Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2008; 14(7): 1077-1083
Published online Feb 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1077
Published online Feb 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1077
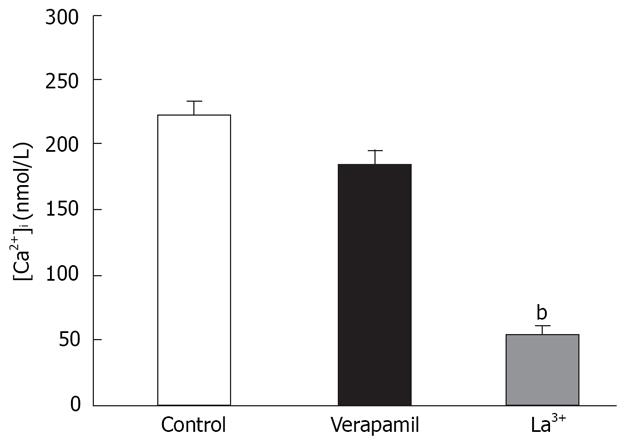
Figure 1 Ca2+ influx through SOCCs in enzymatically dissociated smooth muscle cells of rats distal colon.
After depletion of the SR by thapsigargin in the absence of extracellular Ca2+, subsequent rapid reintroduction of extracellular Ca2+ resulted in activation of CCE via SOCCs. CCE were insensitive to verapamil, but blocked by La3+. bP < 0.01 vs control.
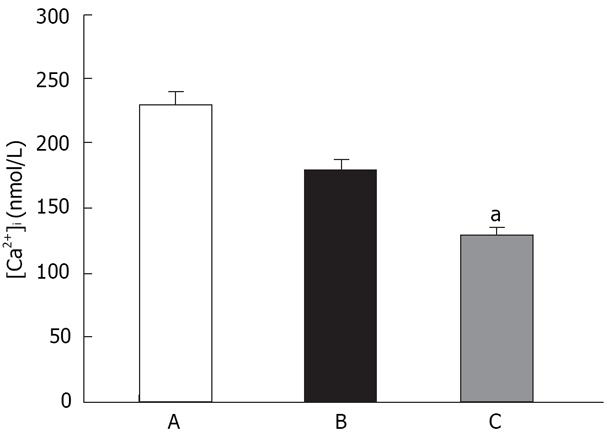
Figure 2 CCE are not mediated via L-type Ca2+ channels.
(A) Controls; (B) 40 mmol/L K+; (C) 60 mmol/L K+. Only 60 mmol/L K+ significantly decreased the Ca2+ influx mediated by CCE. aP < 0.05 vs control.
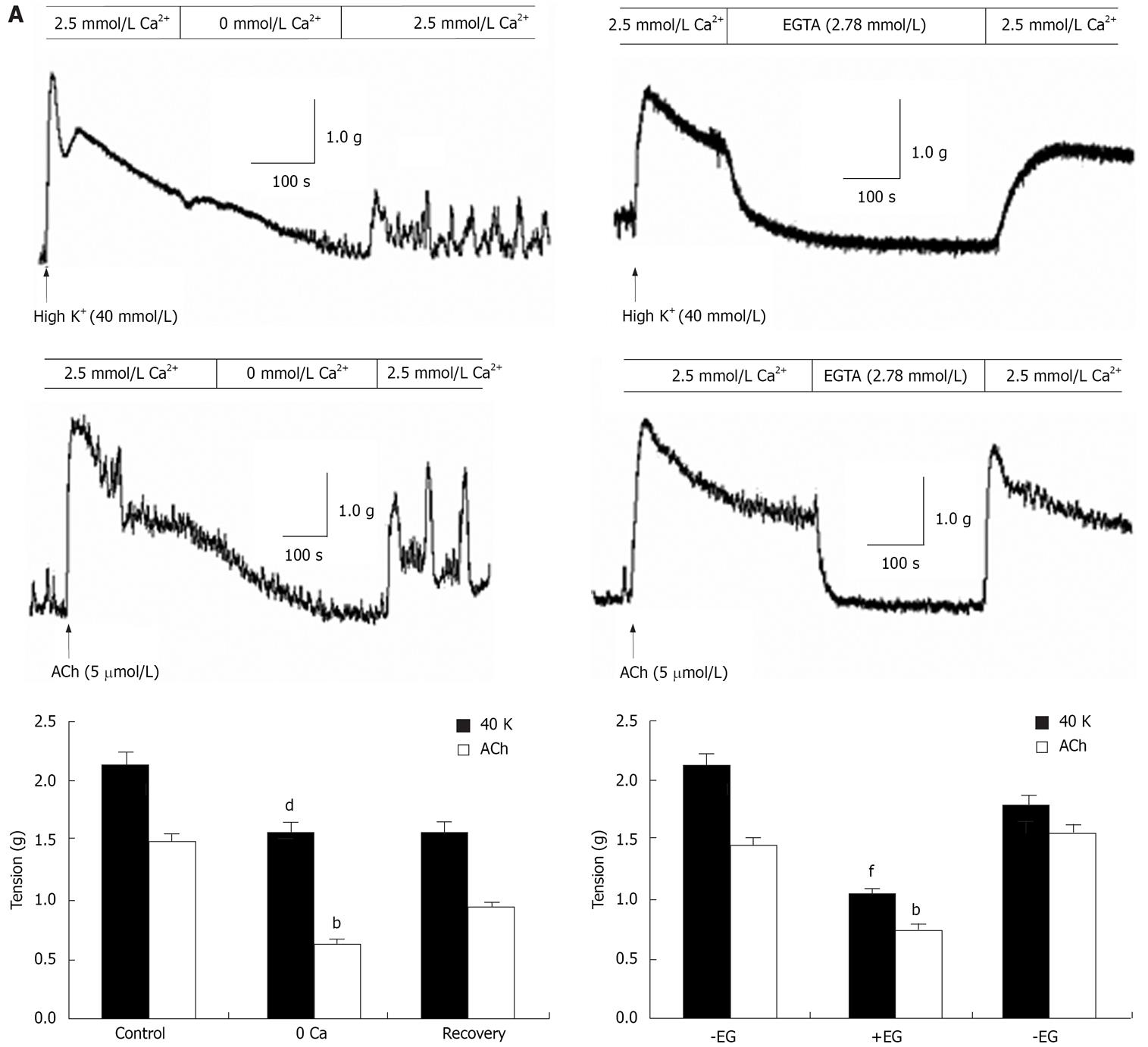
Figure 3 Role of Ca2+ in rat distal colon contraction.
A: Representative results showing that removal of extracellular Ca2+ abolished contraction induced by high K+ and 5 &mgr;mol/L ACh. Summarized data showing that tension induced by high K+ and 5 &mgr;mol/L ACh before, during and after application of Ca2+-free Krebs solution. bP < 0.01, dP < 0.001 vs Control; B: Representative results showing that chelation of extracellular Ca2+ with 2.78 mmol/L EGTA abolished contraction induced by high K+ and 5 &mgr;mol/L ACh. Summarized data showing that tension induced by high K+ and 5 &mgr;mol/L ACh in the presence of EGTA bP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs-EG (before).
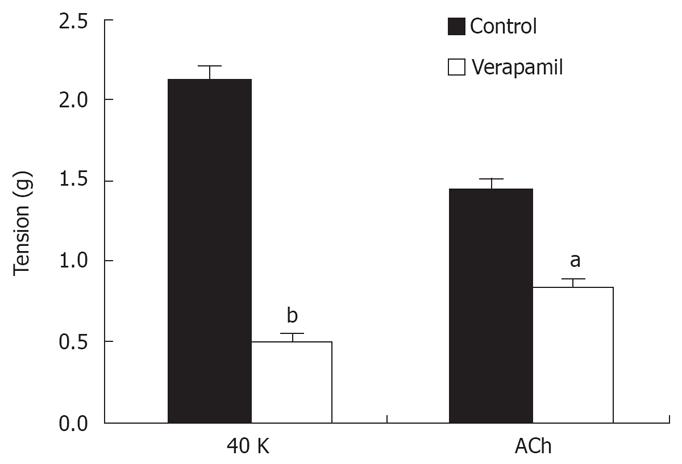
Figure 4 Effects of the VOCC blocker verapamil on distal colon contraction induced by high K+ and ACh.
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001 vs control.
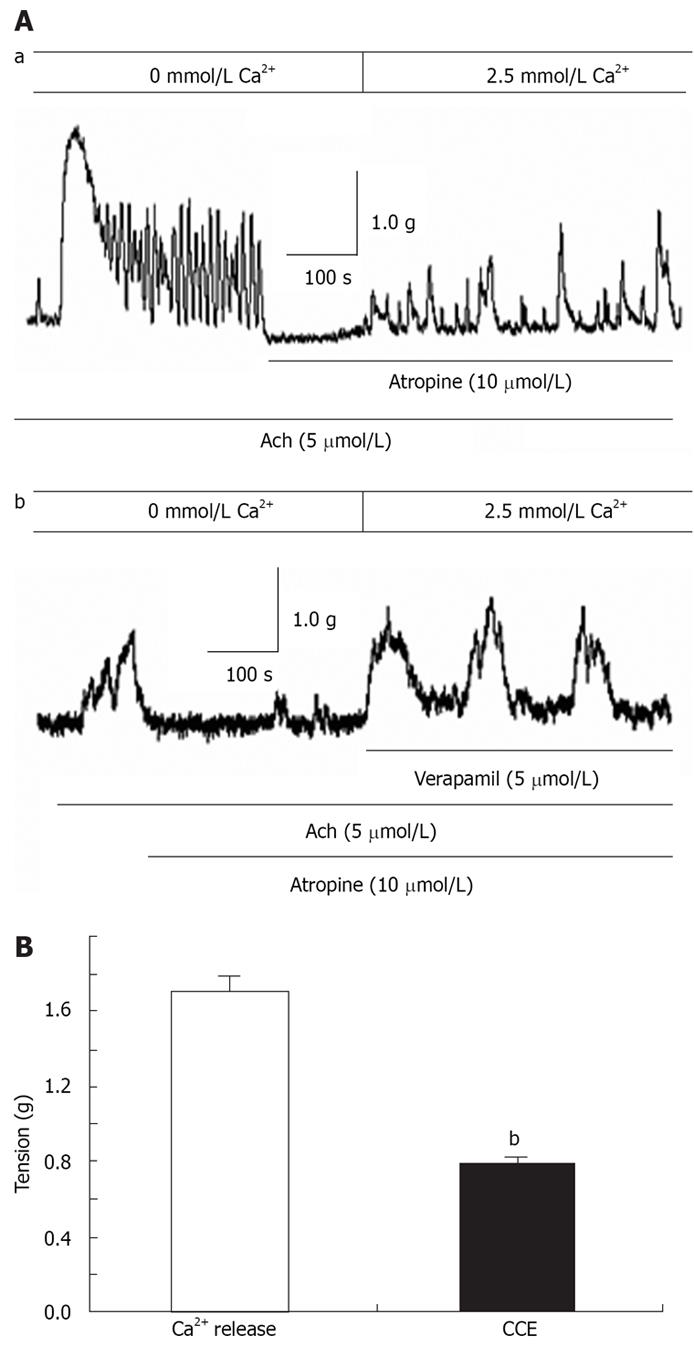
Figure 5 Contribution of Ca2+ release from SR stores and Ca2+ influx via CCE in ACh-induced distal colon contraction.
Aa: In the presence of atropine, restoration of extracellular Ca2+ induced contraction, most likely due to Ca2+ influx via CCE; Ab: VOCC blocker verapamil (5 &mgr;mol/L) negligibly affected CCE-mediated contraction in the presence of atropine; B: Summarized data showing that CCE-mediated contraction is about 0.46-fold greater than the contraction induced by SR Ca2+ release in ACh-induced rat distal colon contraction. bP < 0.001 vs Ca2+ release.
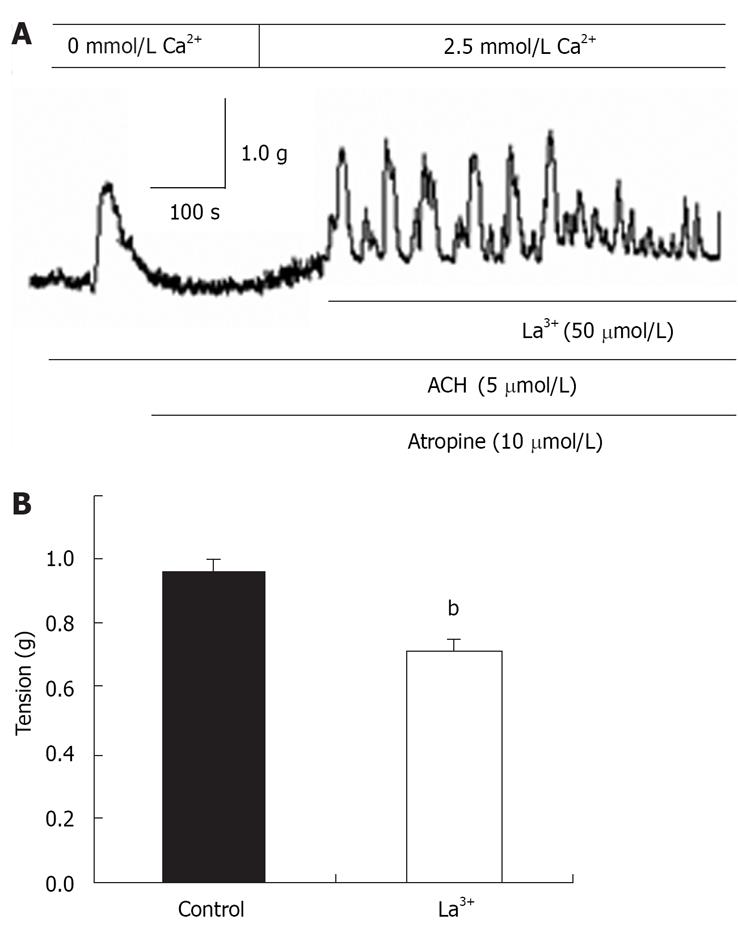
Figure 6 Inhibitory effects of La3+ on CCE-mediated distal colon contraction.
bP < 0.01 vs control. Control: CCE-mediated contraction.
-
Citation: Zhou H, Kong DH, Pan QW, Wang HH. Sources of calcium in agonist-induced contraction of rat distal colon smooth muscle
in vitro . World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(7): 1077-1083 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i7/1077.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.1077