Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2010; 16(23): 2881-2888
Published online Jun 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2881
Published online Jun 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2881
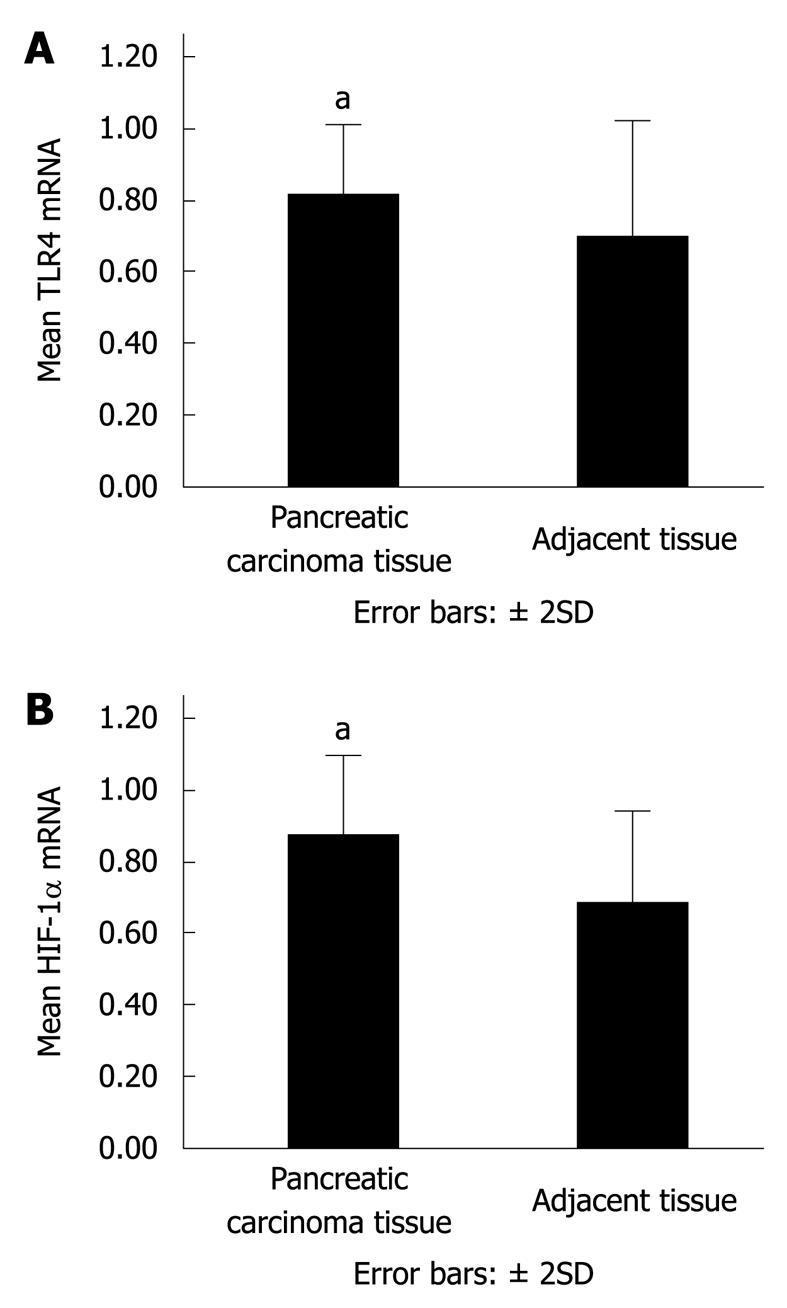
Figure 1 Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 and hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1α (HIF-1α) mRNA in pancreatic carcinoma and adjacent tissues.
aP < 0.05 vs adjacent tissues. A: TLR4 mRNA in 30 cases of pancreatic carcinoma and adjacent tissues was determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR); B: HIF-1α mRNA in 30 cases of pancreatic carcinoma and adjacent tissues was determined by real-time PCR.
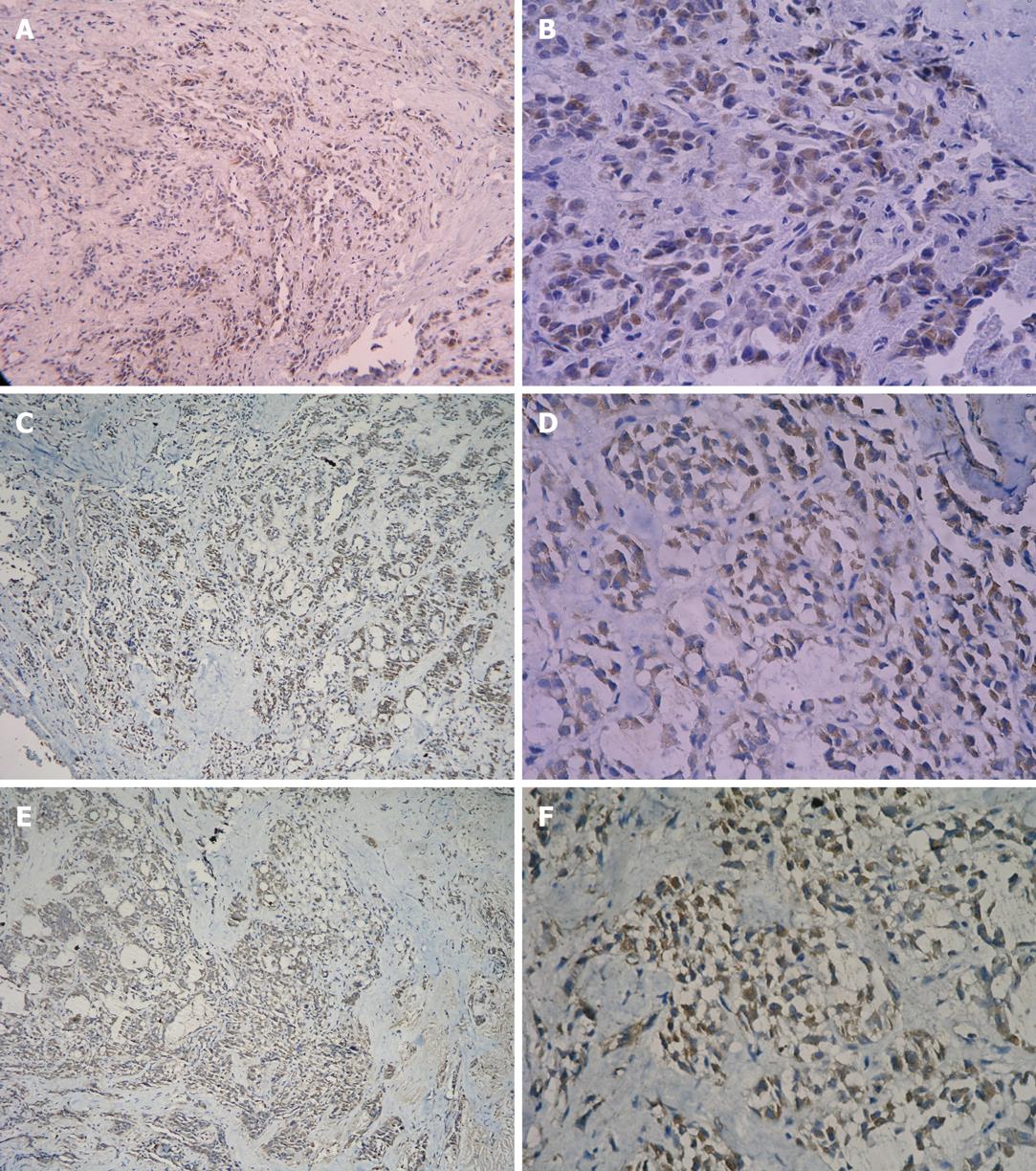
Figure 2 Expression of TLR4 and HIF-1α protein in pancreatic carcinoma tissue.
Brown color displays the positive expression. A: Expression of TLR4 protein in carcinoma tissue (SP, × 100); B: Expression of TLR4 protein in carcinoma tissue (SP, × 400); C: Expression of HIF-1α protein in carcinoma tissue (SP, × 100); D: Expression of HIF-1α protein in carcinoma tissue (SP, × 400); E: Expression of NF-κB p65 protein in carcinoma tissue (SP, × 100); F: Expression of NF-κB p65 protein in carcinoma tissue (SP, × 400).
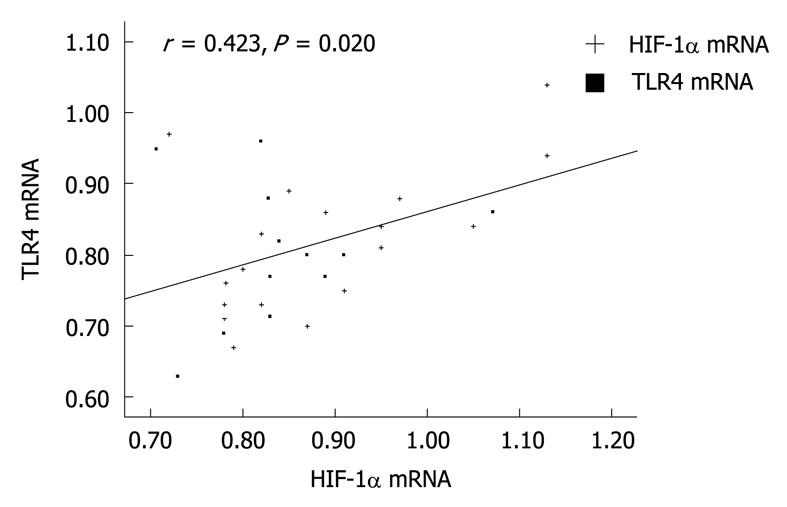
Figure 3 Correlation between TLR4 mRNA and HIF-1α mRNA.
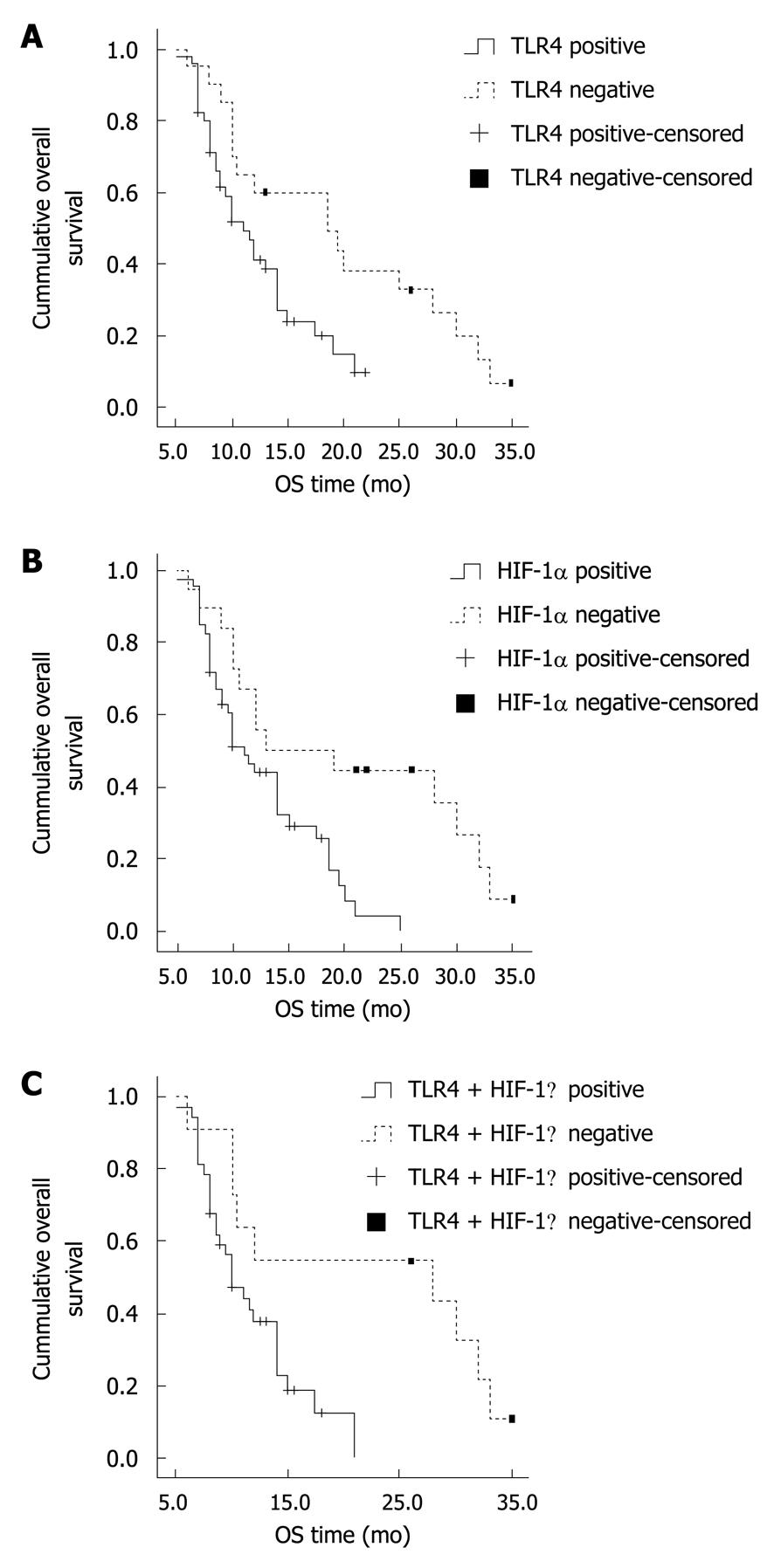
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier analysis overall survival depending on TLR4 and HIF-1α expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
A: The mean survival of patients with negative TLR4 expression in tumor tissues was significantly longer than those with TLR4 positive expression (P = 0.011); B: The mean survival of patients with negative HIF-1α expression in tumor tissues was significantly longer than those with HIF-1α positive expression (P = 0.005); C: Survival of patients with both negative TLR4 and HIF-1α expression was significantly longer than those with both positive TLR4 and HIF-1α expression (P = 0.014).
- Citation: Zhang JJ, Wu HS, Wang L, Tian Y, Zhang JH, Wu HL. Expression and significance of TLR4 and HIF-1α in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(23): 2881-2888
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i23/2881.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2881