Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2009; 15(13): 1625-1629
Published online Apr 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1625
Published online Apr 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1625
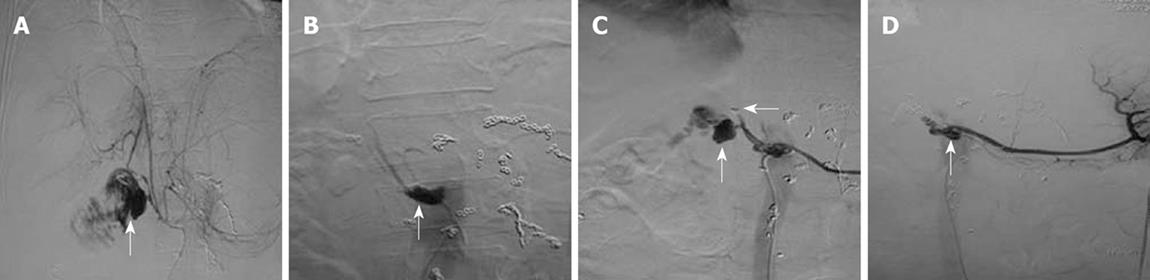
Figure 1 Images from patient 2 (treated using TAE).
A: Angiogram of the gastroduodenal stump bleeding before the first embolization. Arrow: Angiogram of the gastroduodenal stump bleeding; B: Angiogram of the gastroduodenal stump, which stopped bleeding after the first TAE. Arrow: Angiogram of the gastroduodenal stump); C: Angiogram of the stump prior to the second embolization. Angiography indicates that microcoils have entered the hepatic artery, causing renewed bleeding from the stump. Arrows: The second angiogram of the gastroduodenal stump bleeding; D: After the second embolization, angiography confirmed that the bleeding was stopped. Arrow: Angiogram of the gastroduodenal stump.
- Citation: Liu C, Qiu YH, Luo XJ, Yi B, Jiang XQ, Tan WF, Yu Y, Wu MC. Treatment of massive pancreaticojejunal anastomotic hemorrhage after pancreatoduodenectomy. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(13): 1625-1629
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i13/1625.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.1625