Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2008; 14(40): 6254-6260
Published online Oct 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6254
Published online Oct 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6254
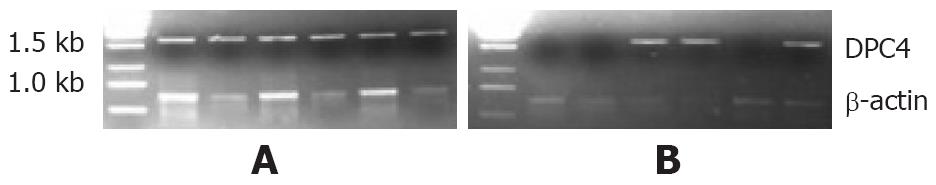
Figure 1 The mRNA of DPC4 by RT-PCR.
A: Non-malignant pancreatic species; B: Malignant pancreatic species.
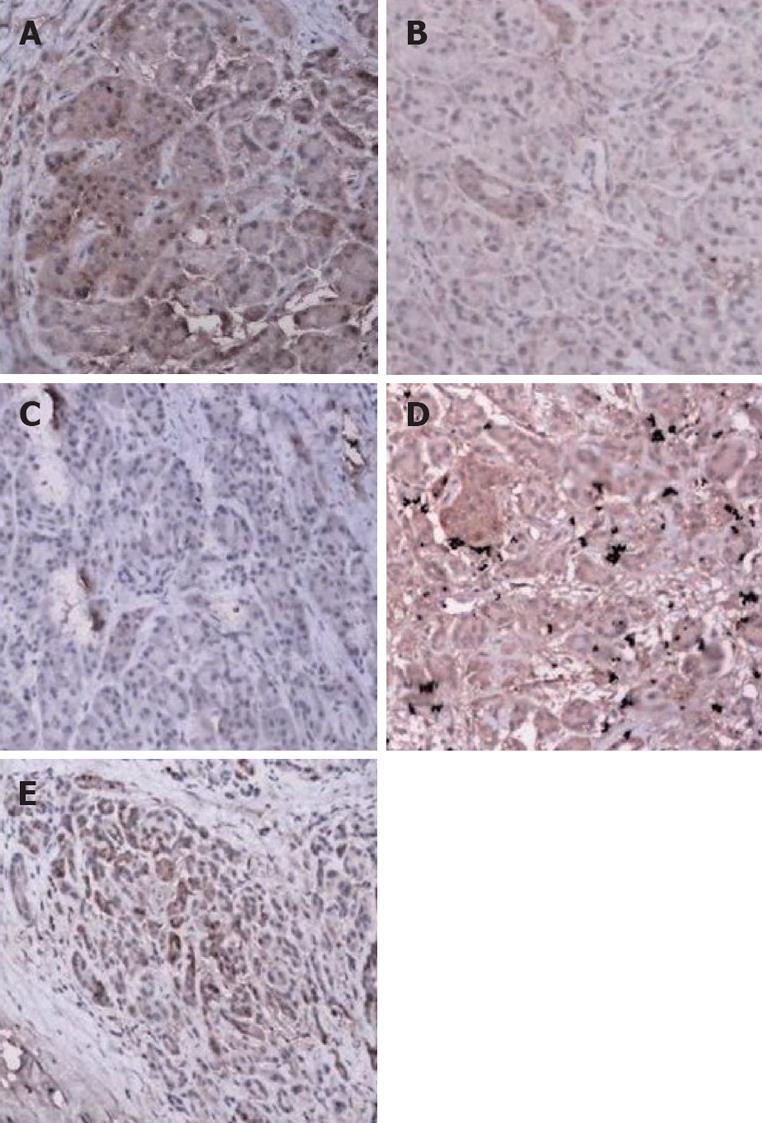
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical staining (× 100).
A: Intense positive expression of DPC4 in the nuclei and/or cytoplasm in the normal pancreatic tissue; B: Weak expression of DPC4 in normal pancreatic tissue; C: Pancreatic carcinoma showed loss of DPC4 expression; D: DPC4 expression in an adenocarcinoma with a wild-type DPC4 gene; E: Intense positive expression of DPC4 in the malignant pancreatic tissue.
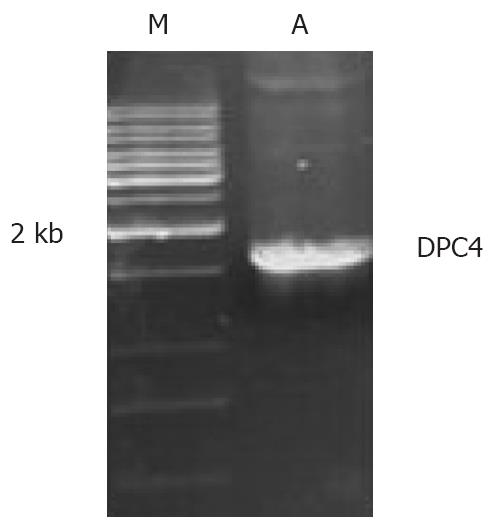
Figure 3 PCR amplification for the DPC4 gene.
A: PCR product; M: Marker.
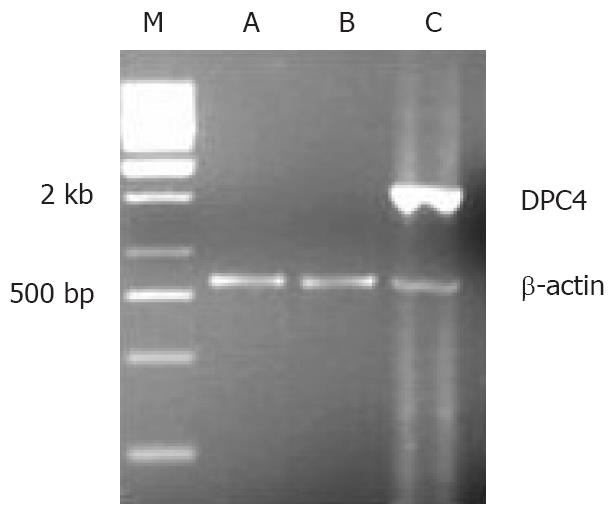
Figure 4 The expression of DPC4 mRNA in BxPC-3.
M: Marker; A: BxPC-3/-; B: BxPC-3/pLXSN; C: BxPC-3/DPC4.
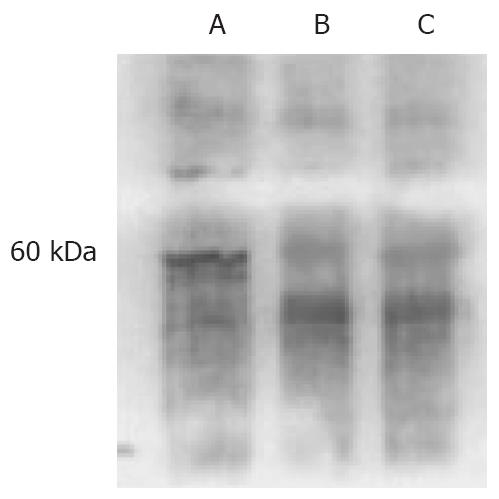
Figure 5 Westen blot for DPC4 in BxPC-3 cells.
A: BxPC-3/DPC4; B: BxPC-3/pLXSN; C: BxPC-3/-.
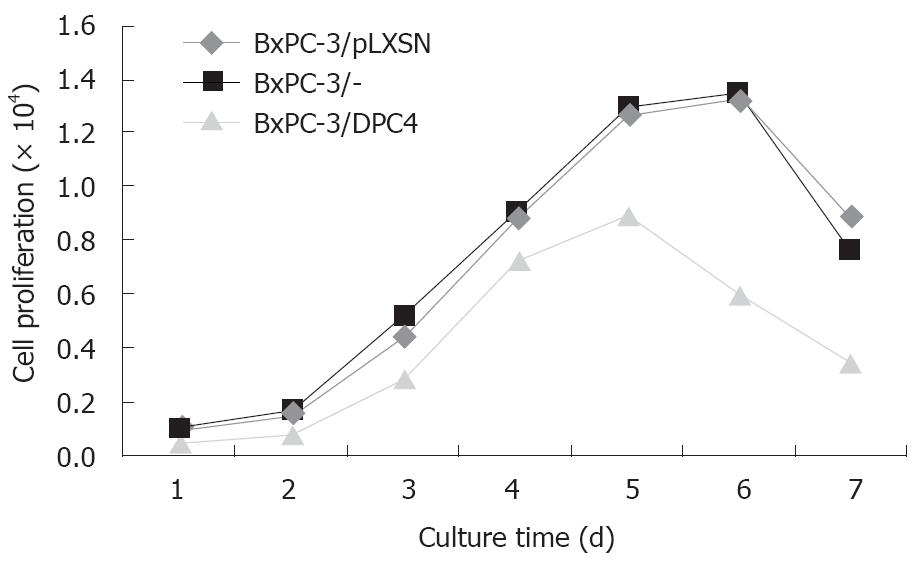
Figure 6 Cell growth curve.
P = 0.0209, BxPC-3/DPC4 vs BxPC-3/pLXSN; P = 0.0160, BxPC-3/DPC4 vs BxPC-3/-.
-
Citation: Shen W, Tao GQ, Li DC, Zhu XG, Bai X, Cai B. Inhibition of pancreatic carcinoma cell growth
in vitro by DPC4 gene transfection. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(40): 6254-6260 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i40/6254.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6254