Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2009; 15(26): 3232-3239
Published online Jul 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3232
Published online Jul 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3232
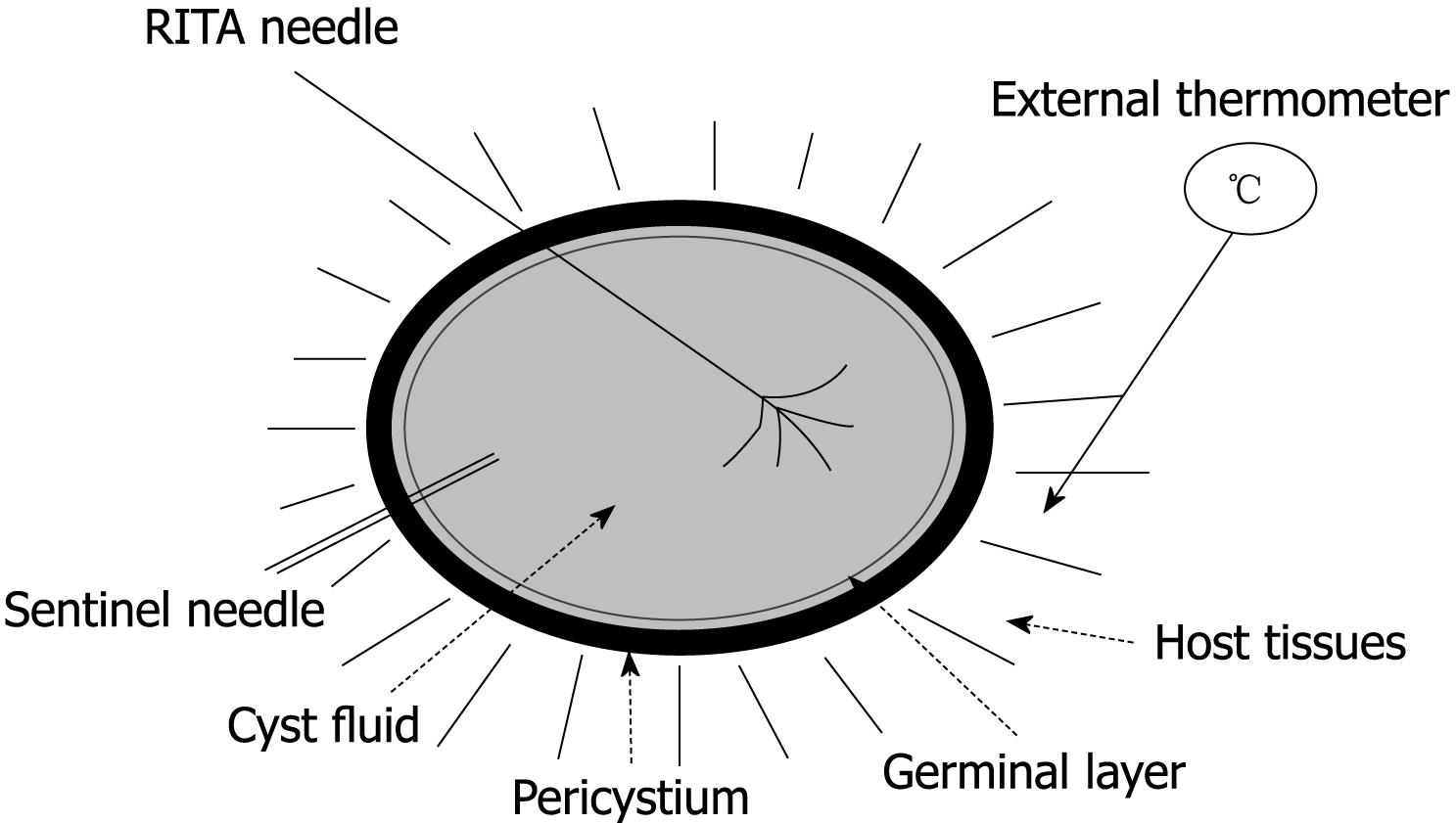
Figure 1 Schematic description of radiofrequency thermal ablation (RTA) on echinococcal cyst.
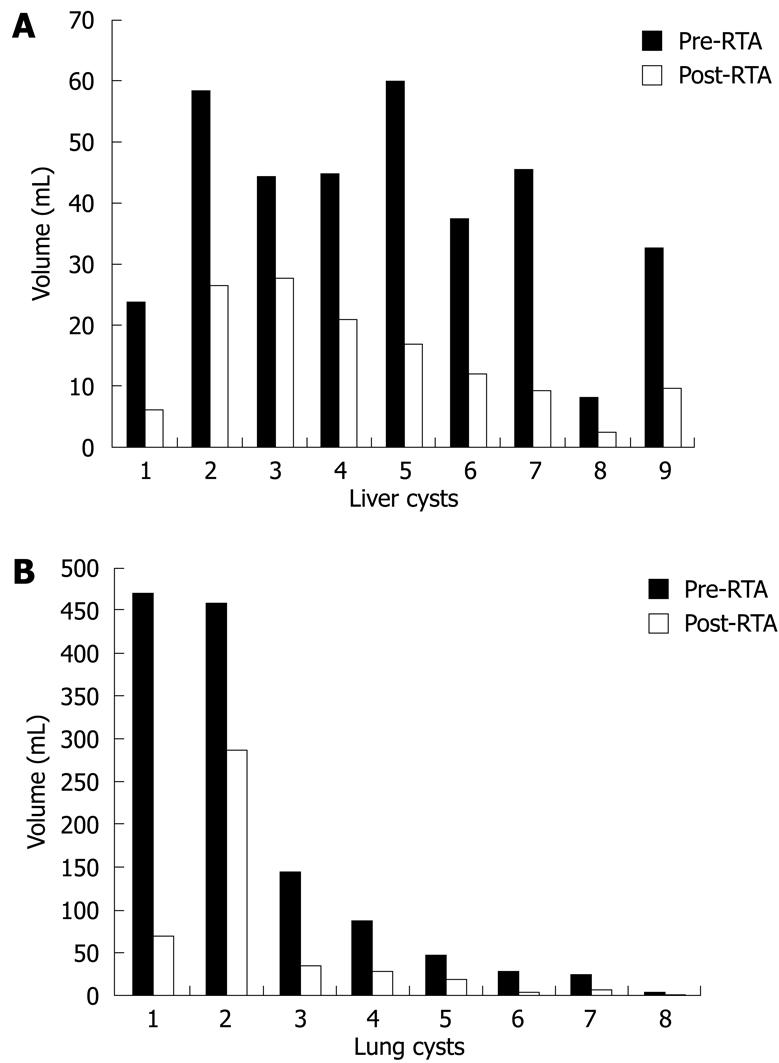
Figure 2 Cyst volume before and after RTA in liver (A) and lung (B).
All treated cysts showed a strong and immediate reduction in volume.
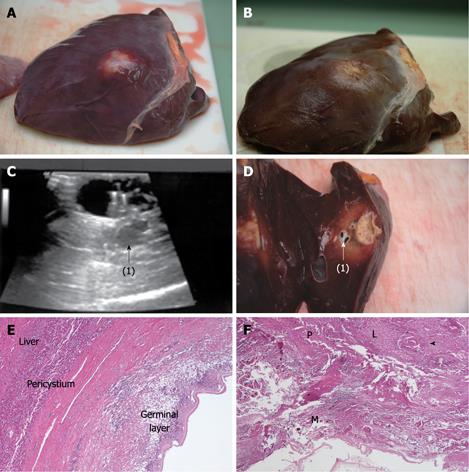
Figure 3 Hydatid cyst of the liver treated with RTA.
The upper panel shows the surface of the liver before (A) and after (B) RTA. The procedure caused cyst retraction. The middle panel shows pre-procedure ultrasound (C) and post-RTA section (D) of the cyst. A transverse US scan shows the RITA needle expanded inside the cyst and a smaller adjacent cyst (1) situated within the necrotic area surrounding the treated cyst. Histology showed the smaller cyst was necrotic and killed despite no direct treatment. In the lower panel, histology (HE stain, × 4) of an untreated cyst (E) is compared with that of the treated one (F). In the former, all structures are well recognizable, while in the latter the cyst layers are totally necrotic. M: Germinal membrane; P: Pericystium; L: Liver parenchyma. Arrow tips indicate necrotic portal tracts. 1: Adjacent cyst.
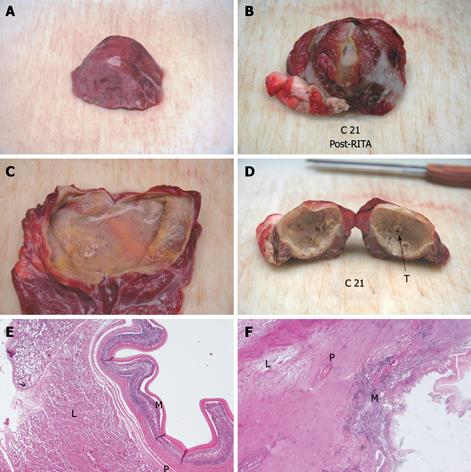
Figure 4 Hydatid cyst of the lung.
Untreated (left) and treated (right) cysts are compared. External surface (upper panel), findings after sectioning (middle panel), and 4 × HE stained histology (lower panel) are shown. Untreated cyst shows normal surface, flaccidity after sectioning, thin and translucid endocyst and well preserved cyst layers at histology. Treated cyst looks dehydrated, rigid, has a thick and papyraceous-like endocyst and is totally necrotic at histology. T: RITA-needle through; M: Germinal membrane; P: Pericystium; L: Lung parenchyma.
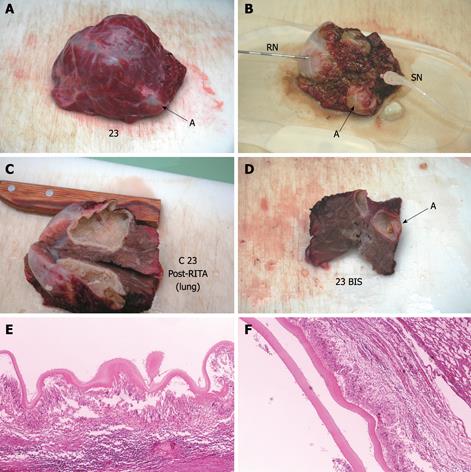
Figure 5 Echinococcus cyst of the lung before (A) and after (B-D) RTA.
External surface of the cyst (upper panel), findings after sectioning (middle panel), and histology (lower panel). After treatment (B) the cyst looks shrunken, rigid and dehydrated. Post-RTA section of the cyst (C) shows the endocyst is thick, papyraceous-like and attached to pericystium. Histology (HE stain, × 4) shows complete necrosis of the cyst wall (E). An adjacent cyst (indicated by arrow A in slides A, B, D) was necrotic and killed at histology (F) despite no direct treatment. RN: RITA needle; SN: Sentinel needle.
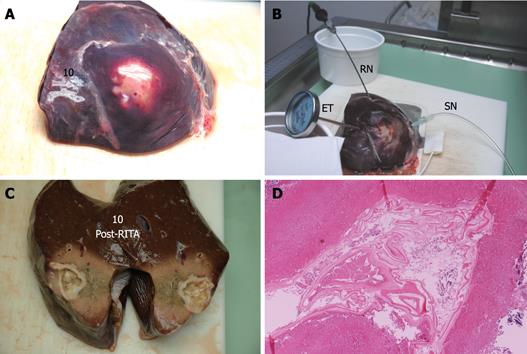
Figure 6 Echinococcus cyst of the liver treated with RTA.
The upper panel shows the surface of the liver before (A) and after (B) RTA. Procedure caused cyst retraction. RITA needle, sentinel needle and external thermometer, still in place, can be seen (B). The left lower panel shows post-RTA section (C) of the cyst. Histology of a paramedian section (right lower panel, HE stain, × 2) shows cyst walls and surrounding liver closest to the cyst are totally necrotic and with granular amorphous aspect (D). RN: RITA needle; SN: Sentinel needle; ET: External thermometer.
-
Citation: Lamonaca V, Virga A, Minervini MI, Di Stefano R, Provenzani A, Tagliareni P, Fleres G, Luca A, Vizzini G, Palazzo U, Gridelli B. Cystic echinococcosis of the liver and lung treated by radiofrequency thermal ablation: An
ex-vivo pilot experimental study in animal models. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(26): 3232-3239 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i26/3232.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.3232