Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2011; 17(19): 2397-2406
Published online May 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i19.2397
Published online May 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i19.2397
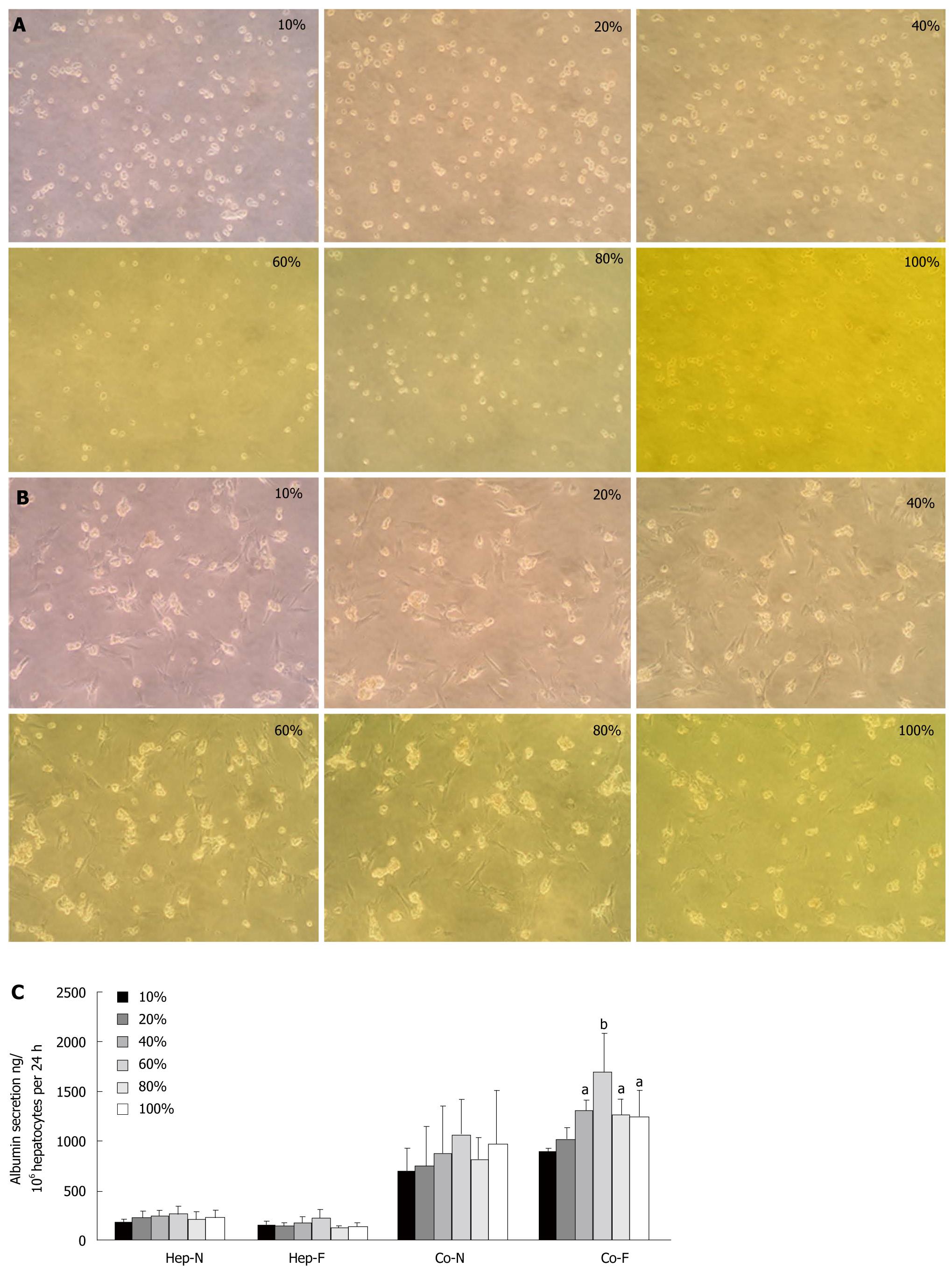
Figure 1 Optimal serum concentrations for co-cultured hepatocytes.
A: Morphology of homo-cultured hepatocytes at different concentrations of liver failure serum (magnification x 100); B: Morphology of hepatocytes co-cultured with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) at different concentrations of liver failure serum (magnification x 100); C: Albumin secretion in hepatocytes homo-cultured with normal serum (Hep-N), liver failure serum (Hep-F) and hepatocytes co-cultured with normal serum (Co-N) and liver failure serum (Co-F). aRepresents the significant difference vs Co-N group; bRepresents the largest significance vs Co-N group.
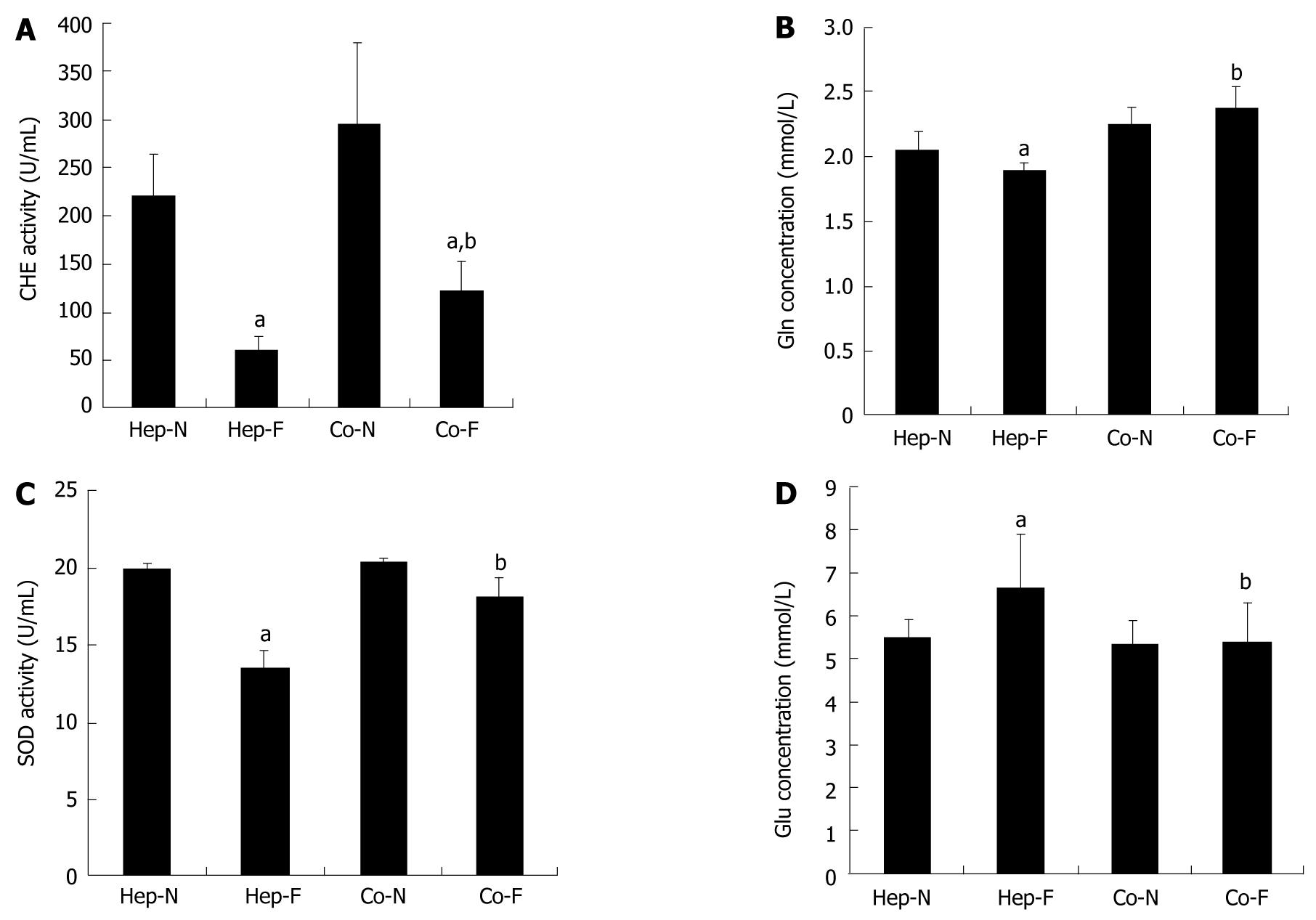
Figure 2 Hepatocyte-specific support functions in human serum.
Concentrations of acetylcholine (CHE) activity (A), glutamine (Gln) synthesis (B), superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity (C) and glucose (Glu) concentrations (D) in the medium of each group. aIndicates significant difference vs Hep-N group; bIndicates significant difference vs homo-hepatocytes cultured by various concentrations of liver failure serum (Hep-F) group. Hep-N: Hepatocytes homo-cultured with normal serum; Co-N:Hepatocytes co-cultured with normal serum; Co-F: Liver failure serum.
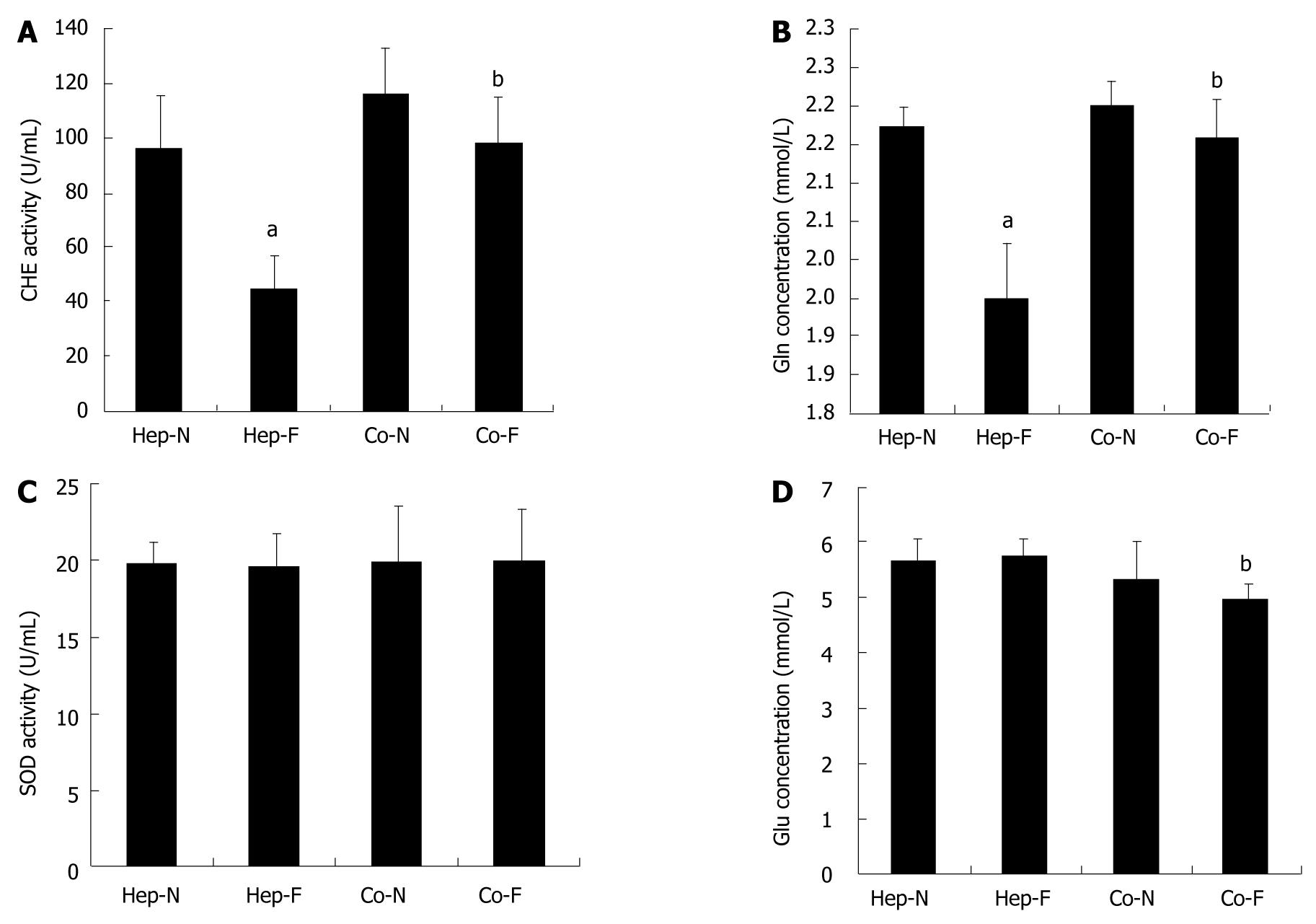
Figure 3 Post-incubation influence of liver failure serum on hepatocyte metabolic functions.
Concentrations of acetylcholine (CHE) activity (A), glutamine (Gln) synthesis (B), superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity (C) and glucose (Glu) concentrations (D) in the medium of each group. aIndicates significant difference vs hepatocytes homo-cultured with normal serum (Hep-N) group; bIndicates significant difference vs homo-hepatocytes cultured by various concentrations of liver failure serum (Hep-F) group. Co-N:Hepatocytes co-cultured with normal serum; Co-F: Liver failure serum.
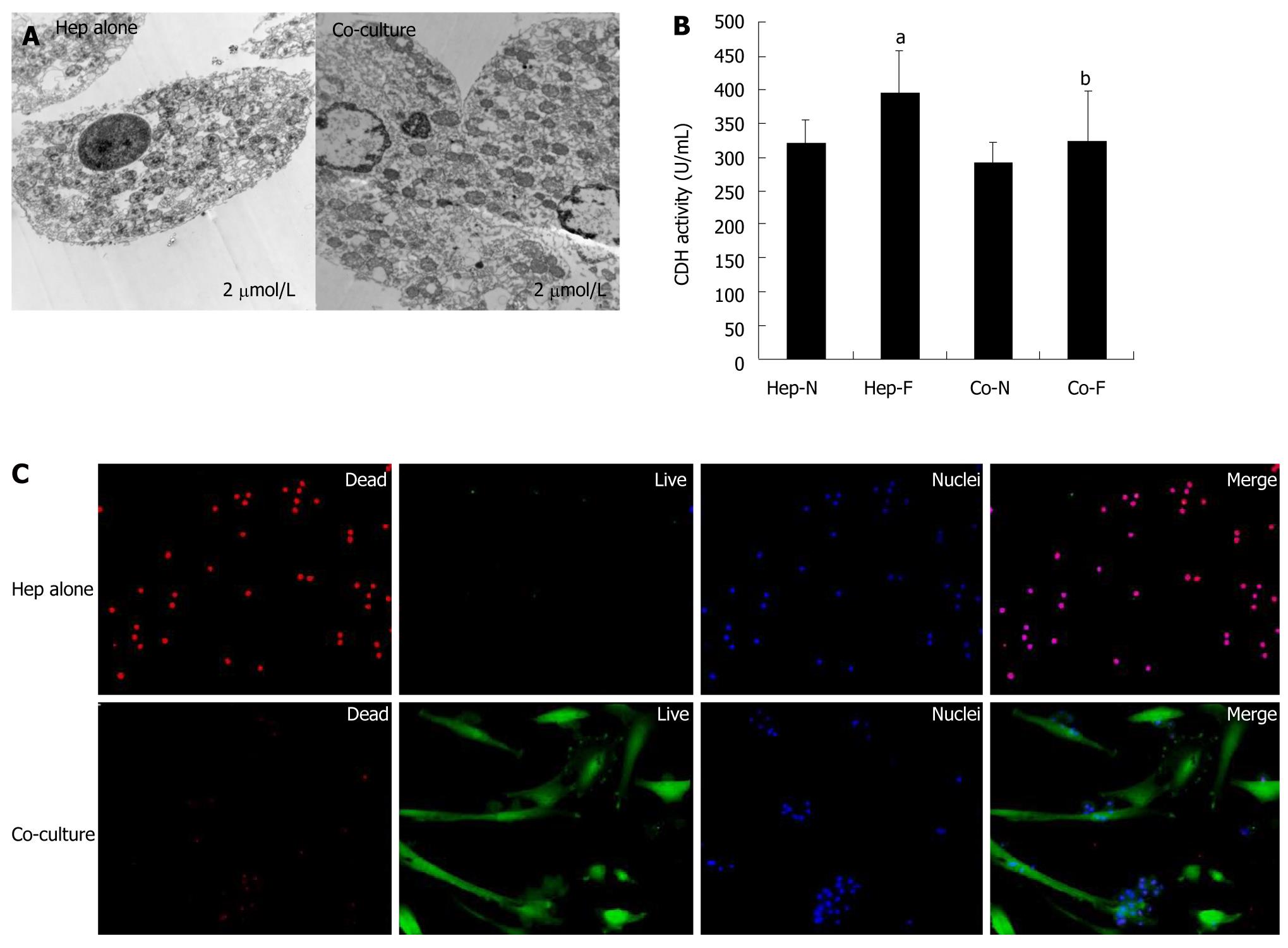
Figure 4 Cytotoxic effects of liver failure serum on hepatocytes cultured alone vs co-cultured hepatocytes.
A: Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis of the homo-cultured hepatocytes (left panel) and hepatocytes co-cultured with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) (righ panel) in the presence of 60% of liver failure serum; B: Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay of hepatocytes was indicated in each group; C: Live/dead assay of homo-cultured hepatocytes (upper panel) and hepatocytes co-cultured with MSCs (lower panel) in the presence of 60% of liver failure serum. aIndicates significant difference vs Hep-N group; bIndicates significant difference vs homo-hepatocytes cultured by various concentrations of liver failure serum (Hep-F) group. Hep-N: Hepatocytes homo-cultured with normal serum; Co-N:Hepatocytes co-cultured with normal serum; Co-F: Liver failure serum.
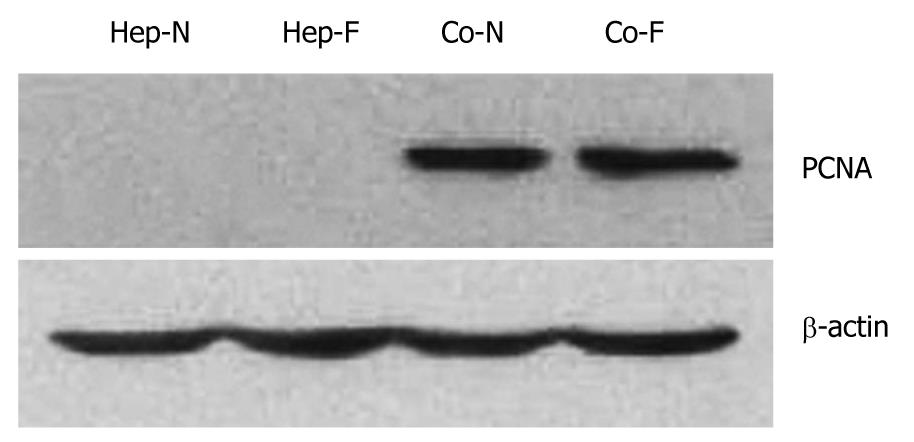
Figure 5 Increased proliferation after incubation with liver failure serum by co-culturing with mesenchymal stem cells.
The proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) levels of hepatocytes cutured alone in Hep-N and Hep-F groups were too low to be detected while a significant increase was observed in the co-cultured groups irrespective of liver serum insult (P < 0.05). Statistical analysis with regard to PCNA level showed no significant difference between Co-N and Co-F groups (P > 0.05). Hep-N: Hepatocytes homo-cultured with normal serum; Co-N:Hepatocytes co-cultured with normal serum; Co-F: Liver failure serum.
-
Citation: Shi XL, Gu JY, Zhang Y, Han B, Xiao JQ, Yuan XW, Zhang N, Ding YT. Protective effects of ACLF sera on metabolic functions and proliferation of hepatocytes co-cultured with bone marrow MSCs
in vitro . World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(19): 2397-2406 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i19/2397.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i19.2397