Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2009; 15(31): 3950-3953
Published online Aug 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3950
Published online Aug 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3950
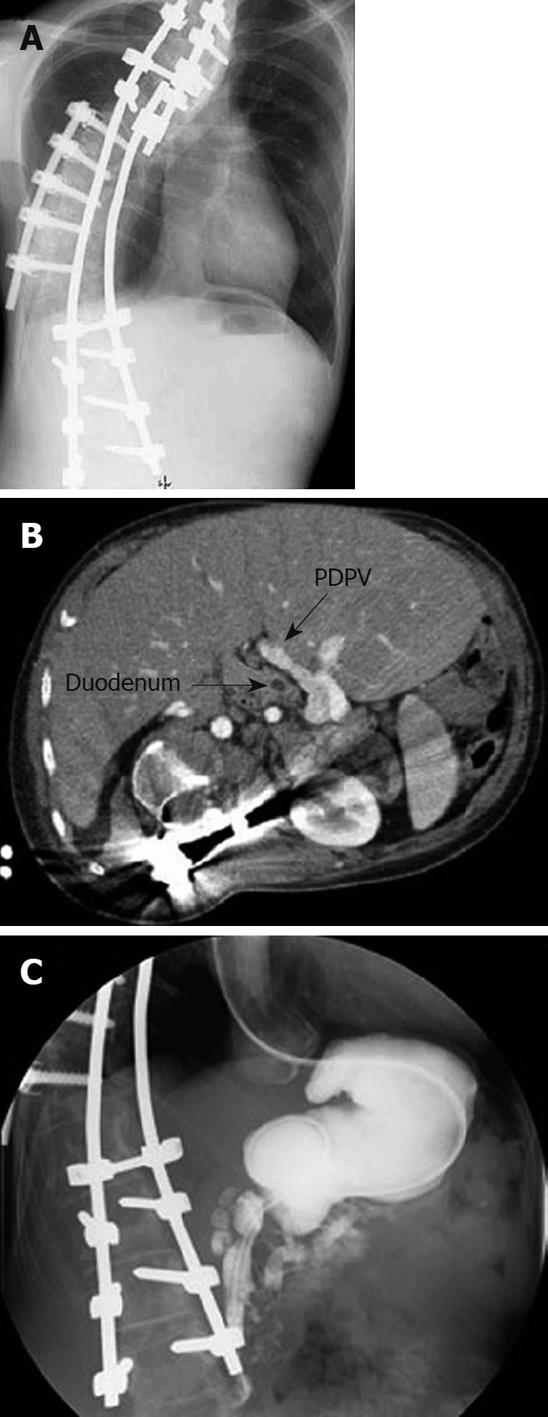
Figure 1 Images at admission.
A: Plain X-ray film. Although the spine was corrected by a previous orthopedic operation, a severe scoliosis with right side protrusion was found at admission; B: Abdominal CT scan. The preduodenal portal vein (PDPV) was found to be located in the anterior side of the duodenum; C: Contrast study of the upper gastrointestinal tract. A contrast study of the duodenum showed a stenosis ranging from the second to third portions. In addition, the contents flowed to both the dilated main pancreatic duct and common bile duct.
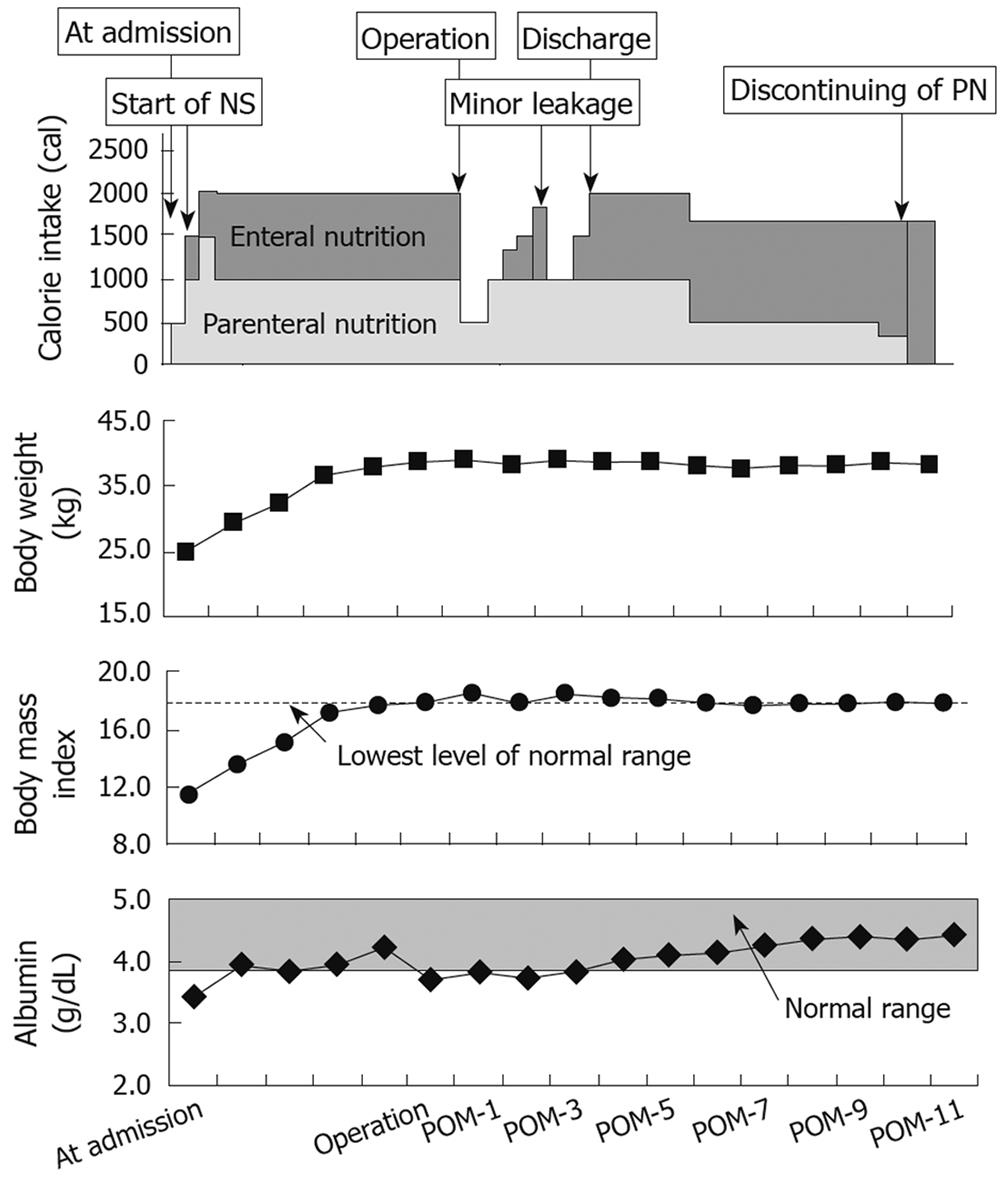
Figure 2 Clinical course of our patient.
This figure shows the clinical course of our patient during the period from admission to the cessation of parenteral nutrition. After the preoperative nutritional support using both parenteral and enteral nutrition for 6 mo, an improvement in body weight and body mass index was seen. After the operation, the calorie intake from parenteral nutrition was gradually reduced. The postoperative anthropological markers were maintained. NS: Nutritional support; POM: Postoperative months.
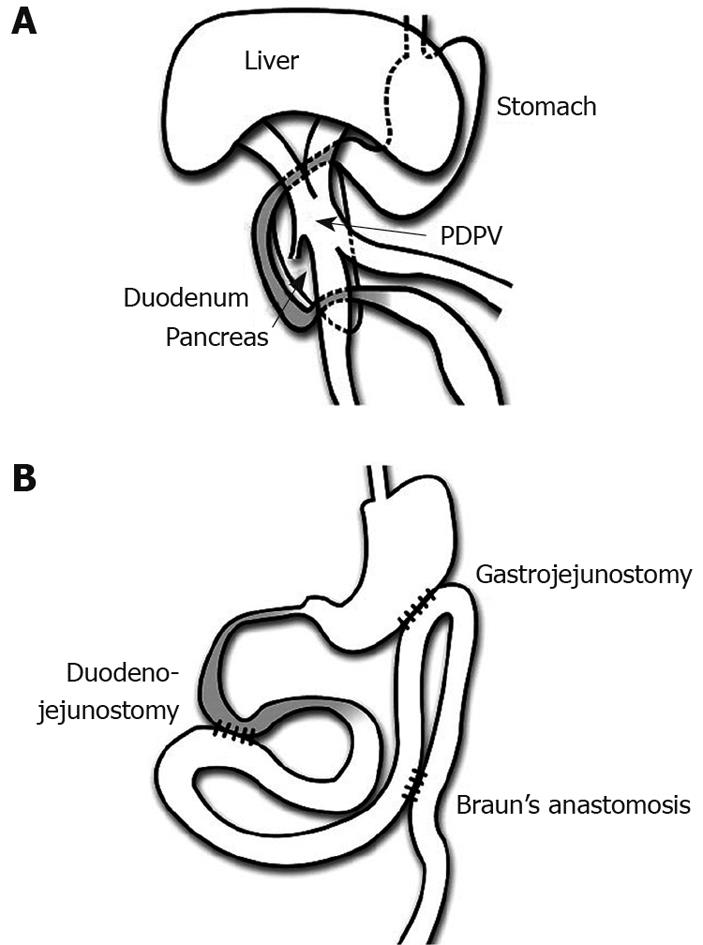
Figure 3 Operative findings and performed procedures in our patient.
A: Operative findings. The PDPV was found to induce the severe stenosis of the duodenal first portion and the stenosis ranging from the second to third portions was the result of stretching by spinal correction. No intestinal malrotation was found. The liver was confirmed to be a symmetrical liver. The head of the pancreas was found to be attached to the stenosis of the first duodenal portion. The duodenum is colored gray in this figure; B: Performed procedures. A gastrojejunostomy with Braun’s anastomosis was performed for the stenosis in the first portion. In addition, a duodenojejunostomy between the duodenal second portion and jejunum was performed for smooth passage of the duodenal contents. The duodenum is also colored gray in this figure.
- Citation: Masumoto K, Teshiba R, Esumi G, Nagata K, Nakatsuji T, Nishimoto Y, Yamaguchi S, Sumitomo K, Taguchi T. Duodenal stenosis resulting from a preduodenal portal vein and an operation for scoliosis. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(31): 3950-3953
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i31/3950.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.3950