Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2008; 14(4): 601-606
Published online Jan 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.601
Published online Jan 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.601
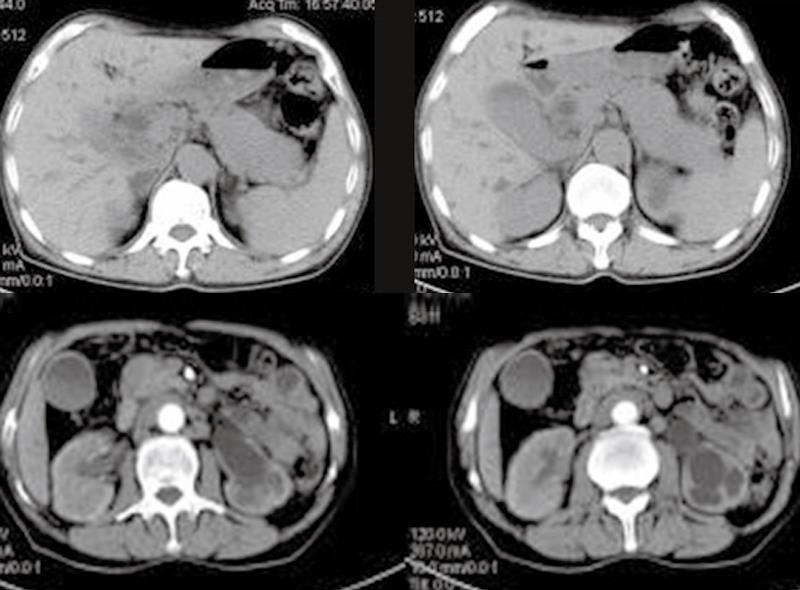
Figure 1 A patient with AIP, CT scan showed a diffusely enlarged pancreas with a sausage-like appearance, together with retroperitoneal fibrosis and nephrydrosis of left kidney.
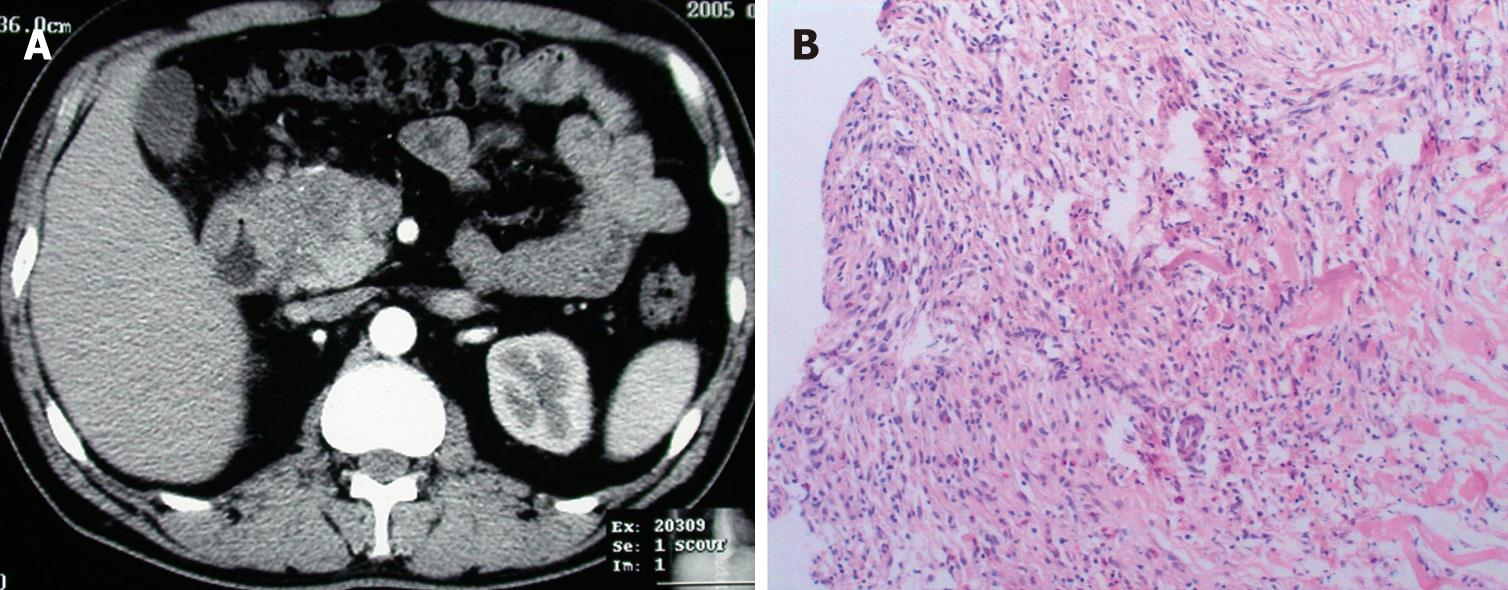
Figure 2 An asymptomatic patient with AIP, CT scan showed an enlarged head of pancreas (A), the diagnosis of AIP was confirmed by histologic findings of the pancreatic biopsy specimen: diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, obliterative phlebitis, dense parenchymal fibrosis and loss of acinar cells (HE, × 100) (B).
He underwent radiofrequency ablation for the enlarged pancreatic head.
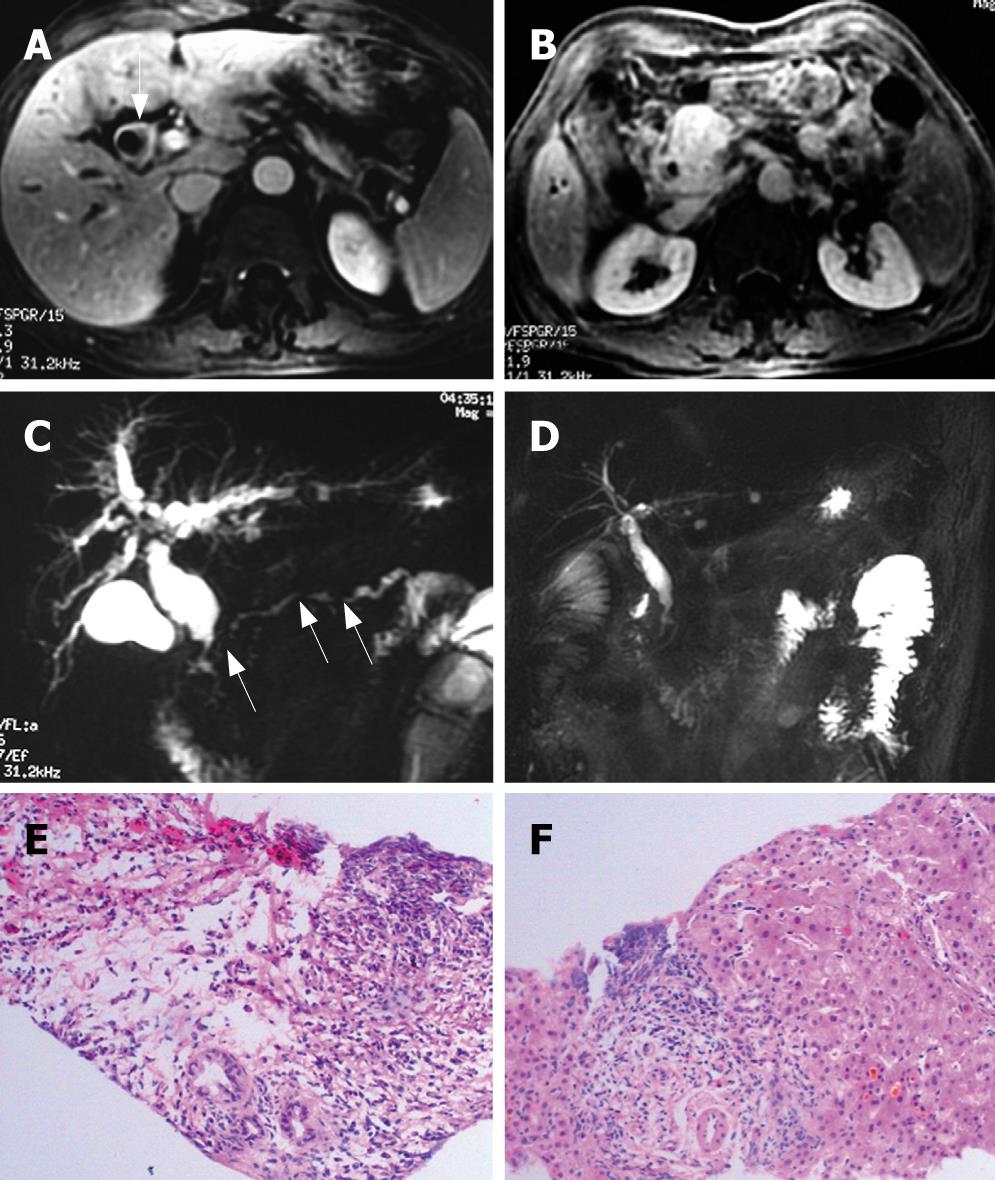
Figure 3 A patient with AIP, MRI imaging before treatment showed dilation of extrahepatic biliary ducts, thickening of hilar biliary wall (arrow) (A); and an enlarged mass in the head of pancreas (B); MRCP showed dilation of intra- and extra-hepatic biliary ducts, stricture of intrapancreatic and hilar bile duct, and segmental narrowing of main pancreatic duct (arrow) (C); after 1 mo of steroid therapy, the radiologic abnormalities resolved (D); The histologic findings of the pancreatic biopsy specimen include: dense fibrosis, diffusely lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, and acinar atrophy (HE, × 100) (E); the liver biopsy tissue also showed lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, cholestasis, and cloudy swelling of hepatocytes, especially at the portal area (HE, × 200) (F).
- Citation: Song Y, Liu QD, Zhou NX, Zhang WZ, Wang DJ. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune pancreatitis: Experience from China. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(4): 601-606
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i4/601.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.601