Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2012; 18(38): 5418-5426
Published online Oct 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5418
Published online Oct 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5418
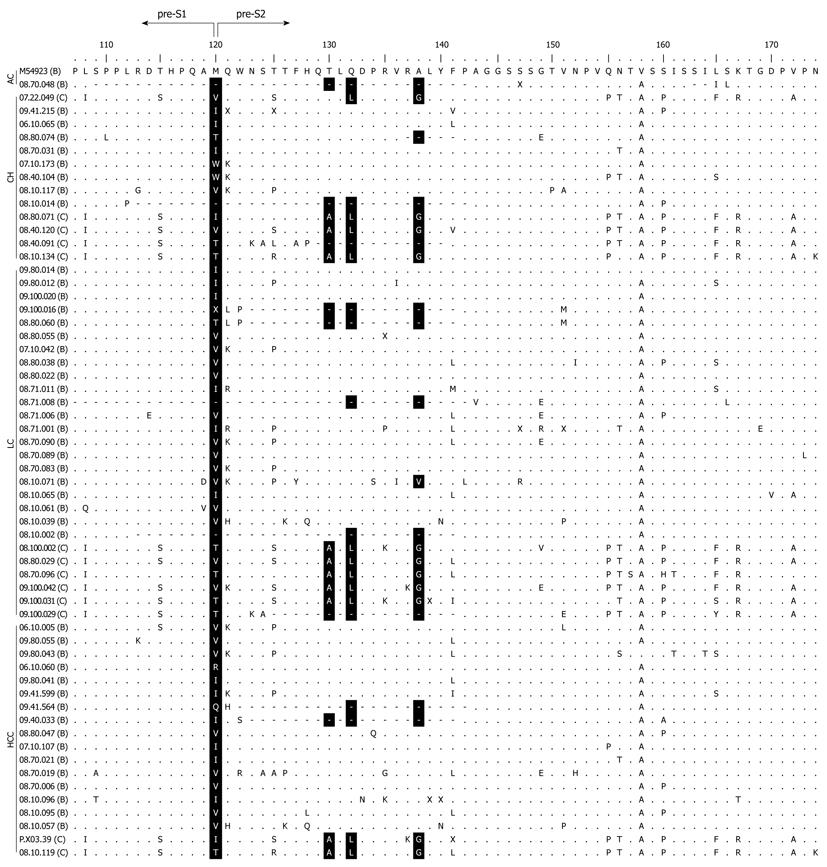
Figure 1 Amino acid alignment of 59 hepatitis B virus sequences harboring pre-S2 start codon mutation with wild type reference M54923 (genotype B).
Positions of mutations are shown in black shades (M120, T130, Q132, and A138). Dots represent identical amino acids to the consensus sequence. Dashes represent deletion mutation. The names of the samples are indicated with each respective genotype in parentheses. AC: Asymptomatic carrier; CH: Chronic hepatitis; LC: Liver Cirrhosis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
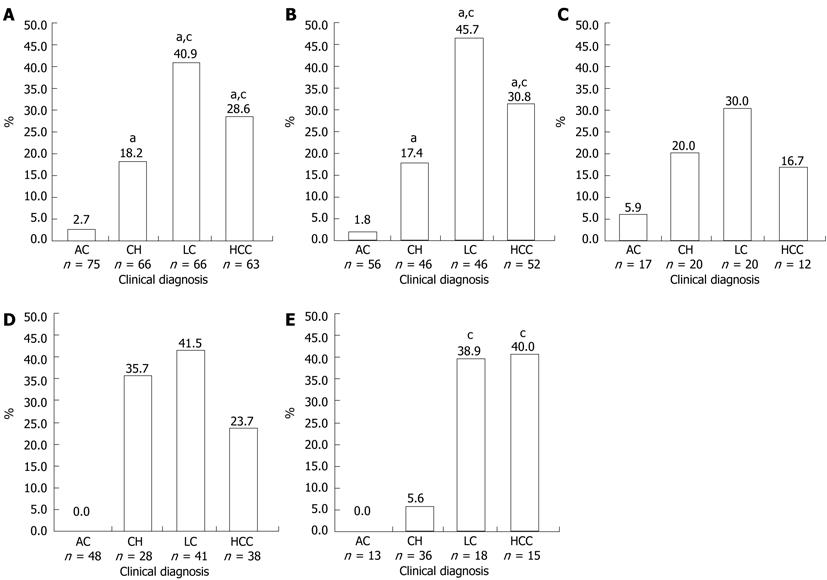
Figure 2 Prevalence of pre-S2 start codon mutation in all samples and in patients infected with hepatitis B virus/B, hepatitis B virus/C, hepatitis B e antigen (+), hepatitis B e antigen (-).
A: Prevalence of pre-S2 start codon mutation in all samples; B: Prevalence of pre-S2 start codon mutation in patients infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV)/B; C: Prevalence of pre-S2 start codon mutation in patients infected with HBV/C; D: Prevalence of pre-S2 start codon mutation in patients with hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) (-); E: Prevalence of pre-S2 start codon mutation in patients with HBeAg(+). aP < 0.05 vs AC; cP < 0.05 vs CH. AC: Asymptomatic carrier; CH: Chronic hepatitis; LC: Liver cirrhosis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Utama A, Siburian MD, Fanany I, Intan MDB, Dhenni R, Kurniasih TS, Lelosutan SA, Achwan WA, Zubir N, Arnelis, Lukito B, Yusuf I, Lesmana LA, Sulaiman A. Hepatitis B virus pre-S2 start codon mutations in Indonesian liver disease patients. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(38): 5418-5426
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i38/5418.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5418