Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2009; 15(22): 2805-2808
Published online Jun 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2805
Published online Jun 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2805
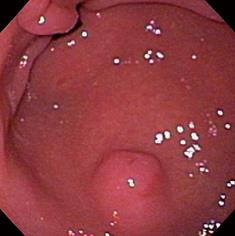
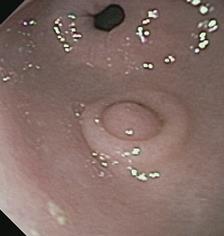
Figure 1 Endoscopic view of heterotopic pancreas of the stomach showing a medium-sized subepithelial nodule with central umbilication and normal overlying mucosa.
The pylorus is visible distally.
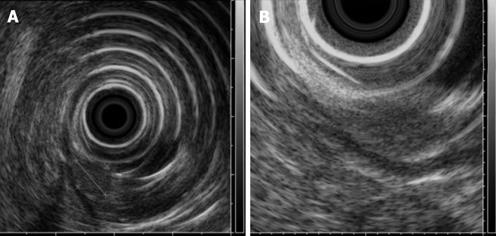
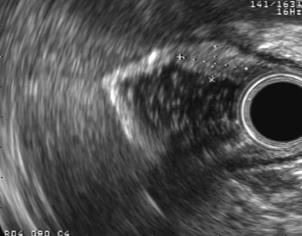
Figure 2 Radial EUS images.
A pancreatic rest showing an 8 mm × 6 mm hypoechoic subepithelial mass appearing to involve the mucosa (A) and submucosa (B). The tumor was confirmed as submucosal in origin after resection without involvement of the mucosa.
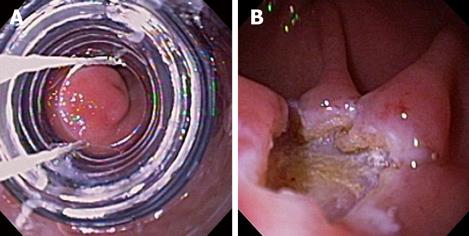
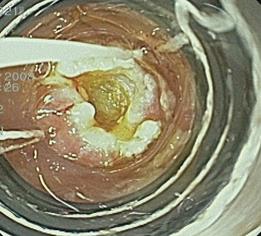
Figure 3 Ligation-assisted EMR of pancreatic rest.
The banding device was positioned over the target lesion (A), suction was applied and a band was deployed. The lesion was then resected using electrocautery snare. Residual ulcer is shown (B).
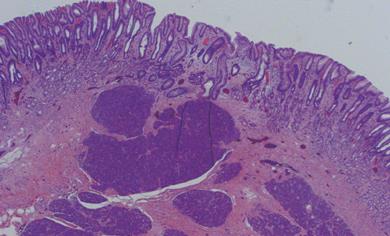
Figure 4 Photomicrograph of the resection specimen showing pancreatic tissue within the gastric submucosa (HE, × 10).
Figure 5 Endoscopic view of heterotopic pancreas of the stomach showing a medium-sized subepithelial nodule with central umbilication and normal overlying mucosa.
The pylorus is visible distally.
Figure 6 Radial EUS images of a pancreatic rest showing a 9 mm × 7 mm hypoechoic subepithelial mass appearing to involve the deep mucosa and submucosa.
The tumor was confirmed as submucosal in origin after resection without involvement of the mucosa.
Figure 7 Ligation-assisted EMR of pancreatic rest.
- Citation: Khashab MA, Cummings OW, DeWitt JM. Ligation-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection of gastric heterotopic pancreas. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(22): 2805-2808
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i22/2805.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.2805