Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2009; 15(47): 5972-5975
Published online Dec 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5972
Published online Dec 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5972
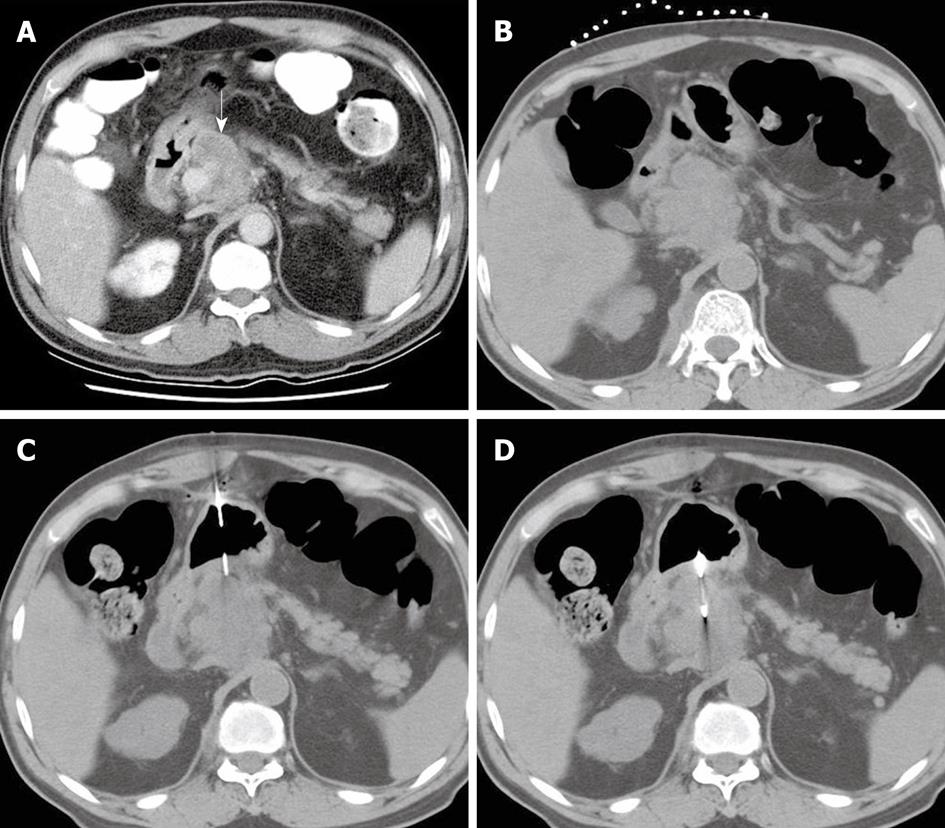
Figure 1 A 67-year-old man with a pancreatic mass who had no safe route for approaching the target lesion during biopsy.
A: Contrast-enhanced axial computed tomography (CT) scan shows a mass lesion (white arrow) in the pancreatic head; B: The patient was in the supine position, with opaque catheters placed on the abdominal wall as reference lines; C: Noncontrast CT image shows a 17-gauge coaxial introducer needle perpendicularly penetrating the gastric wall and the needle tip positioned at the edge of the target lesion; D: Noncontrast CT image shows an 18-gauge biopsy needle tip in the pancreatic mass.
- Citation: Tseng HS, Chen CY, Chan WP, Chiang JH. Percutaneous transgastric computed tomography-guided biopsy of the pancreas using large needles. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(47): 5972-5975
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i47/5972.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.5972