Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2009; 15(2): 192-197
Published online Jan 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.192
Published online Jan 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.192
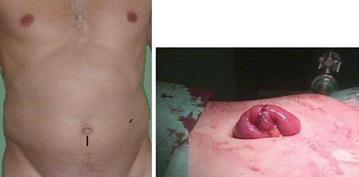
Figure 1 Laparoscopically-assisted full thickness jejunal biopsy.
The port sites are shown. After finding a suitable proximal jejunal loop, the bowel is exteriorised by extending slightly the umbilical port incision and biopsy and suture closure performed extracorporeally (Courtesy of B Nyborg, Huddinge, Stockholm).
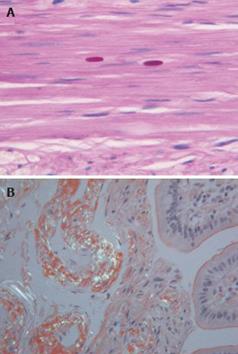
Figure 2 Tinctorial stains used in GI neuromuscular histopathology.
A: Periodic acid Schiff staining showing polyglucosan bodies in a patient with intestinal pseudo-obstruction; B: Bifringence from amyloid visualised by Congo red staining (× 25-40).
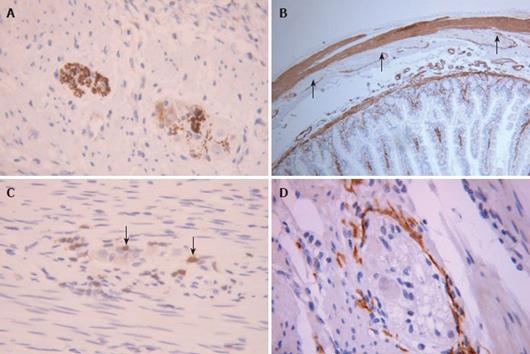
Figure 3 Immunohistochemistry using antibodies to.
A: Neuron specific enolase allowing clear visualisation of myenteric ganglia, neuronal number and size; B: Smooth muscle alpha actin showing absent staining in the circular muscle layer of the jejunum (arrows) in a patient with enteric dysmotility; C: CD3 showing small numbers of periganglionic T lymphocytes (arrows) in numbers that most would deem abnormal and indicative of ganglionitis; D: CD117 staining showing normal myenteric plexus interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC-MP). (Original magnification × 40-100).
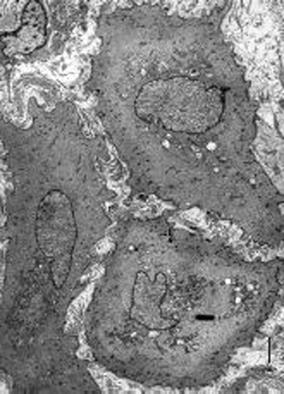
Figure 4 Electron micrograph of smooth muscle cells showing increased Golgi indicative of transition to a more secretory phenotype in a patient with enteric myopathy and pseudo-obstruction.
(× 50 000).
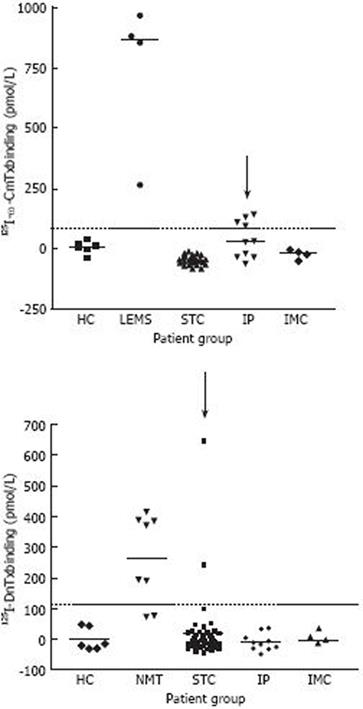
Figure 5 Radioimmunoprecipitation assays of sera from patients with GINMD and negative and positive controls.
Assays for antineuronal antibodies directed to anti-voltage-gated calcium (anti-VGCC P/Q-type) and potassium channels (VGKC) are shown. Four IP sera are weakly positive for anti-VGCC P/Q-type antibodies, and 2 STC sera strongly positive for anti-VGKC (arrowed). Dotted line: mean + 3SD; HC: Healthy controls; LEMS: Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome; STC: Slow transit constipation; IP: Intestinal pseudo-obstruction; IMC: Idiopathic megacolon; NMT: Neuromyotonia.
- Citation: Knowles CH, Martin JE. New techniques in the tissue diagnosis of gastrointestinal neuromuscular diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(2): 192-197
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i2/192.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.192