Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2011; 17(29): 3398-3406
Published online Aug 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i29.3398
Published online Aug 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i29.3398
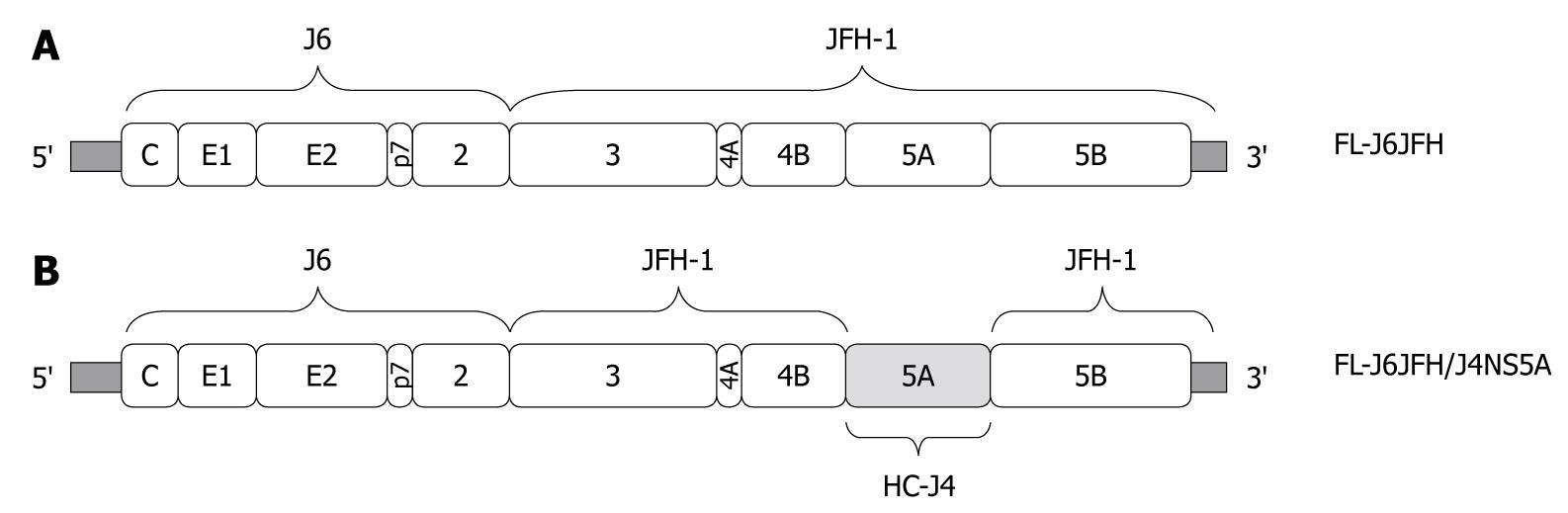
Figure 1 Construction of chimeric FL-J6JFH/J4NS5A genome containing genotype 1b (HC-J4) NS5A domain.
FL-J6JFH/J4NS5A was constructed by inserting full length gene of HC-J4 NS5A into FL-J6JFH1 using overlapping polymerase chain reaction combined with enzyme restriction reaction. A: Prototype FL-J6JFH1; B: Chimera FL-J6JFH/J4NS5A. Vertical bars: HC-J4 NS5A.
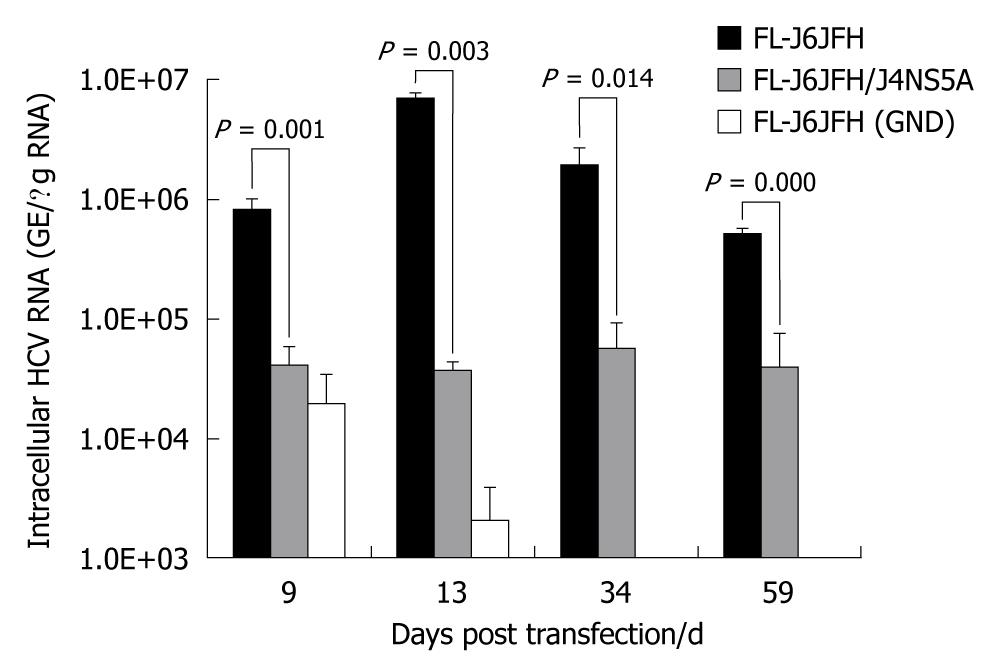
Figure 2 Fluorescence quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay for hepatitis C virus RNAs in cell lysis of RNA transcripts transfected Huh-7.
5 cells. Five micrograms in vitro transcribed RNAs were electroporated into 3 × 105 Huh-7.5 cells. Transfected cells were harvested at the indicated time points after transfection. Intracellular hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA was analyzed by fluorescence quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and displayed as genome equivalents per microgram total RNA (GE/μg RNA).
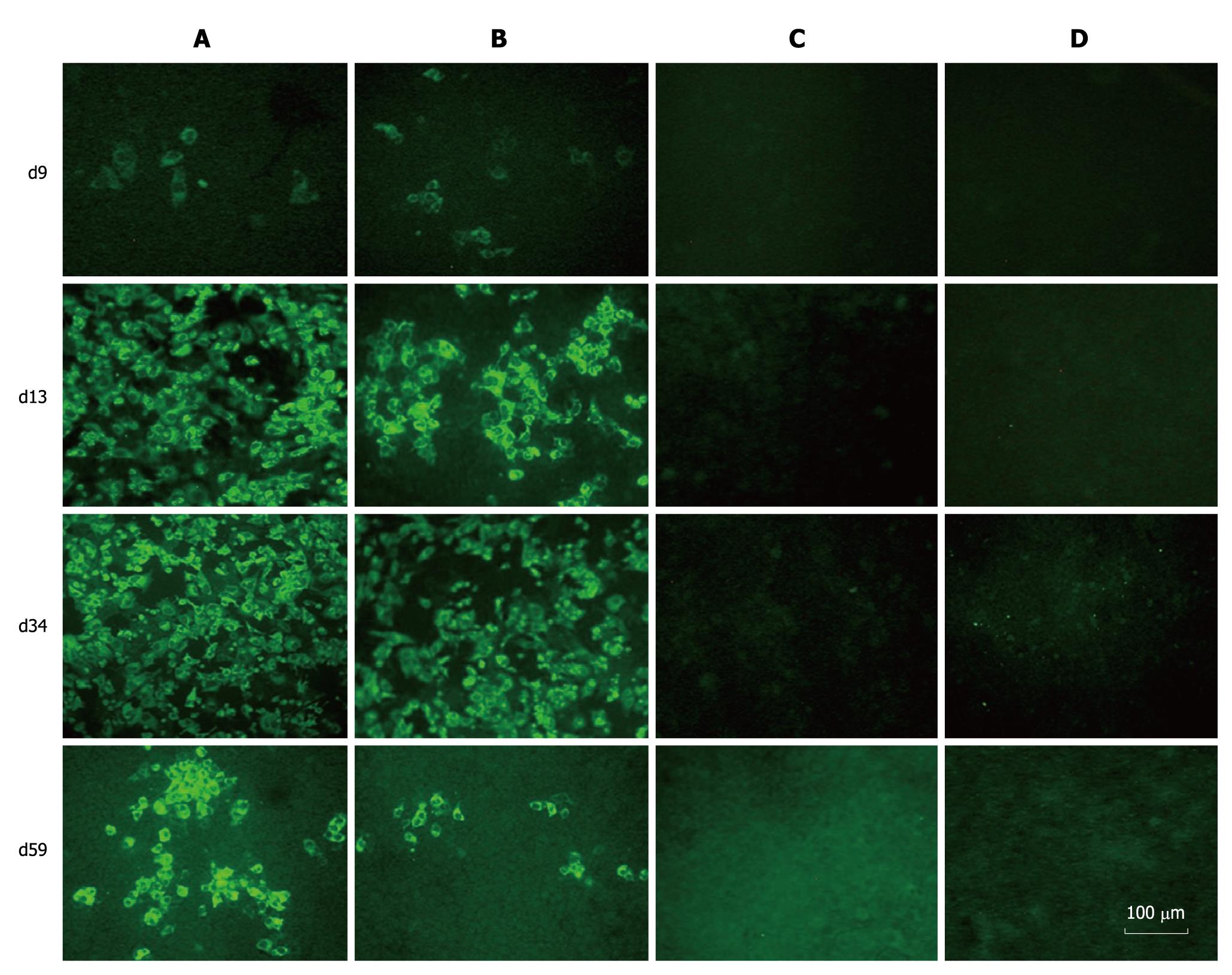
Figure 3 Immunofluorescence assay of hepatitis C virus proteins in RNAs transfected Huh-7.
5 cells. Huh-7.5 cells were passaged at day 9, 13, 34 and 59 after transfection, and cultured in 96-well plates for the detection of hepatitis C virus (HCV) proteins using sera from HCV patients as primary antibody. A: FL-J6JFH1-transfected cells; B: FL-J6JFH/J4NS5A-transfected cells; C: FL-J6JFH1 (GND)-transfected cells; D: FL-J6JFH1-transfected cells incubated with normal sera as primary antibody.
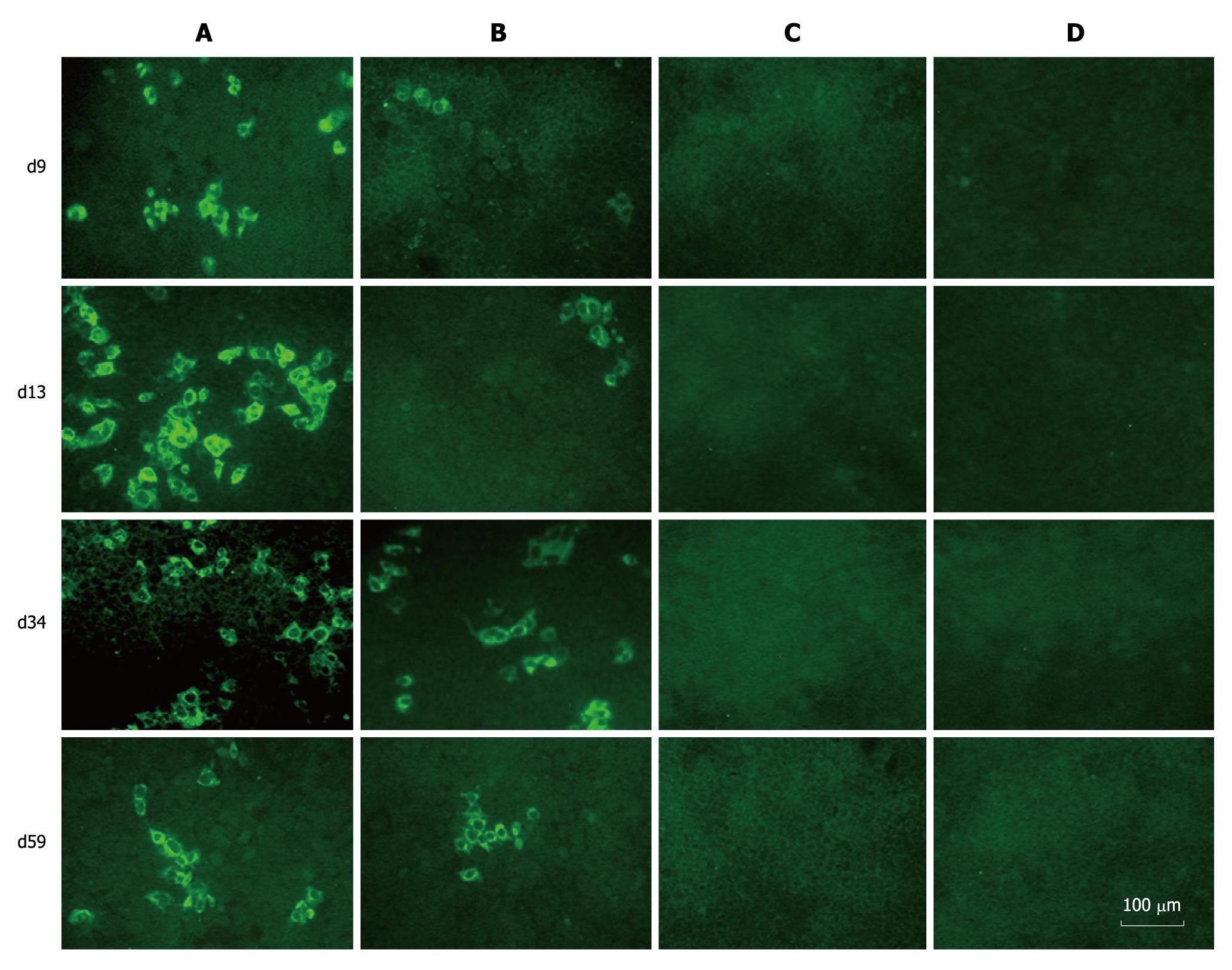
Figure 4 Immunofluorescence assay of hepatitis C virus proteins in naïve Huh-7.
5 cells infected with cell supernatants from prototype and chimera transfected Huh-7.5 cells. The naïve Huh-7.5 cells were inoculated with supernatants collected at different time points during the experiment. Three days after transfection, the cells were subjected to immunofluorescence assay using sera from hepatitis C virus patients as primary antibody. A: Cells inoculated with supernatants from FL-J6JFH1-transfected cells; B: Cells inoculated with supernatants from FL-J6JFH/J4NS5A-transfected cells; C: Cells inoculated with supernatants from FL-J6JFH1 (GND)-transfected cells; D: Cells inoculated with supernatants from FL-J6JFH1-transfected cells incubated with normal sera as primary antibody.
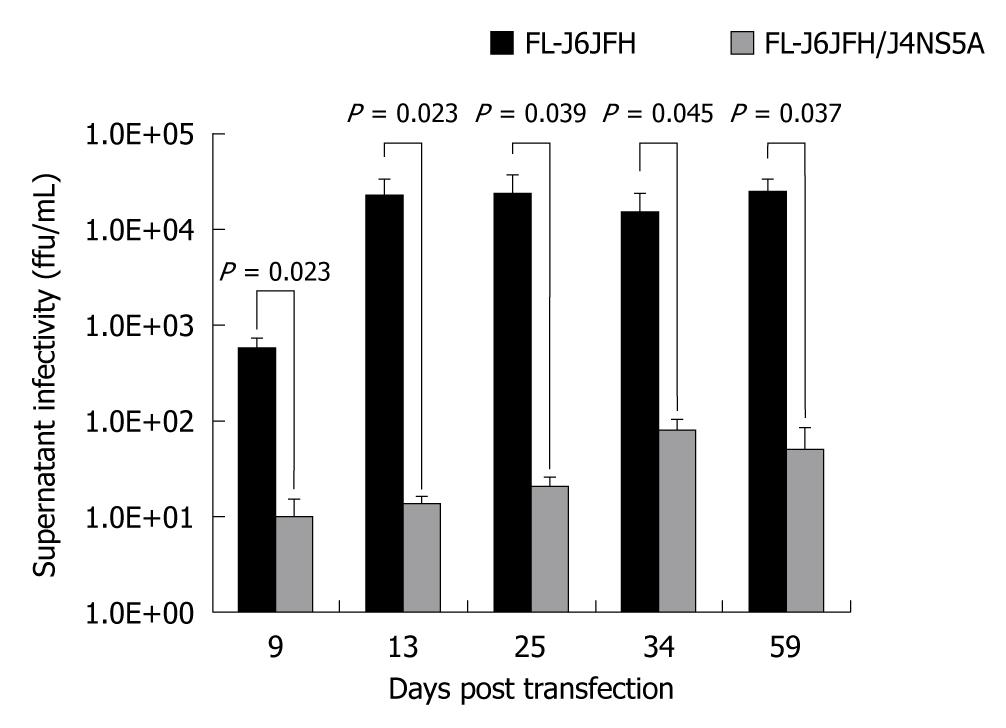
Figure 5 Comparison of cell culture-produced hepatitis C virus produced by chimera and prototype.
The full-length RNA transcripts of the prototype and chimera were transfected into Huh-7.5 cells. The supernatants were harvested at the indicated time points after transfection. The infectivity titers of the supernatants were determined, and the values were presented as focus forming unit per milliliter (ffu/mL).
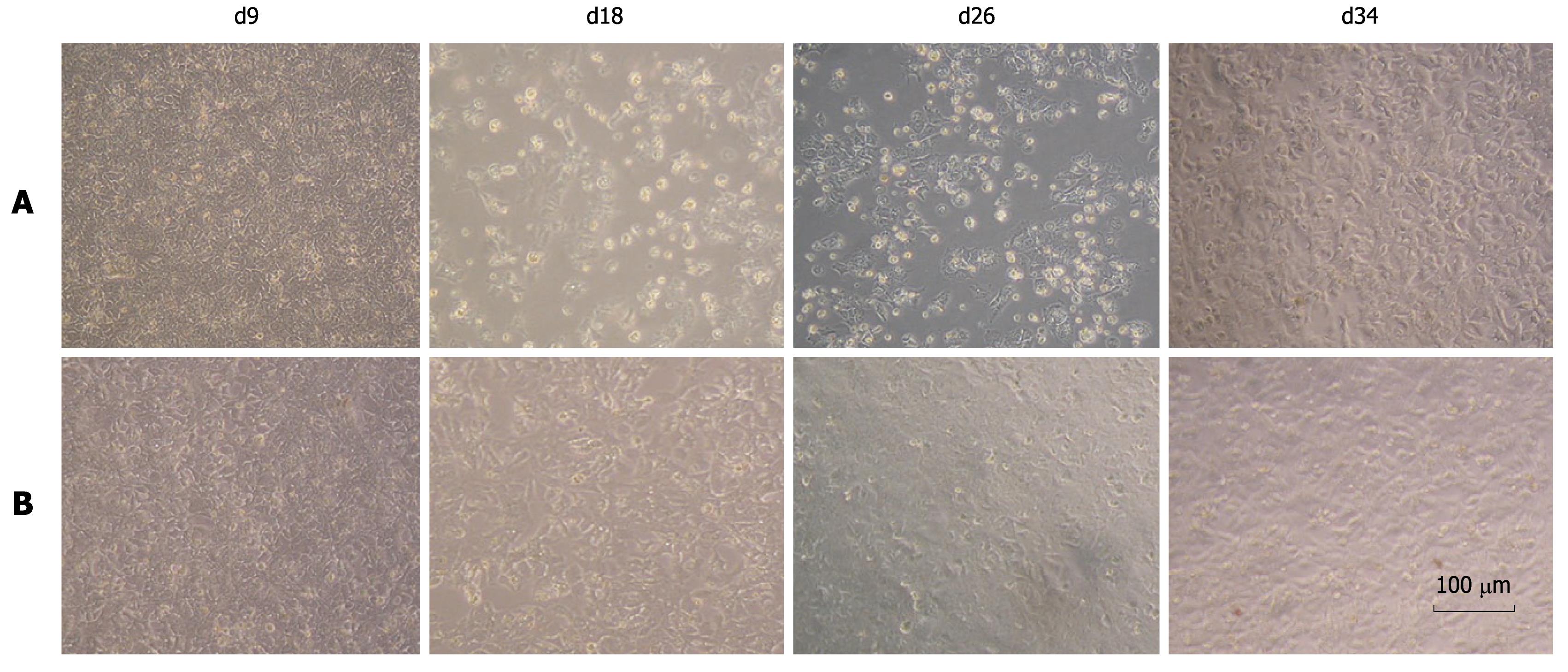
Figure 6 Cell morphology of chimera and prototype genome RNA transfected cells.
The cytopathic effect was observed in prototype RNA tansfected Huh-7.5 cells under phase-contrast microscopy from day 9 to day 34 after transfection. No cytopathic effect was observed in the chimeric RNA transfected cells. A: FL-J6JFH1-transfected cells; B: FL-J6JFH/J4NS5A-transfected cells.
- Citation: Wang YZ, Wang WB, Cao MM, Wang W, Zhao LJ, Xu G, Ren H, Qi ZT. Function of nonstructural 5A protein of genotype 2a in replication and infection of HCV with gene substitution. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(29): 3398-3406
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i29/3398.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i29.3398