Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2008; 14(3): 428-434
Published online Jan 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.428
Published online Jan 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.428
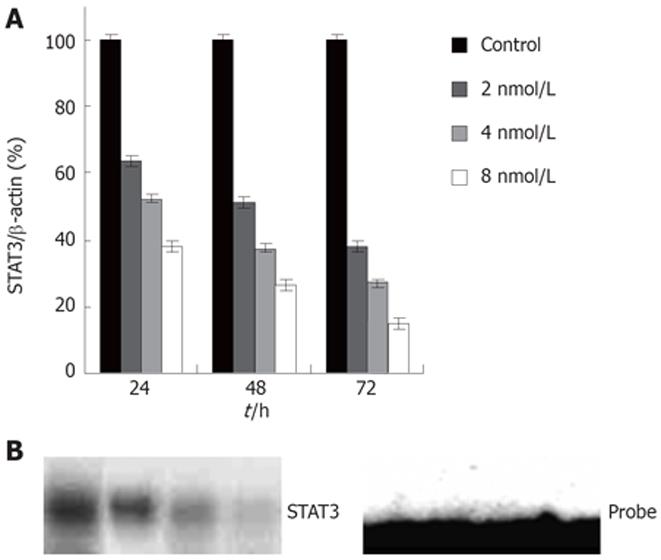
Figure 1 A: Expression of STAT3 protein in HT29 cells; B: STAT3 DNA-binding activity by EMSA in HT29 cells.
1: Control; 2, 3, 4: siRNA 2, 4, 8 nmol/L.
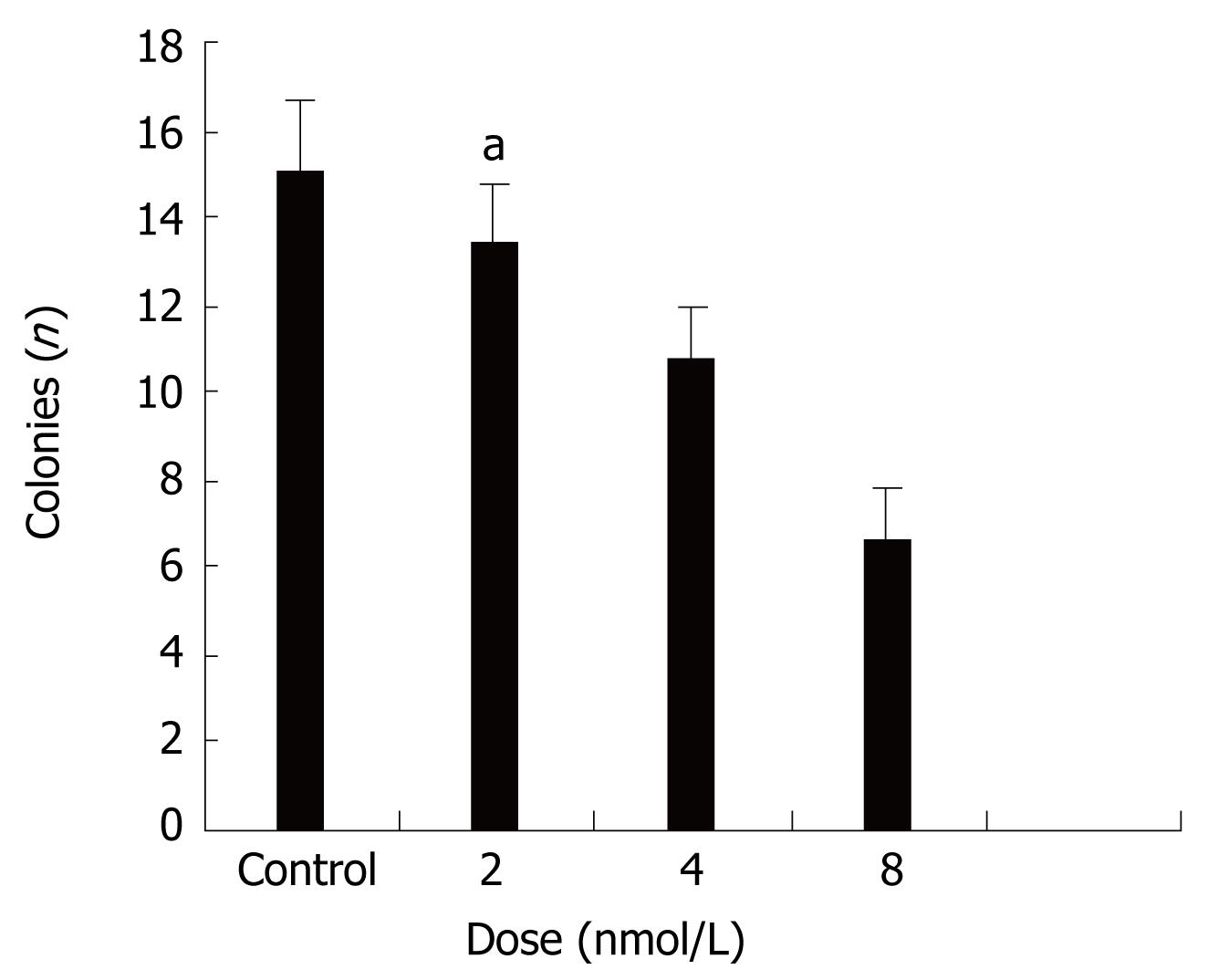
Figure 2 Effects of STAT3 siRNA on anchorage-independent growth of HT29 cells.
It shows that treatment with STAT3 siRNA inhibit anchorage-independent growth in a dose-dependent manner. aP < 0.05 between siRNA 8 nmol/L and control groups.
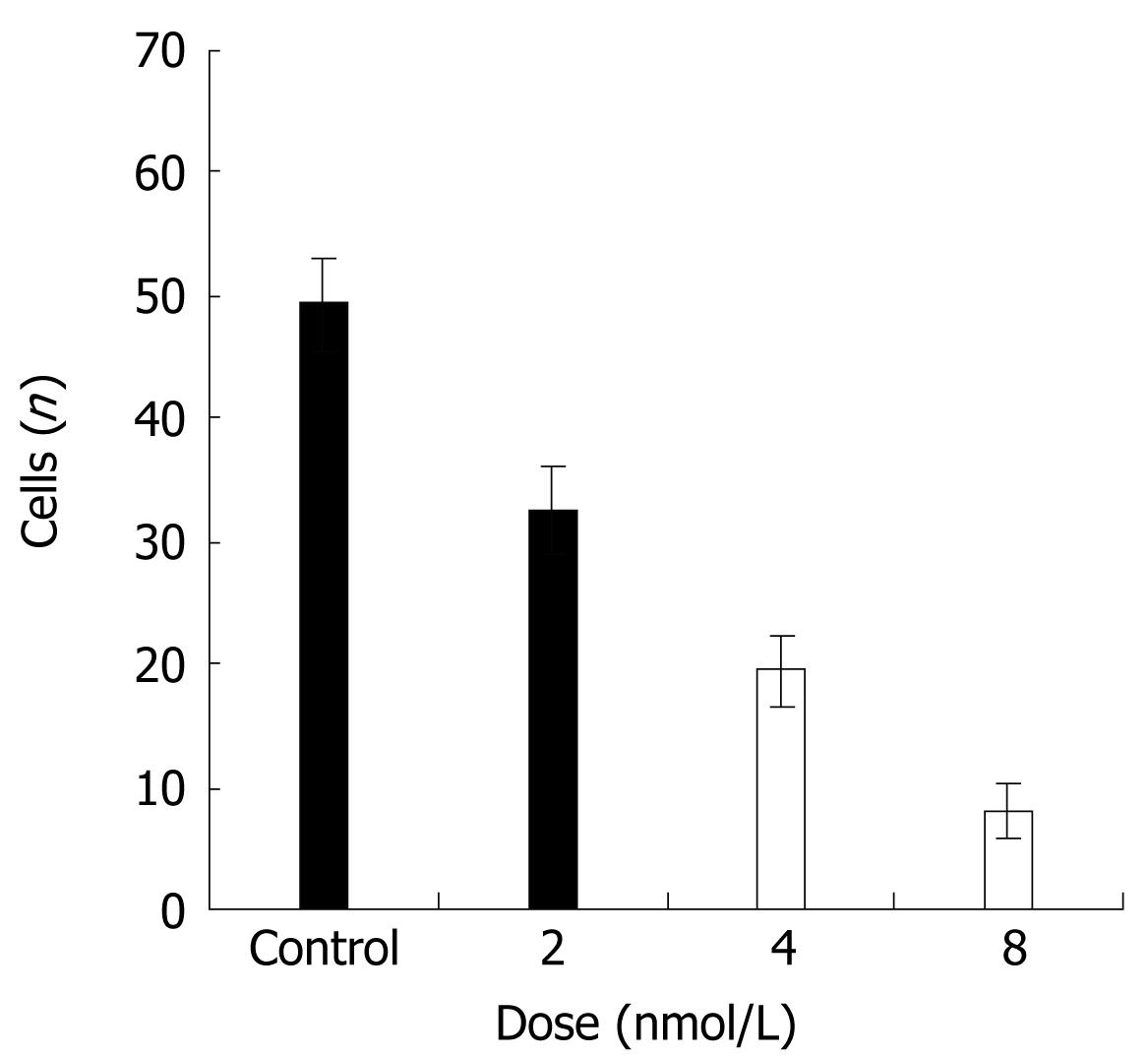
Figure 3 Effects of STAT3 suppression on the invasion ability of HT29 cells.
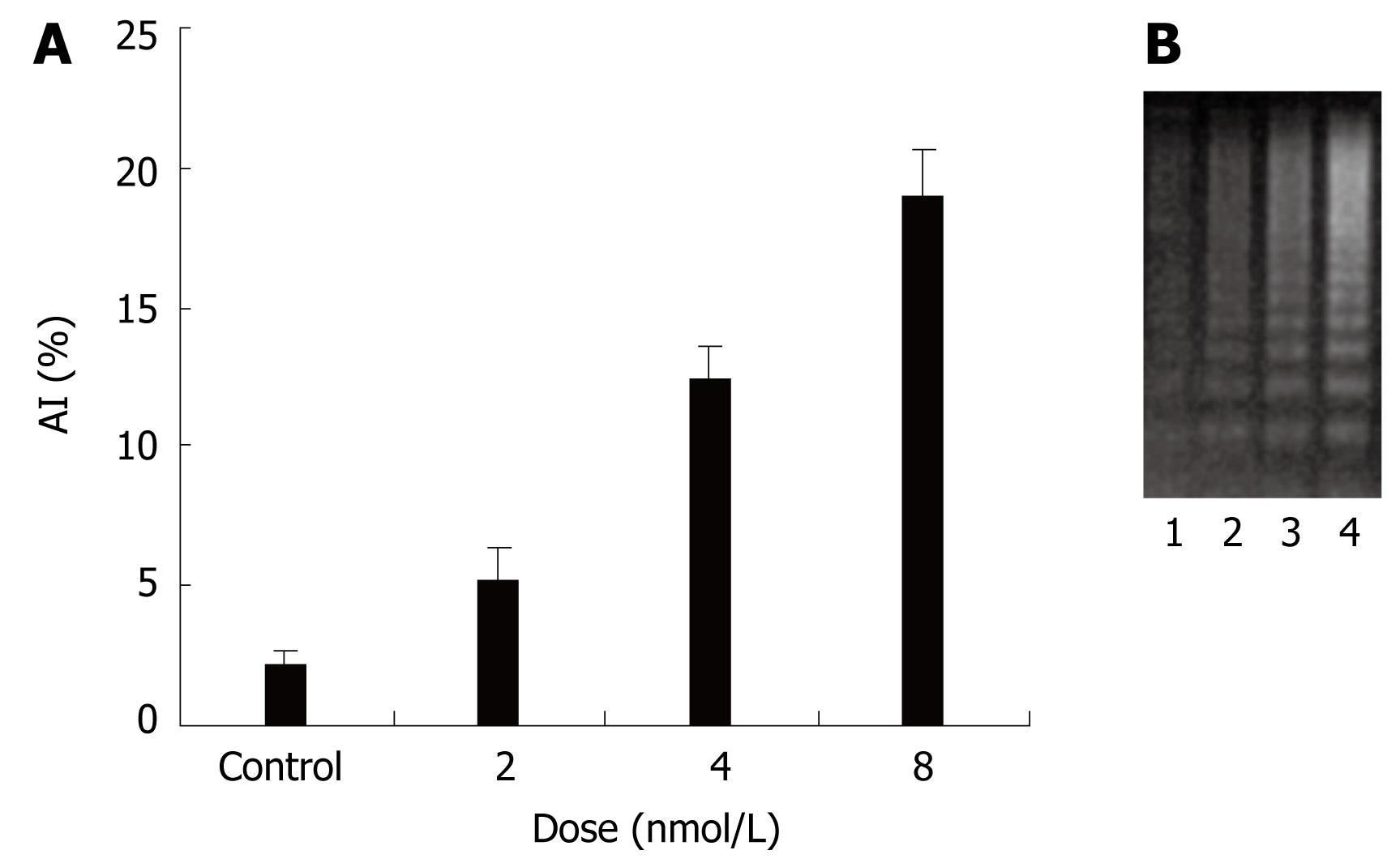
Figure 4 Effects of STAT3 siRNA on anoikis of human colon cancer cell line HT29.
A: AI (Apoptosis index) induced with STAT3 siRNA in HT29 cells; B: DNA ladder by STAT3 siRNA in HT29 cells. 1: Control; 2, 3, 4: siRNA, 2, 4, 8 nmol/L.
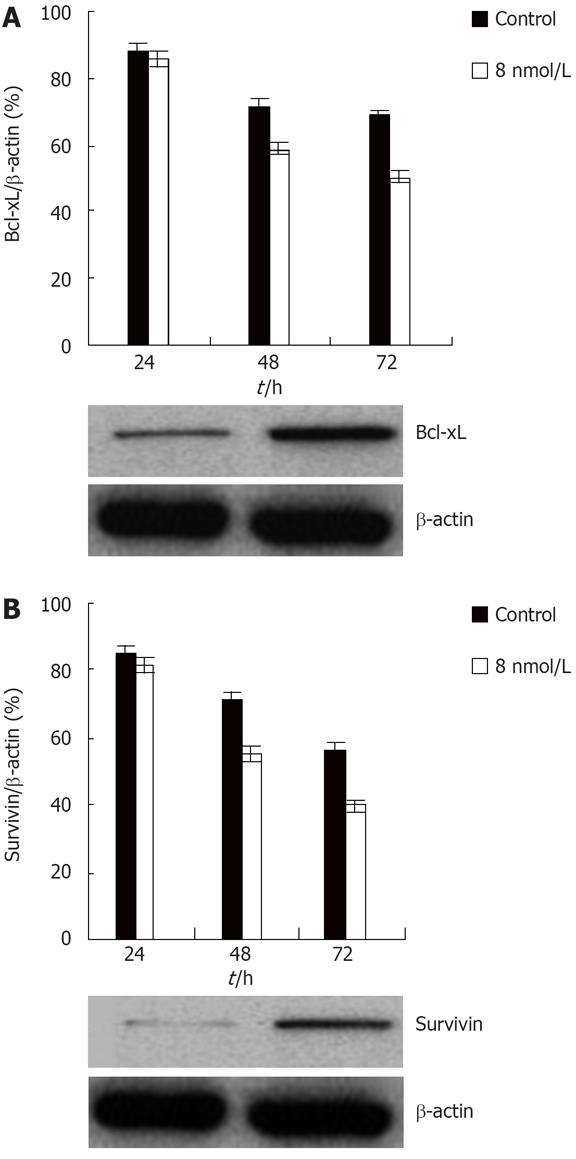
Figure 5 Knockdown of STAT3 expression downregulates Bcl-xL and survivin protein level in the HT29 human colon cancer cell line.
A: Inhibition of transfection with STAT3 siRNA on Bcl-xL expression of colon cancer HT29 cell; B: Suppression of transfection with STAT3 siRNA on survivin expression of colon cancer HT29 cell.
- Citation: Fan Y, Zhang YL, Wu Y, Zhang W, Wang YH, Cheng ZM, Li H. Inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 expression by RNA interference suppresses invasion through inducing anoikis in human colon cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(3): 428-434
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i3/428.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.428