Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2009; 15(6): 705-712
Published online Feb 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.705
Published online Feb 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.705
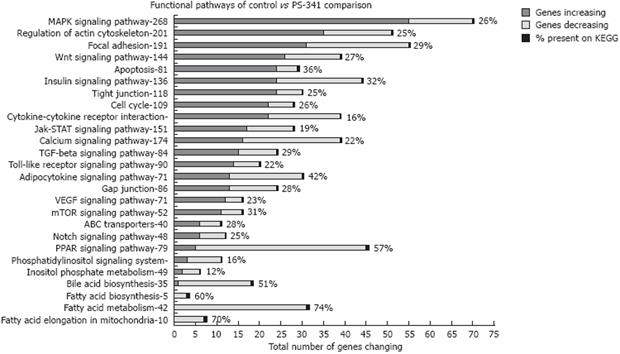
Figure 1 Kegg functional pathway changes in gene expression induced by proteasome inhibition.
Both ethanol feeding and proteasome inhibition affected almost all pathways.
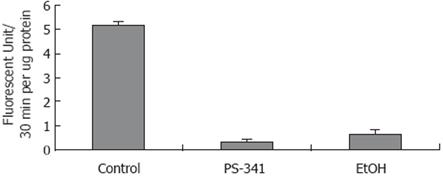
Figure 2 Nuclear proteasome chymotrypsin-like activity.
20S proteasome chymotrypsin-like activity was measured in isolated nuclei from the liver of rats fed ethanol chronically and from the liver of rats given PS-341.
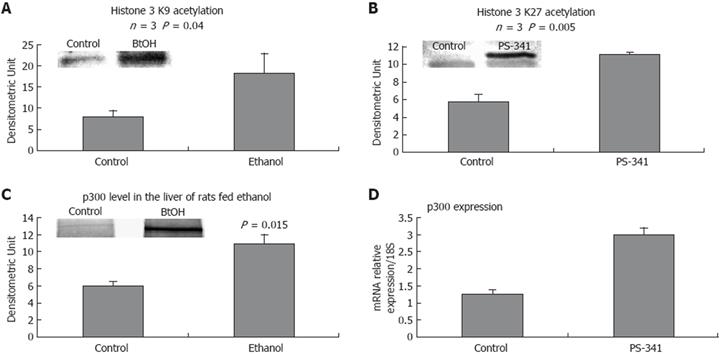
Figure 3 Role of proteasome inhibition in histone acetylation.
A: Proteasome inhibition caused a significant increase in histone acetylation as shown in the liver nuclear extracts of rats fed ethanol and in the liver nuclear extracts of rats given PS-341(B). C: p300 protein level was increased in the nuclear extract from the livers of rats fed ethanol chronically, and in the liver nuclear extracts of rats given PS-341, as shown by real time PCR (D), P = 0.003. (mean ± SE, n = 3).
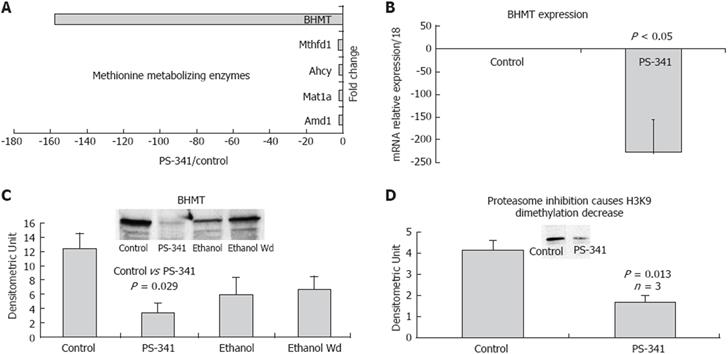
Figure 4 Role of proteasome inhibition in the remethylation pathway.
A: Proteasome inhibition by PS-341 (PS) markedly decreased BHMT gene expression; B: Real time PCR analysis of BHMT expression; C: Western blot analysis of BHMT level in the liver of rats fed ethanol chronically and the liver of rats given PS-341. Note that the BHMT level was significantly reduced in the liver of rats treated with PS-341; D: Proteasome inhibition caused a decrease in histone methylation.
- Citation: Oliva J, Dedes J, Li J, French SW, Bardag-Gorce F. Epigenetics of proteasome inhibition in the liver of rats fed ethanol chronically. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(6): 705-712
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i6/705.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.705