Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2009; 15(27): 3417-3420
Published online Jul 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3417
Published online Jul 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3417
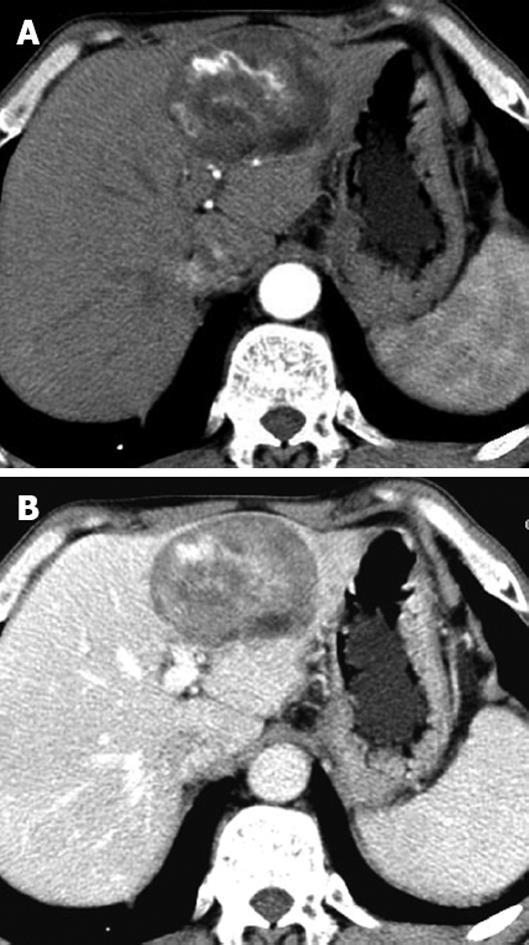
Figure 1 Patient with sporadic hepatic angiomyolipoma.
A: Enhanced CT showed one well-defined, fat-containing nodule with prominent central vessels in the arterial phase; B: Enhanced CT showed sustained contrast enhancement of the intratumoral non-fat component in the portal venous phase.
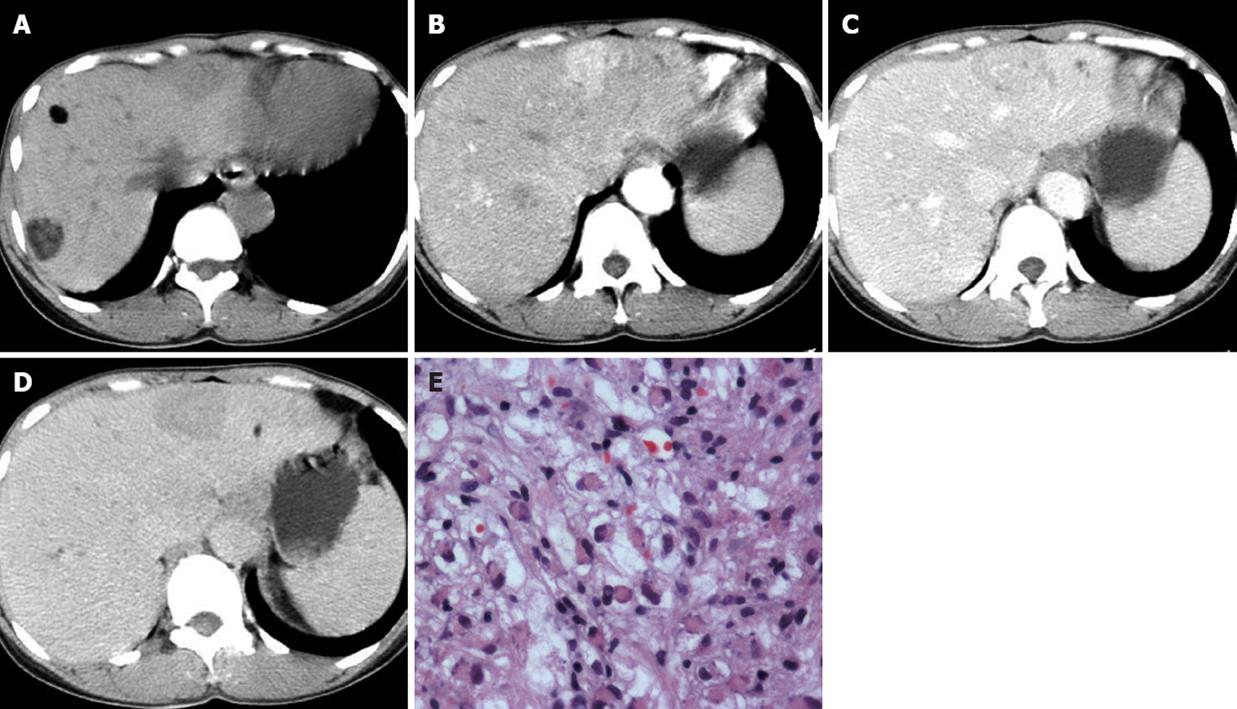
Figure 2 Patient with hepatic angiomyolipoma and TSC.
A: Plain CT showed two fat-containing nodules in the right liver lobe, and one unenveloped fat-deficient nodule in the left liver lobe; B: Enhanced CT showed a fat-deficient nodule with marked hyperdensity, with intratumoral vessels in the arterial phase; C: Enhanced CT showed a fat-deficient nodule with mild hypodensity, with prominent central vessels in the portal venous phase; D: Enhanced CT showed a fat-deficient nodule with homogeneous hypodensity in the delayed phase; E: Microscopic examination demonstrated vacuolated lipocytes, blood vessels and scattered epithelioid cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and peripherally located nuclei (HE, original magnification × 40).
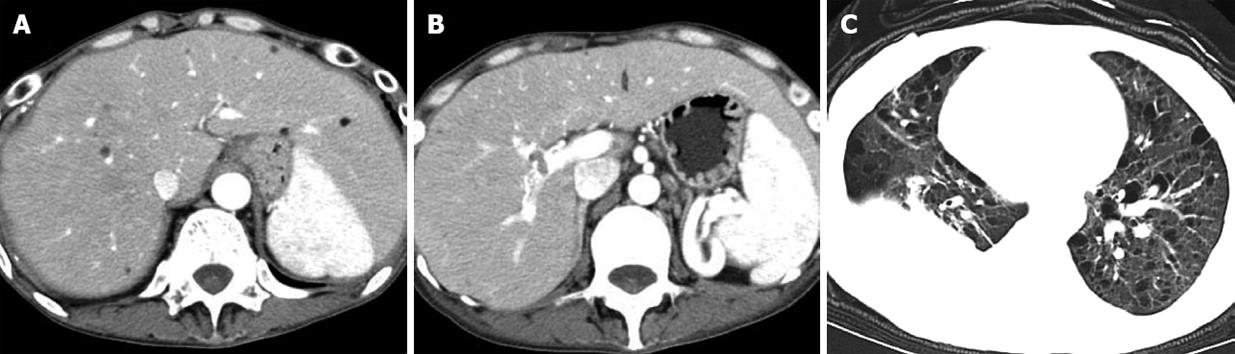
Figure 3 Patient with TSC and hepatic angiomyolipoma and LAM.
A: Enhanced CT showed multiple fat-containing nodules in the liver; B: Enhanced CT showed an intra-portal-venous lesion and several enlarged periaortic lymph nodes; C: Chest CT showed multiple, thin-walled lung cysts and right hydrothorax.
- Citation: Yang B, Chen WH, Li QY, Xiang JJ, Xu RJ. Hepatic angiomyolipoma: Dynamic computed tomography features and clinical correlation. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(27): 3417-3420
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i27/3417.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.3417