Copyright
copy;2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2010; 16(33): 4237-4242
Published online Sep 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i33.4237
Published online Sep 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i33.4237
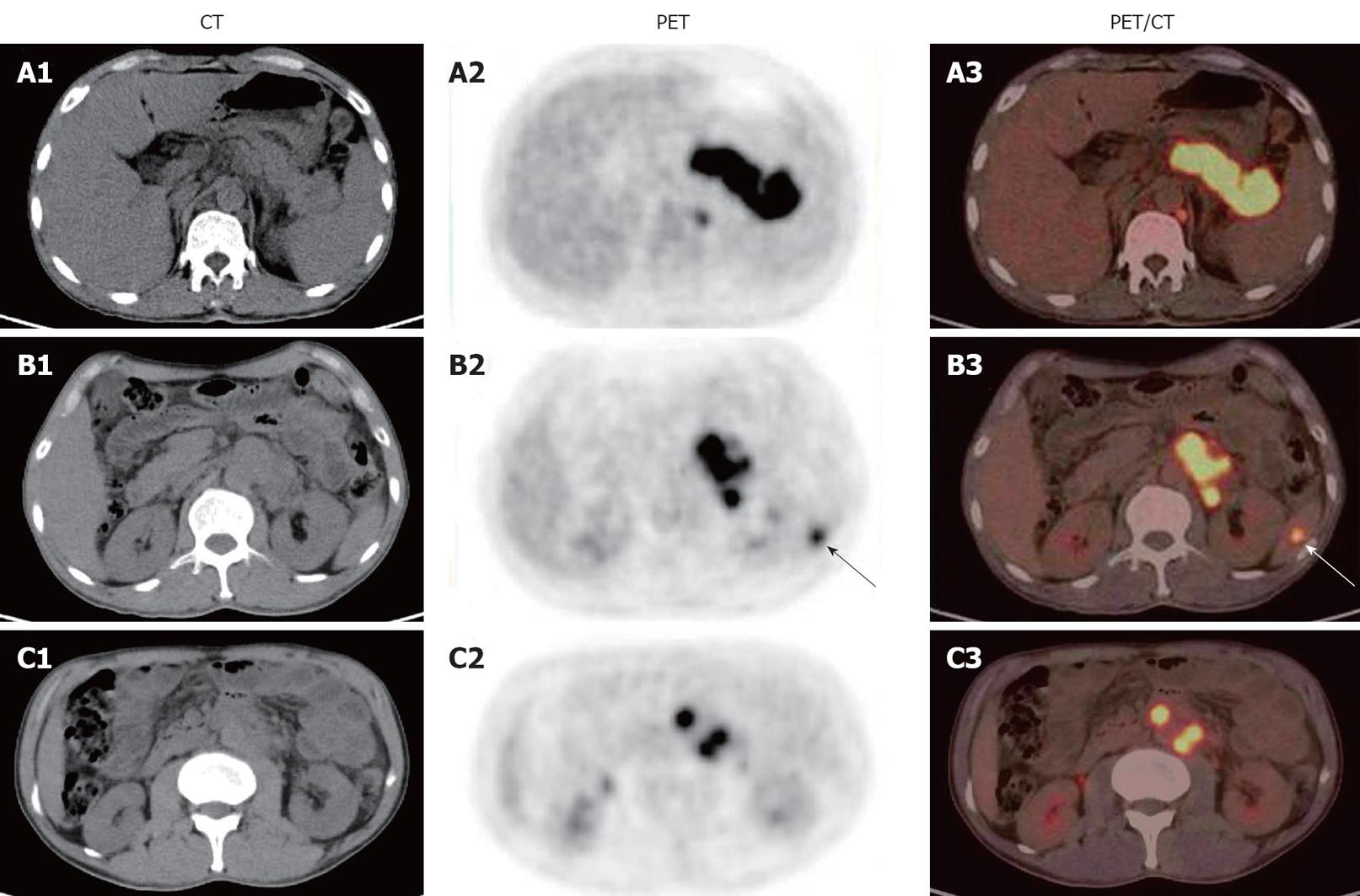
Figure 1 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission/computed tomography images of patient 1 showing a mass-like area with an intense 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake extending up behind the pancreatic body and tail (A1-A3), a focal area with an intense 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in spleen (arrows) (B1-B3), and multiple focal areas with an intense 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake around the abdominal aorta (C1-C3).
CT: Computed tomography; PET: Positron emission tomography.
Figure 2 Hematoxylin and eosin staining of laparoscopic biopsy specimen (× 200) from mass extending to behind the pancreas showing amorphous, eosinophilic and granular debris, as well as Langhans giant cells (arrows) in granulomas.
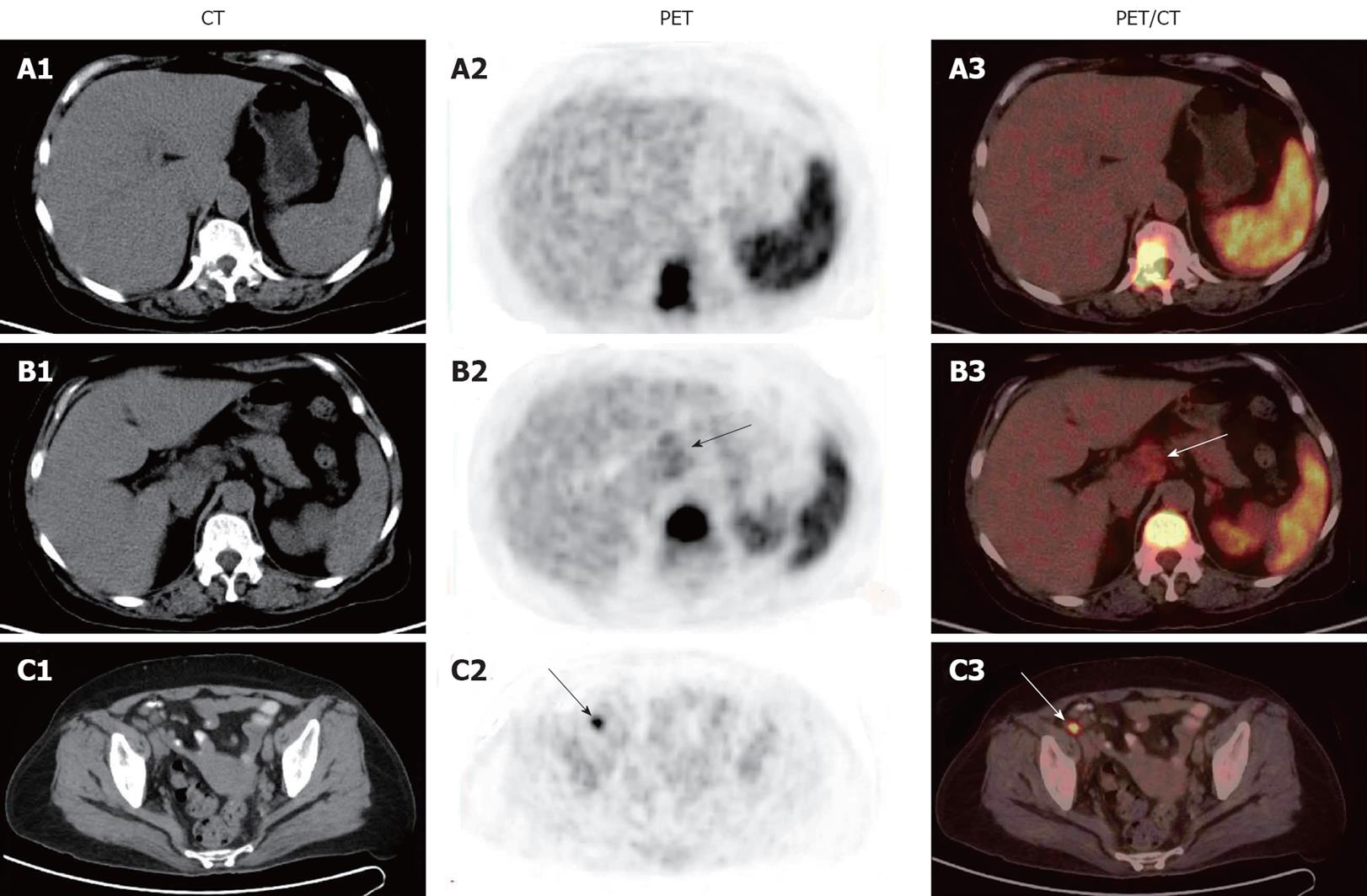
Figure 3 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission/computed tomography images of patient 2 showing diffuse intense uptake of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose in spleen and intense 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in thoracic vertebrae (A1-A3), a mass-like area with an intense 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in hepatic hilar region (arrows) and thoracic vertebrae (B1-B3), and a focal intense uptake of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose in right iliac arterial region (arrows) (C1-C3).
CT: Computed tomography; PET: Positron emission tomography.
Figure 4 Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the biopsy specimen from the 1st lumbar vertebra and the mass in hepatic hilar region showing thickened irregular bone trabeculae with a slight infiltration of lymphocytes and plasmocytes (arrow) (A), granulomatous lymphadenitis and amorphous, eosinophilic and granular debris, and Langhans giant cells in granulomas (arrows) (B).
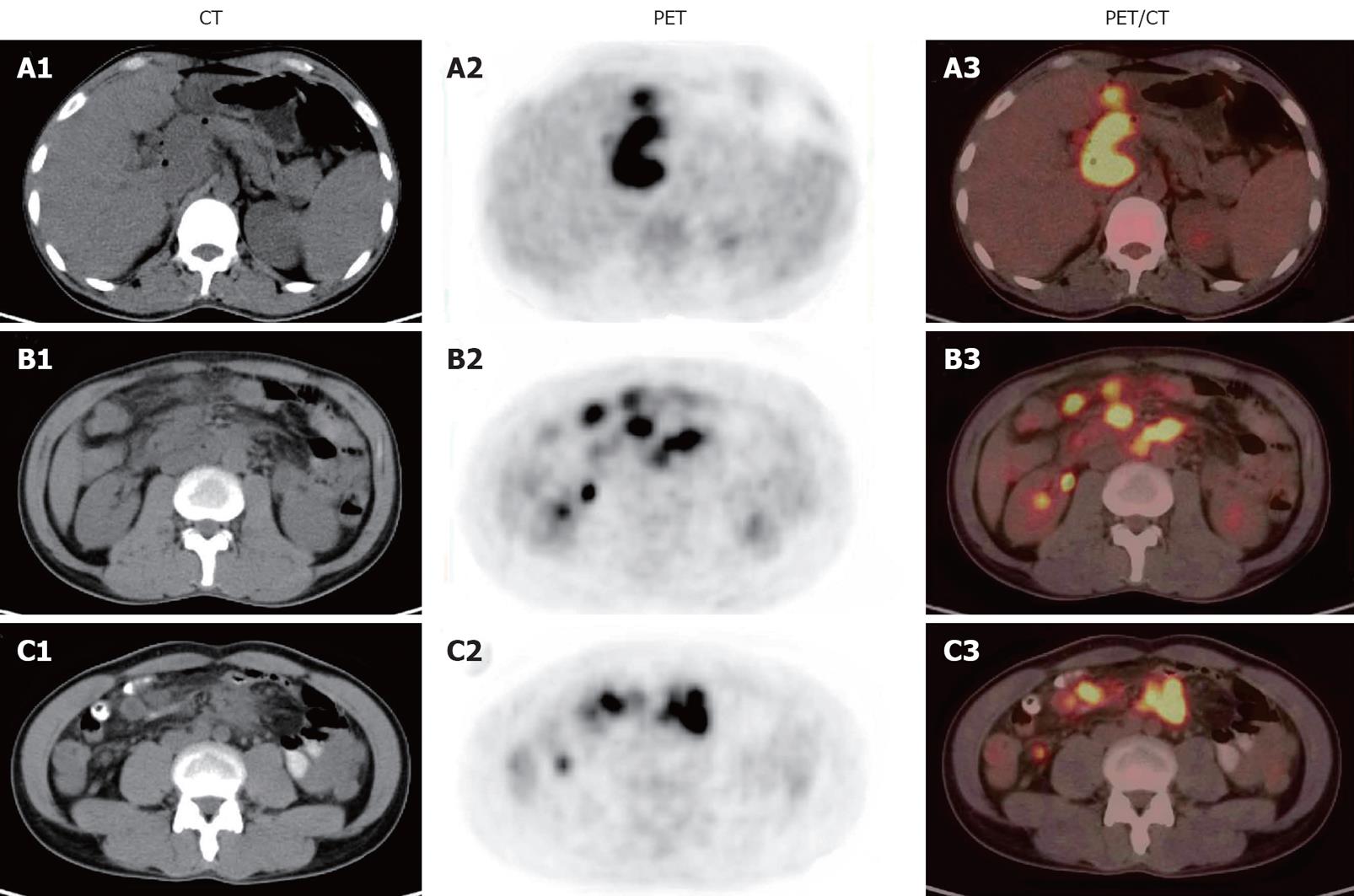
Figure 5 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission/computed tomography images of patient 3 A showing a mass-like area with an intense 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in hepatic hilar region (A1-A3), multiple focal lesions (B1-B3) or multiple lamellar lesions (C1-C3) with an intense 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in peritoneal cavity, retroperitoneal space, and peritoneum.
CT: Computed tomography; PET: Positron emission tomography.
- Citation: Tian G, Xiao Y, Chen B, Guan H, Deng QY. Multi-site abdominal tuberculosis mimics malignancy on 18F-FDG PET/CT: Report of three cases. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(33): 4237-4242
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i33/4237.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i33.4237