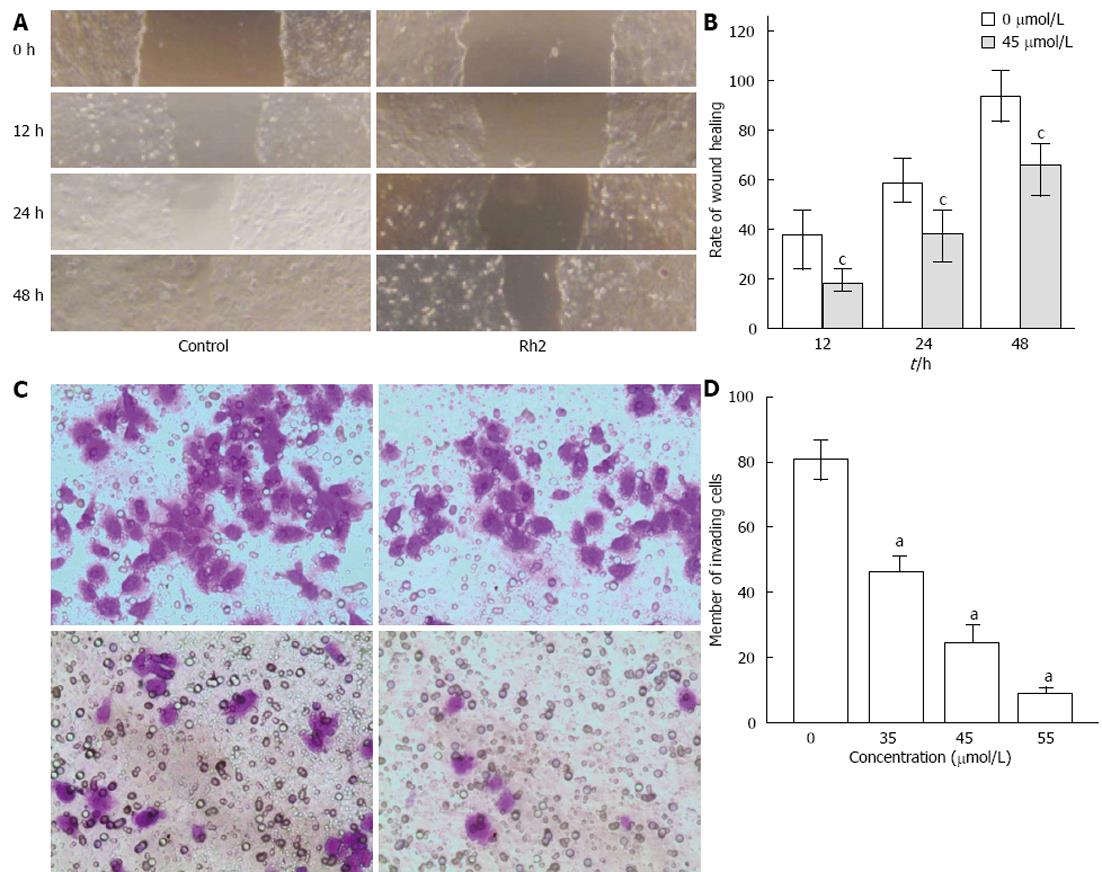
Figure 5 Rh2 inhibits Bxpc-3 cell invasion and migration.
A, B: Viability of cell migration was assessed with a scratch wound healing assay and expressed by a wound healing area. Rh2 decreased the rate of scratch wound healing; C, D: Vability of cell invasion was assessed by Matrigel invasion assay and expressed by the number of invading cells. Rh2 decreased the number of invading cells, aP < 0.05 vs 0 μmol /L group; cP < 0.05 vs control group.
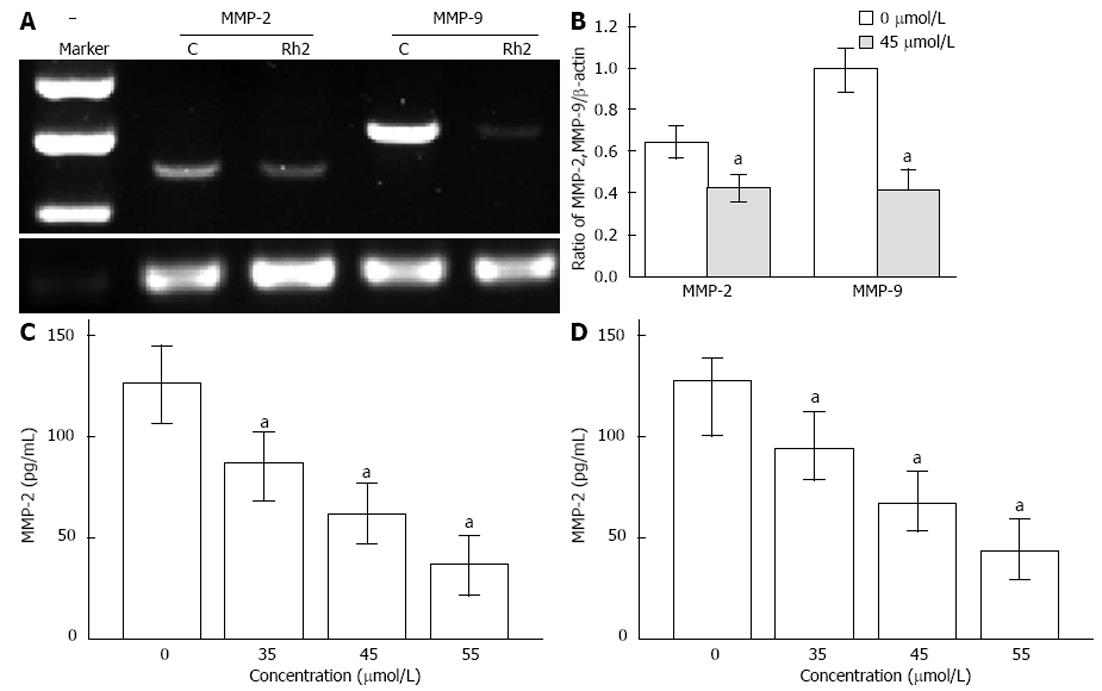
Figure 6 Effects of Rh2 on protein and mRNA expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in Bxpc-3 cells.
A, B: Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction was used to examine the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 mRNA. Rh2 (45 μmol/L) downregulated expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNA; C, D: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to examine protein expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Rh2 downregulated protein expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in supernatants of Bxpc-3 cells in a dose-dependent manner, aP < 0.05 vs 0 μmol /L group.
- Citation: Tang XP, Tang GD, Fang CY, Liang ZH, Zhang LY. Effects of ginsenoside Rh2 on growth and migration of pancreatic cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(10): 1582-1592
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i10/1582.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i10.1582