Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2008; 14(41): 6318-6326
Published online Nov 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6318
Published online Nov 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6318
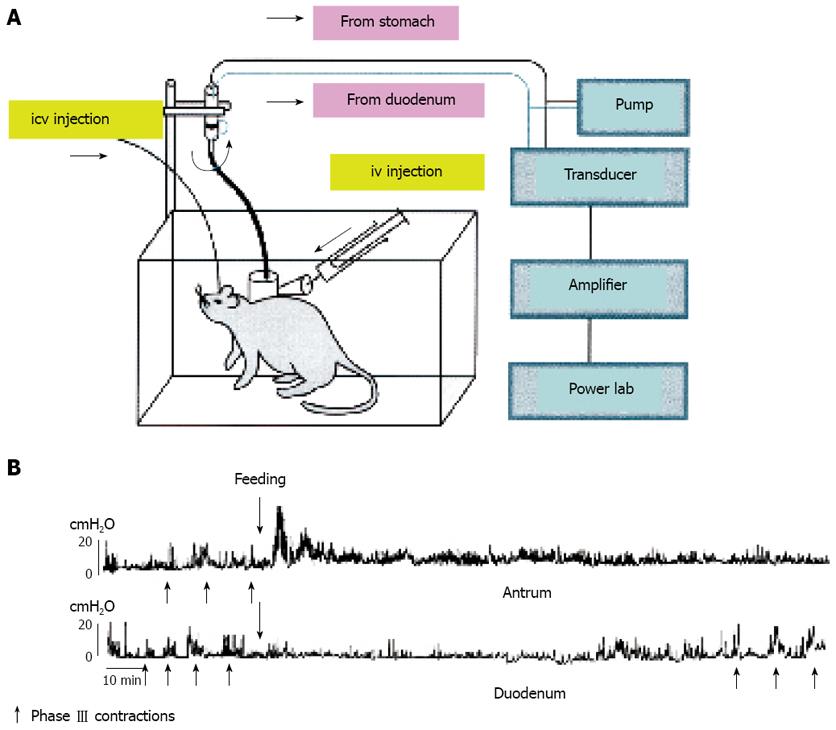
Figure 1 Measurement of gastrointestinal motility.
A: Manometric measurement of gastroduo-denal motility in freely moving conscious rats; B: Fasted and fed motor activities in the antrum and duodenum. Phase III-like contractions are indicated by arrows.
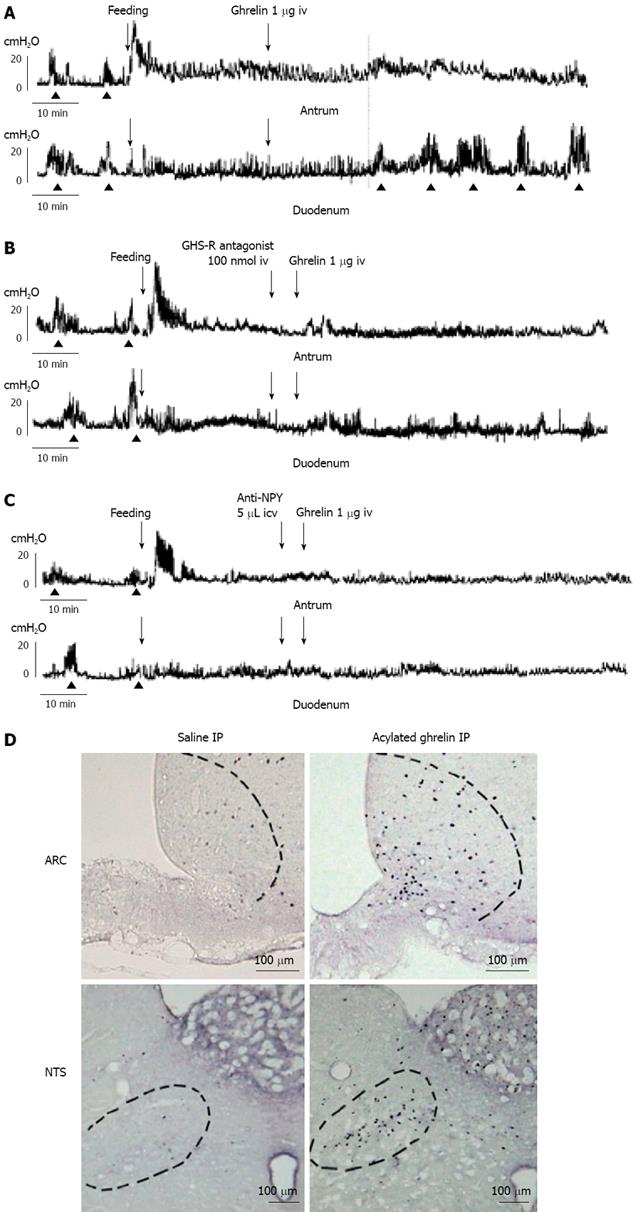
Figure 2 Ghrelin and gastro-duodenal motility.
A: Effects of iv injection of ghrelin on the fed motor activity of the antrum and duodenum. Iv injection of ghrelin induces the fasted pattern in the duodenum and increases the motor activity in the antrum; B: Iv injection of GHS-R antagonist completely blocks the effect of iv injection of ghrelin; C: Icv injection of NPY antiserum completely blocks the effect of iv injection of ghrelin; D: The density of c-Fos-positive cells in the arcuate nucleus (ARC) and nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) increases with ip injection of ghrelin compared to saline-injected control.
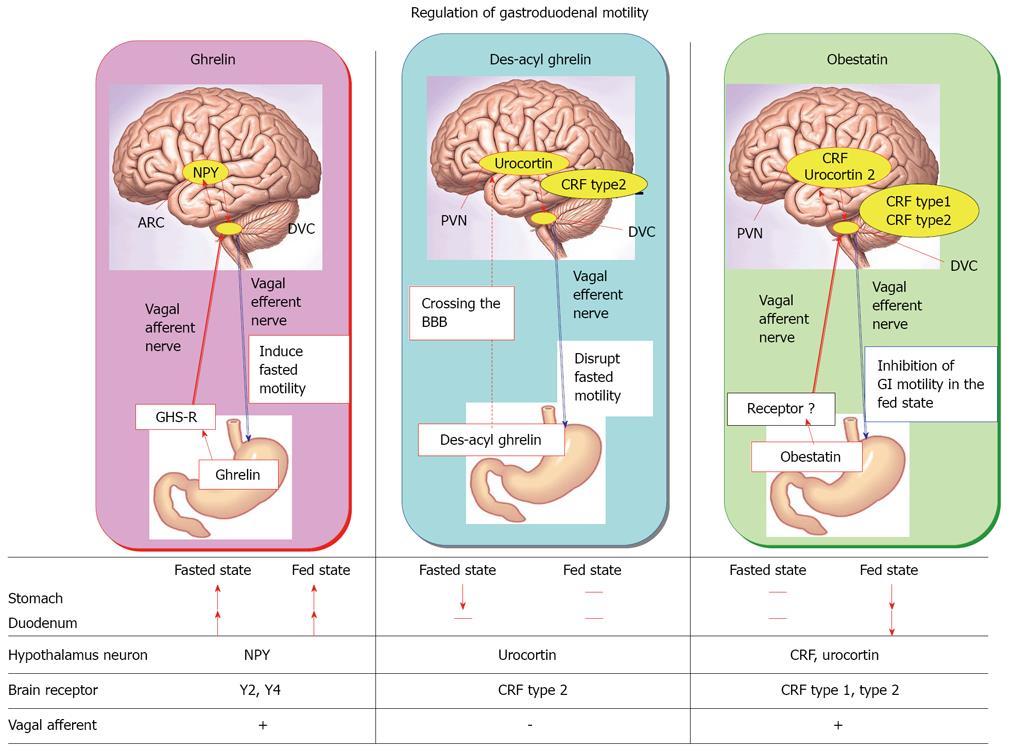
Figure 3 Summary diagram of different effects of ghrelin, des-acyl ghrelin and obestatin on the gastroduodenal motility and brain mechanisms mediating the action of these peptide.
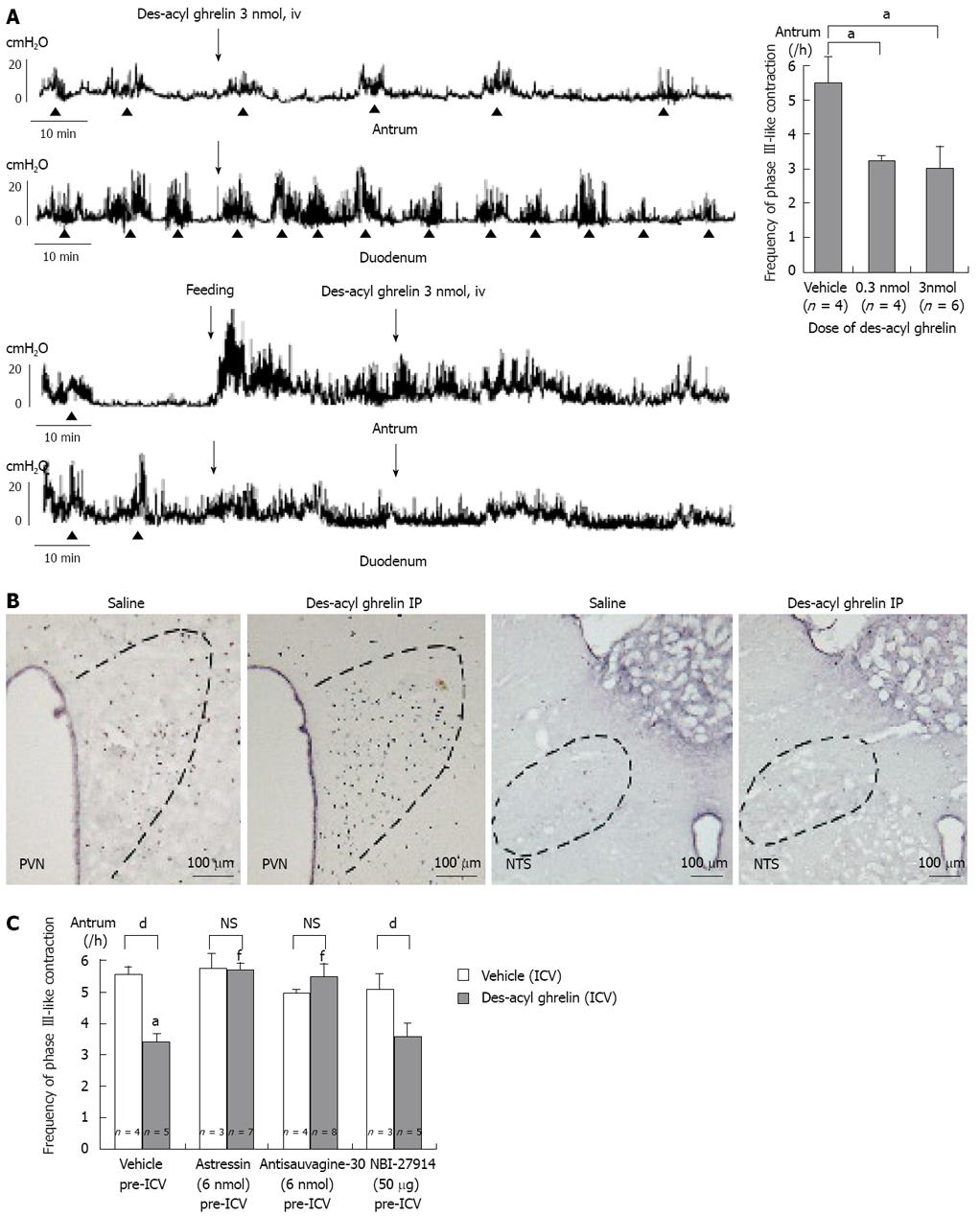
Figure 4 Des-acyl ghrelin and gastroduodenal motility.
A: Effects of iv injection of des-acyl ghrelin on the fasted and fed motor activities of the antrum and duodenum. Iv injection of des-acyl ghrelin decreases the frequency of phase III-like contractions in the antrum, but not in the duodenum. Iv injection of des-acyl ghrelin does not affect fed motor activity in both antrum and duodenum. aP < 0.05; B: The density of c-Fos-positive cells in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) is increased by ip injection of des-acyl ghrelin compared to saline-injected control, whereas that in the NTS is not altered; C: The decreased frequency of phase III-like contractions induced by iv injection of des-acyl ghrelin is restored to normal in pretreatment of nonselective CRF receptor antagonist astressin and the selective CRF type 2 receptor antagonist antisauvagine-30, but not CRF type 1 receptor antagonist NBI-27914. dP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 compared with a.
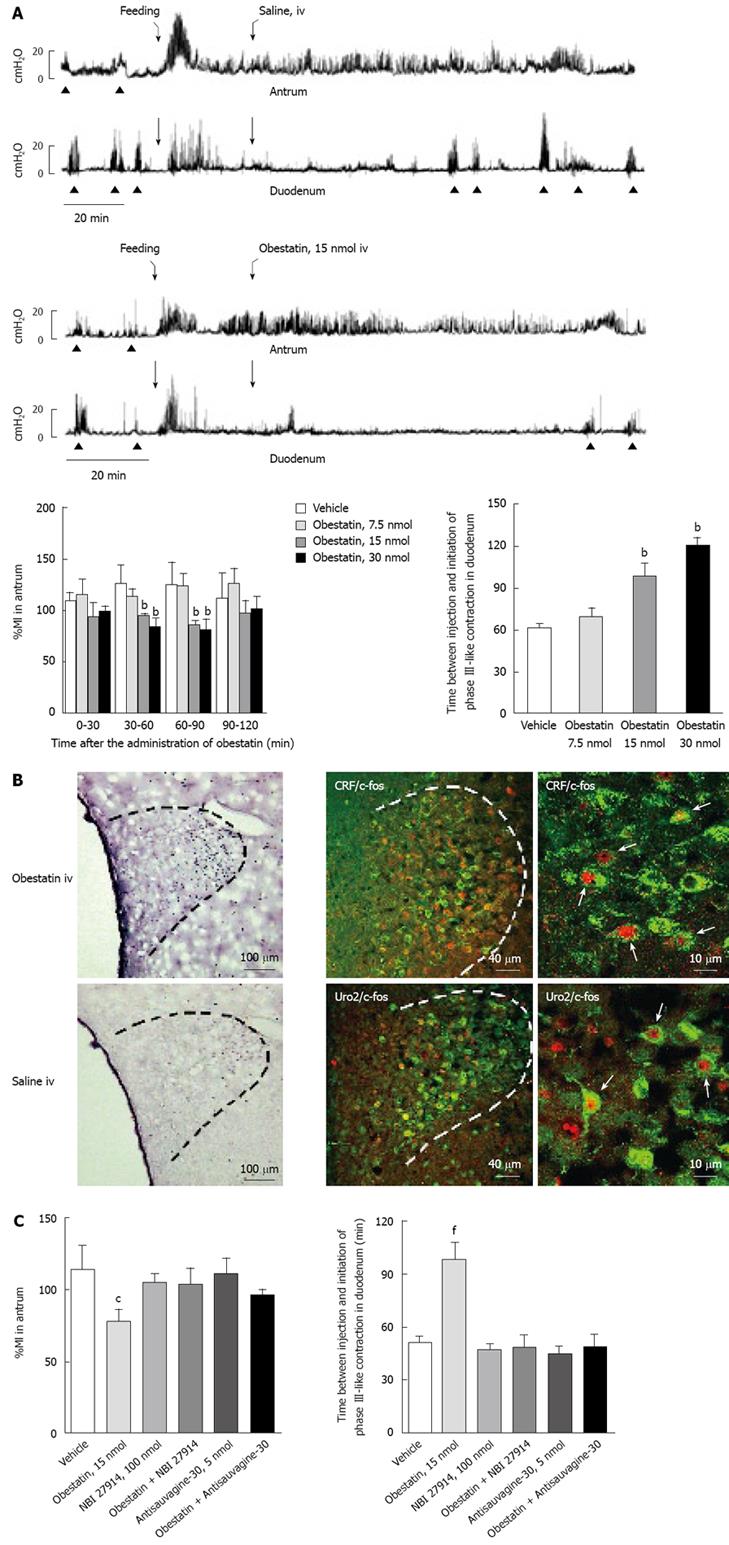
Figure 5 Obestatin and gastroduodenal motility.
A: Effects of iv injection of obestatin on the fed motor activity of the antrum and duodenum. Iv injection of obestatin dose dependently decreases the %MI during the 30-90-min period after injection of obestatin in the antrum, and prolongs the time between the initiation of phase III-like contractions and injection of obestatin in the duodenum. bP < 0.01, compared with vehicle-injected controls; B: The density of c-Fos-positive cells in the PVN is increased by iv injection of obestatin compared to saline-injected control. CRF-positive or urocortin 2-positive neurons are overlapped with c-Fos-positive neurons in the PVN; C: The decrease in %MI that is observed 30-60 min after iv injection of obestatin is reversed by icv injection of the CRF type 1 antagonist NBI-27914 and the CRF type 2 receptor antagonist antisauvagine-30. The elongation of the time between injection of obestatin and initiation of phase III-like contractions in the duodenum induced by iv injection of obestatin is also reversed by icv injection of NBI-27914 and antisauvagine-30. cP < 0.05, fP < 0.01, compared with vehicle-injected controls.
- Citation: Fujimiya M, Asakawa A, Ataka K, Kato I, Inui A. Different effects of ghrelin, des-acyl ghrelin and obestatin on gastroduodenal motility in conscious rats. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(41): 6318-6326
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i41/6318.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6318