Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2011; 17(39): 4349-4364
Published online Oct 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i39.4349
Published online Oct 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i39.4349
Figure 1 Classification of the various types of groove pancreatitis.
A: Typical finding of groove pancreatitis (purple area); B: Segmental head pancreatitis: the scar tissue (dark blue) expands towards the duodenum; C: Pancreatitis of the head: the scar tissue (dark blue) expands to the duodenal area, determining duodenal stenosis and displacement of the common bile duct.
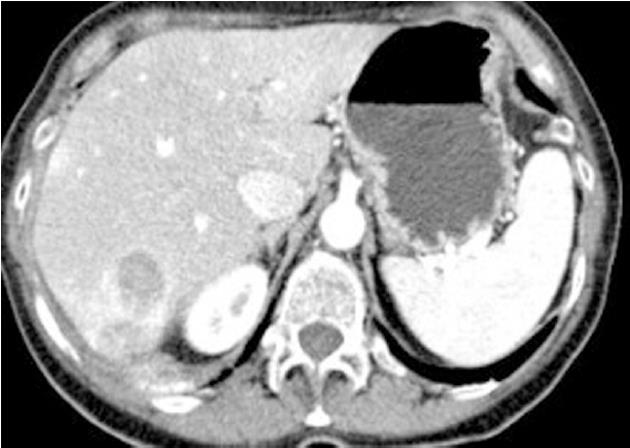
Figure 2 Case No.
1 computer tomography liver evaluation. Liver multiple hypodense lesions compatible with abscesses.
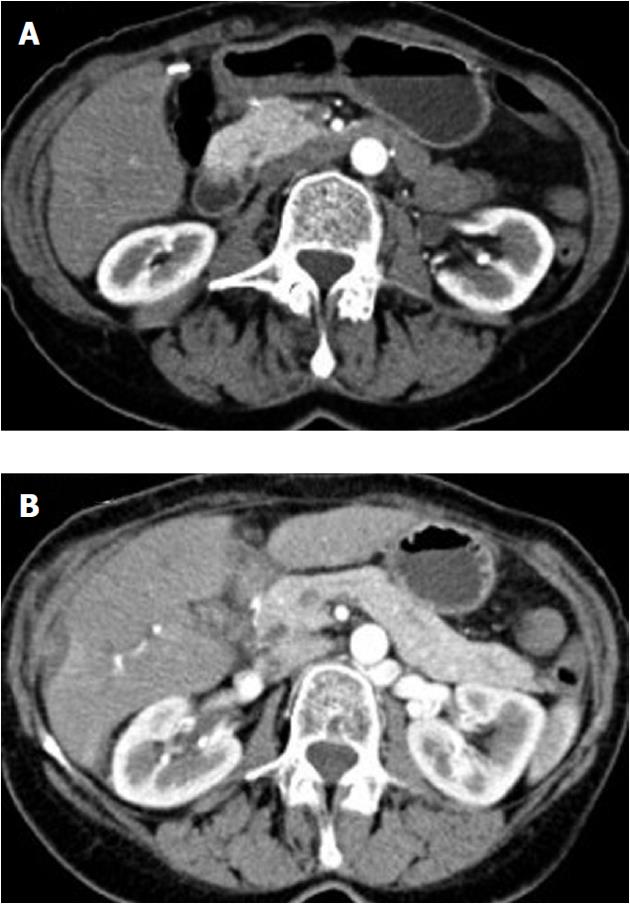
Figure 3 Case No.
1 computer tomography duodenal and pancreatic gland evaluation. A: Presence of duodenal bulging; B: Normal appearance of the pancreatic gland.
Figure 4 Case No.
1 computer tomography duodenal and pancreatic gland evaluation. A: Presence of duodenal bulging; B: Presence of cysts in the duodenal wall.
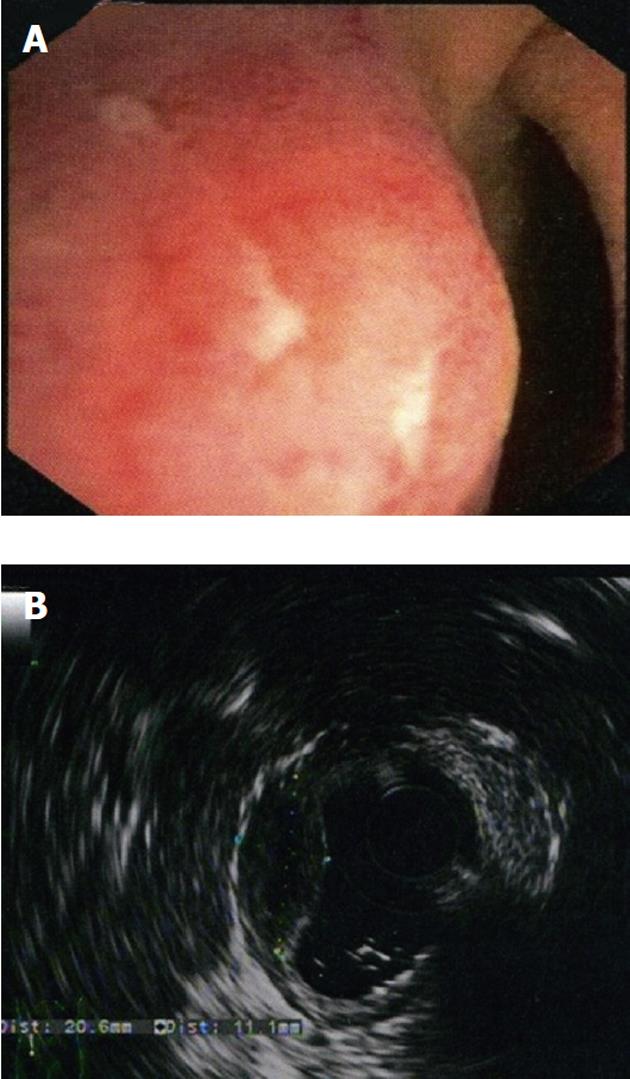
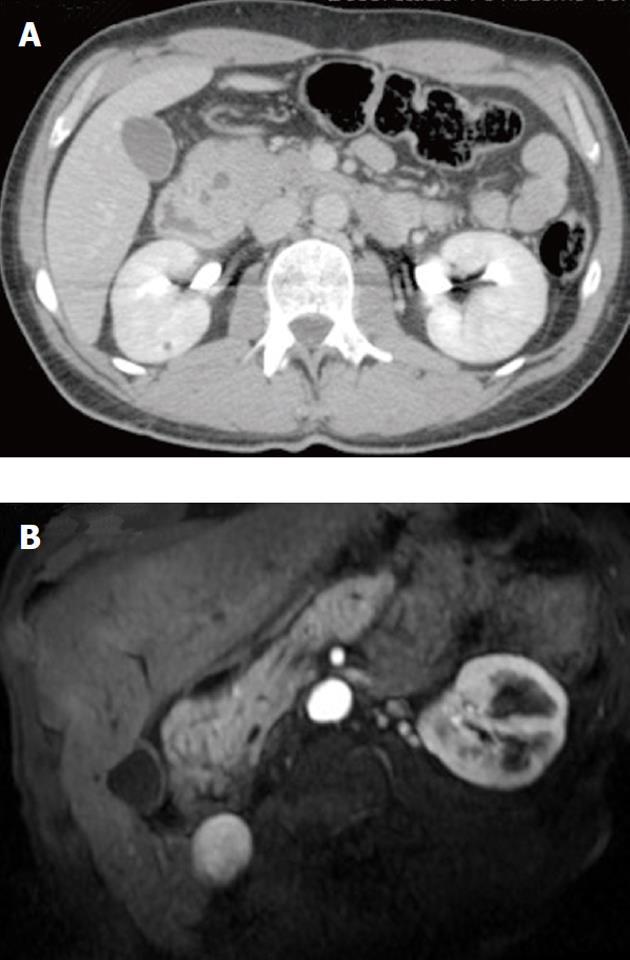
Figure 5 Case No.
2 computer tomography duodenal and pancreatic gland evaluation. A: Enlarged pancreatic head and the presence of multiple cysts between the enlarged pancreatic head and the duodenum (multidetector computer tomography); B: The remaining pancreas was normal as demonstrated by the magnetic resonance imaging.
Figure 6 Case No.
2 pancreatic and duodenal surgical specimens. A: Resected specimen showing cystic dystrophy of the duodenal wall with hypertrophy of the Brunner glands and the presence of an ectopic pancreas (arrows); B: Chronic pancreatitis in the remaining pancreas together with cystic dystrophy of the duodenal wall.
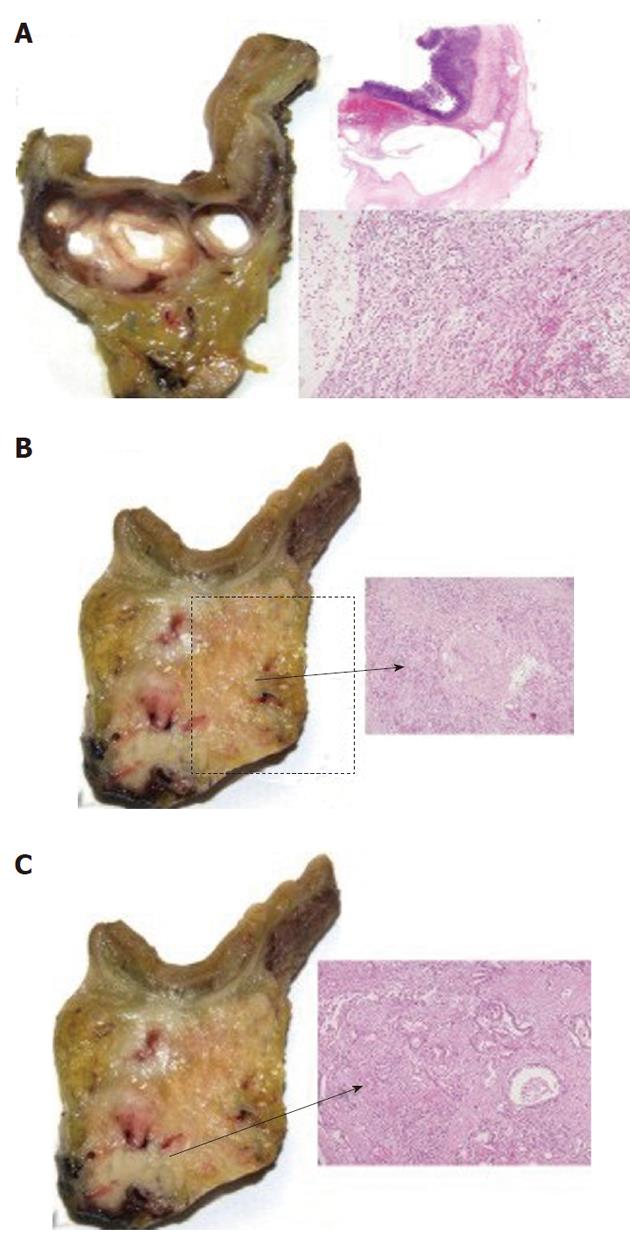
Figure 7 Case No.
3 pancreatic and duodenal pathological specimens. A: Cystic dystrophy of the duodenal wall with aspects of chronic pancreatitis in the heterotopic pancreas; B: Aspects of autoimmune pancreatitis (arrow); C: Groove adenocarcinoma extending to the pancreatic head (arrow).
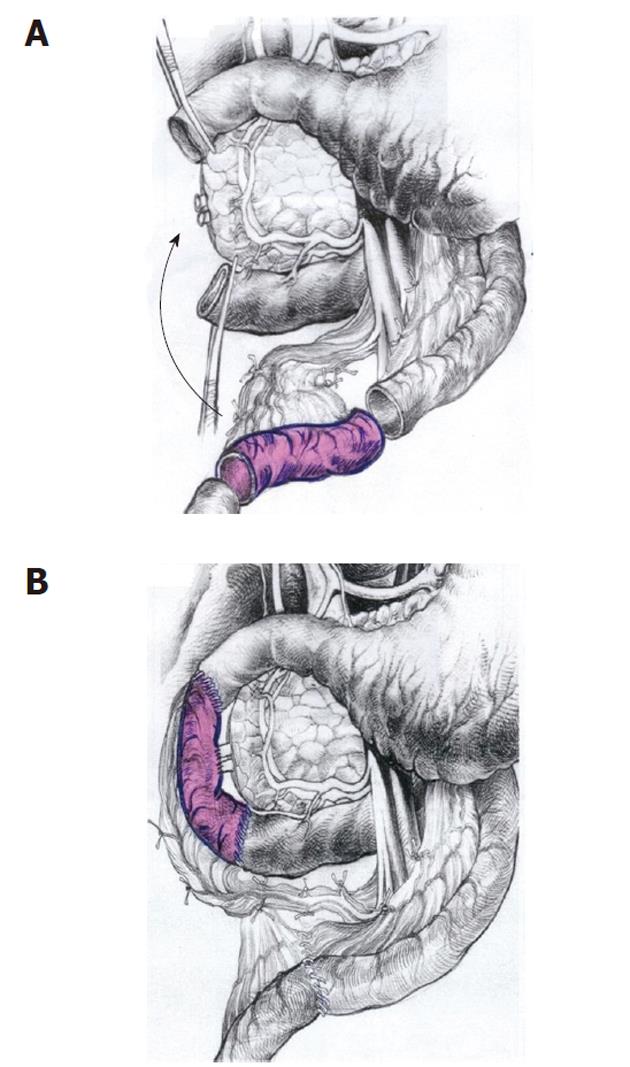
Figure 8 New surgical option for patients having cystic dystrophy of duodenal wall.
A: Scheme of the pancreas-preserving resection of the second portion of the duodenum. The second part of the duodenum, including the main papilla, is removed and the segment of the proximal jejunum supplied by the artery and vein is cut out and prepared for transposition between the 1st and 3rd portions of the duodenum; B: The shifted segment is interposed between the 1st and the 3rd parts of the duodenum. Jejuno-jejuno- and duodeno-jejuno-anastomoses are performed. The bile and the pancreatic ducts were implanted in the neodudenum 4 cm below the proximal duodeno-jejuno-anastomosis (from Egorov et al[70] with the kind permission of the authors).
- Citation: Pezzilli R, Santini D, Calculli L, Casadei R, Morselli-Labate AM, Imbrogno A, Fabbri D, Taffurelli G, Ricci C, Corinaldesi R. Cystic dystrophy of the duodenal wall is not always associated with chronic pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(39): 4349-4364
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i39/4349.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i39.4349