Copyright
copy;2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2010; 16(36): 4589-4593
Published online Sep 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4589
Published online Sep 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4589
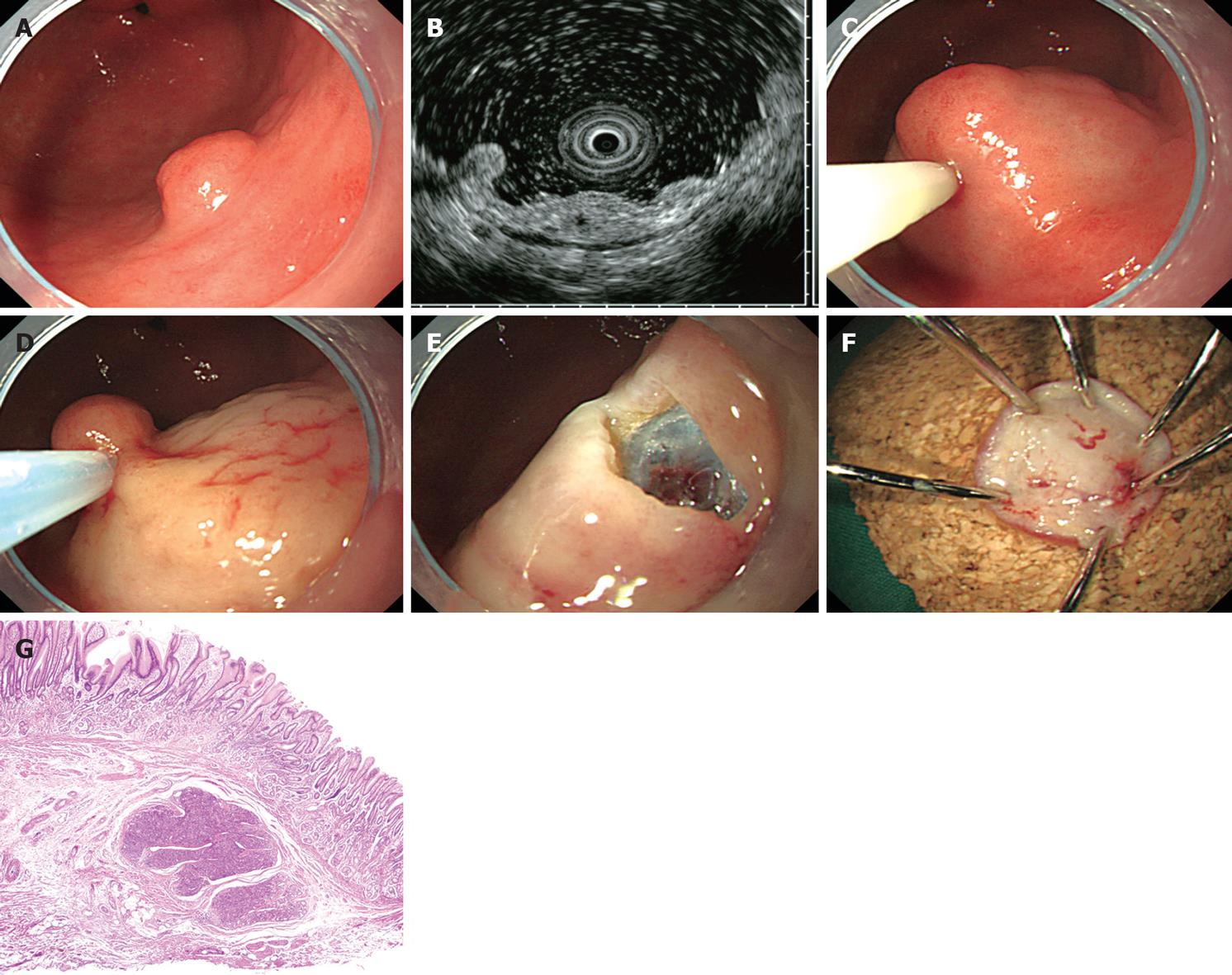
Figure 1 Endoscopic mucosal resection of ectopic pancreas by injection-and-cut technique (case 3).
A: A subepithelial lesion is observed on the greater curvature of the antrum; B: Endoscopic ultrasonography image obtained with a 20 MHz catheter probe. An indistinct, heterogeneous, and hypoechoic lesion with a small anechoic space is located within the submucosal layer; C: Saline with indigo carmine is injected into the submucosa beneath the lesion; D: The lesion is resected using an electrocautery snare; E: The lesion is completely removed; F: The inner surface of the resected specimen; G: Histologically, the ectopic pancreas is located in the submucosa (HE, × 40).
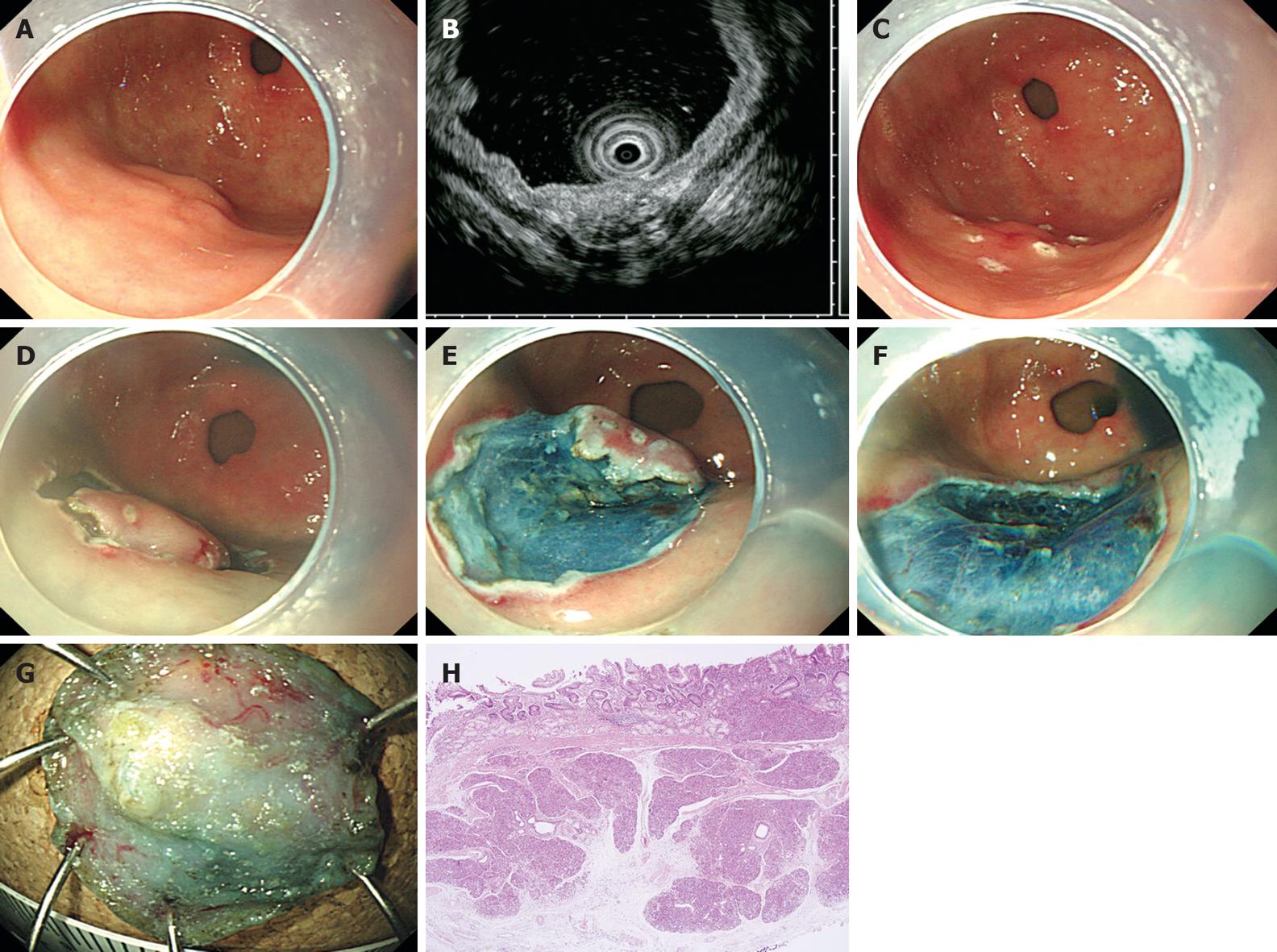
Figure 2 Endoscopic submucosal dissection of ectopic pancreas (case 7).
A: A subepithelial lesion with a tiny erosion due to a previous biopsy is observed on the greater curvature of the antrum; B: Endoscopic ultrasonography image obtained with a 20 MHz catheter probe. An indistinct, heterogeneous, and hypoechoic lesion with small anechoic spaces is located within the deep mucosal and submucosal layer; C: By using a standard needle knife, a mark is made on the margin of the lesion; D: Saline injection with epinephrine and indigo carmine is injected into the submucosa beneath the lesion, and then a complete circumference incision is made using an IT knife; E: The IT knife is used to dissect the submucosa; F: The lesion is completely removed; G: The inner surface of the resected specimen; H: Histologically, the ectopic pancreas tissue is located in the deep mucosa and submucosa (HE, × 40).
- Citation: Ryu DY, Kim GH, Park DY, Lee BE, Cheong JH, Kim DU, Woo HY, Heo J, Song GA. Endoscopic removal of gastric ectopic pancreas: An initial experience with endoscopic submucosal dissection. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(36): 4589-4593
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i36/4589.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4589