Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2010; 16(14): 1727-1734
Published online Apr 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1727
Published online Apr 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1727
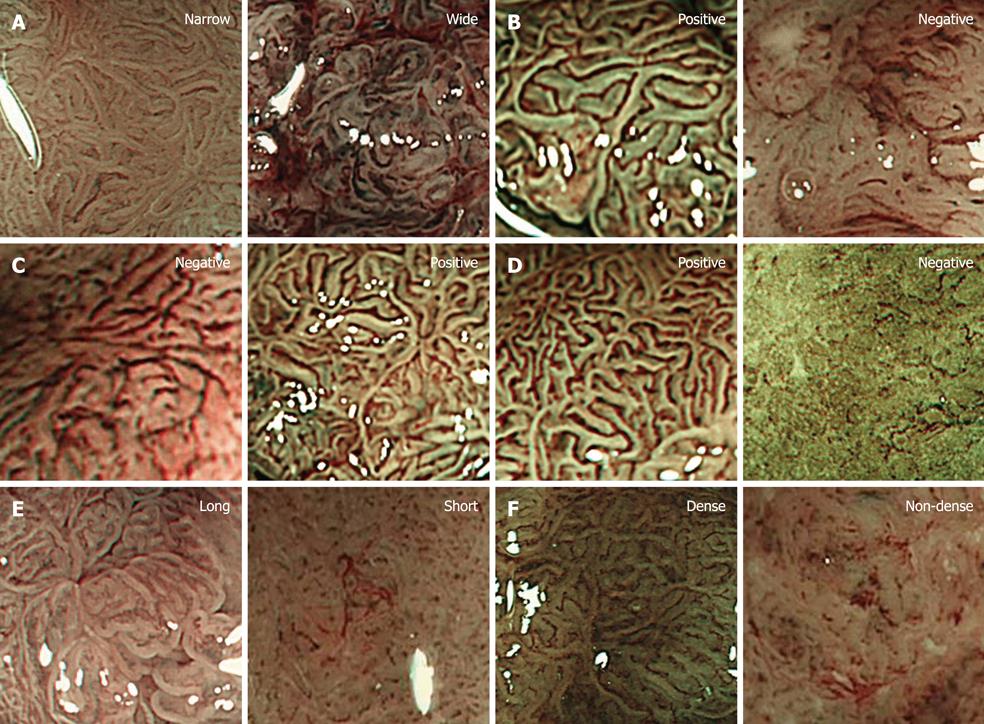
Figure 1 Microvascular architecture.
A: Caliber, narrow: Capillaries are narrow diameter. Caliber, wide: Capillaries are wide diameter; B: Caliber regularity, positive: Capillaries are uniform thickness. Caliber regularity, negative: Capillaries are unequal thickness; C: Meandering, negative: Capillaries are linear. Meandering, positive: Capillaries are meandering; D: Vessel regularity, positive: Capillaries surround mucosal glands regularly. Vessel regularity, negative: Capillaries irregularly branching; E: Vessel length, long: Long capillaries. Vessel length, short: Short capillaries; F: Vessel density, dense: Dense capillaries. Vessel density, non-dense: Sparse capillaries.
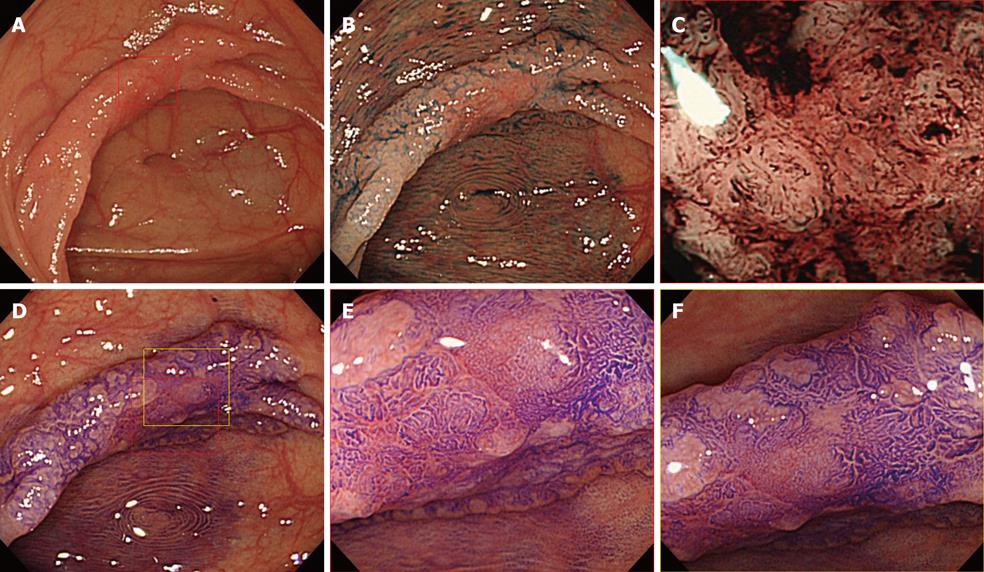
Figure 2 35 mm laterally spreading tumor, non-granular (LST-NG) type, located in the ascending colon.
A: Conventional colonoscopy image; B: Conventional colonoscopy image following 0.4% IC dye spraying; C: Narrow-band imaging (NBI) with magnification image at center of the lesion enclosed by the red box in A. Microvascular architecture consisted of non-dense vessel density and negative vessel regularity; D: Crystal violet staining image; E: Magnification view of the portion enclosed by the red box in D revealed a noninvasive pattern; F: Magnification view of the portion enclosed by the yellow box in D also revealed a noninvasive pattern, such the estimated depth was intramucosal and this LST-NG lesion was treated by endoscopic submucosal dissection.
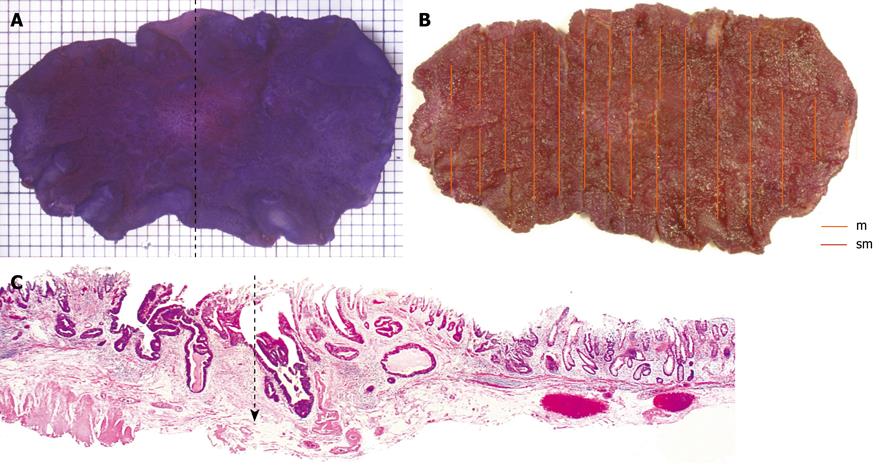
Figure 3 Stereomicroscopic view and histological images.
A: Stereomicroscopic view; B: Red lines indicate submucosal penetration of the tumor; C: Histological diagnosis at dotted line in A was a well-differentiated adenocarcinoma and depth of invasion was sm (1300 mm) shown with the arrow. Invasion depth diagnosis using NBI with magnification was correct, based on findings of non-dense vessels and negative vessel regularity, but pit pattern diagnosis of this lesion was inaccurate.
- Citation: Fukuzawa M, Saito Y, Matsuda T, Uraoka T, Itoi T, Moriyasu F. Effectiveness of narrow-band imaging magnification for invasion depth in early colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(14): 1727-1734
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i14/1727.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1727