Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2008; 14(38): 5868-5875
Published online Oct 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5868
Published online Oct 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5868
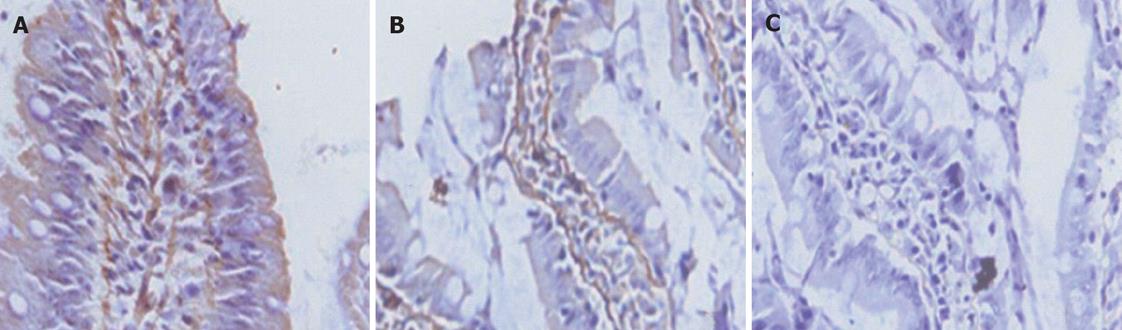
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical expression of occludin in the rat terminal ileum (× 40).
A: Control, sham-operated, the total of epithelia cell lining villi express occludin; B: End of CPB, loss of occludin expression in about 50% enterocytes at the villi; C: 2 h after CPB, loss of occludin expression in about 85% enterocytes at the villi.
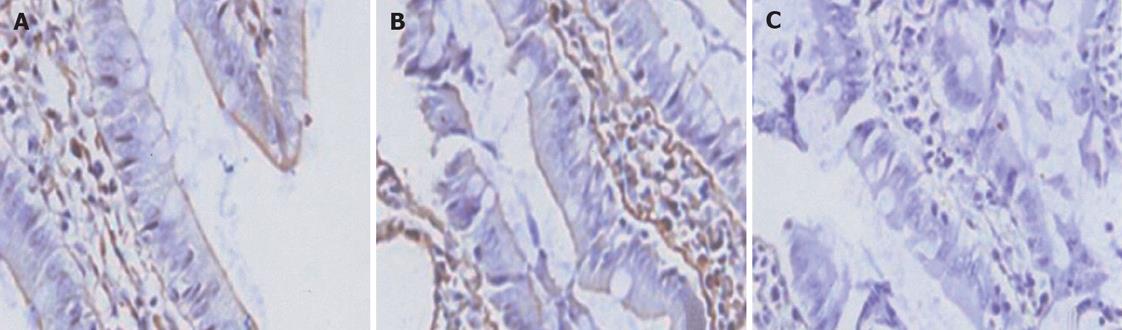
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical expression of ZO-1 in the rat terminal ileum (× 40).
A: Control, shame-operated: the total of epithelia cell lining villi express ZO-1; B: End of CPB: loss of ZO-1 expression in about 50% enterocytes at the villi; C: 2 h after CPB: loss of ZO-1 expression in about 80% enterocytes at the villi.
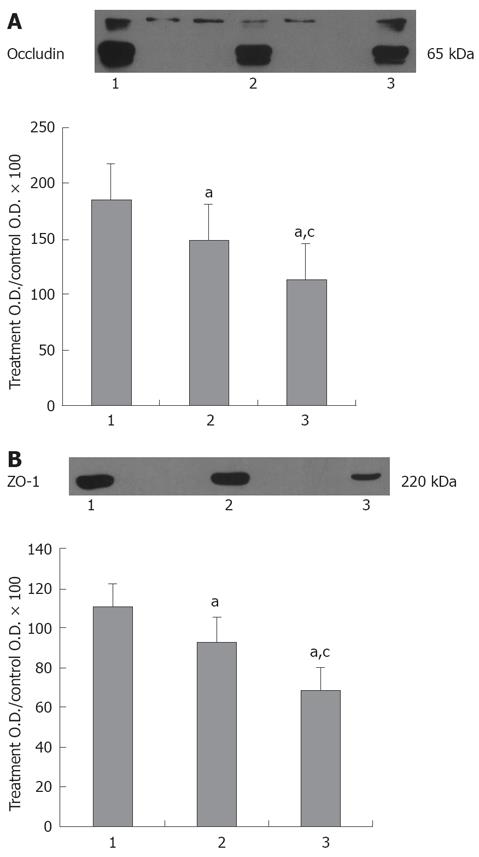
Figure 3 Western blot analysis of occludin and ZO-1 in terminal ileums.
Lane 1: Control group; Lane 2: End of CPB; Lane 3: 2 h after CPB. A: Oclludin protein expression; B: ZO-1 protein expression. Total protein was extracted from rat terminal ileums. Band densities were normalized to the mean density of saline bands and expressed as % relative content. Gel staining was used as a loading control. Bars are mean % relative content ± SE, n = 10 for each group.
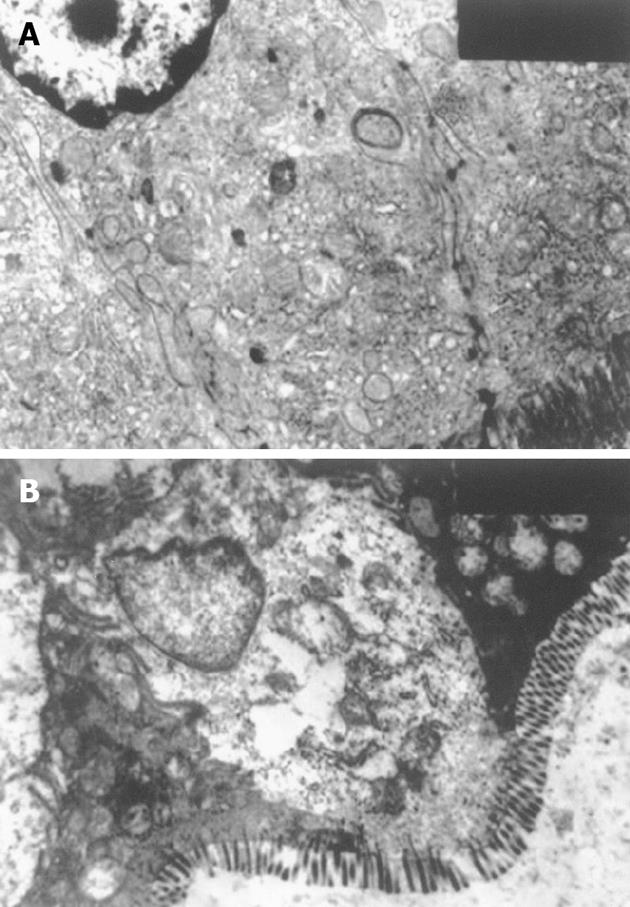
Figure 4 Effect of CPB on the ileum epithelia cells (× 7200).
A: CPB group, epithelia damage was demonstrated by swollen mitochondria and loss of cristae, tight junction was disrupted; B: Control group, regularly-aligned microvilli in intestinal epithelium, integral mitochondria and RER and distinct junction complex were observed.
- Citation: Sun YJ, Chen WM, Zhang TZ, Cao HJ, Zhou J. Effects of cardiopulmonary bypass on tight junction protein expressions in intestinal mucosa of rats. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(38): 5868-5875
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i38/5868.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.5868