Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishidengs.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2008; 14(29): 4684-4689
Published online Aug 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4684
Published online Aug 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4684
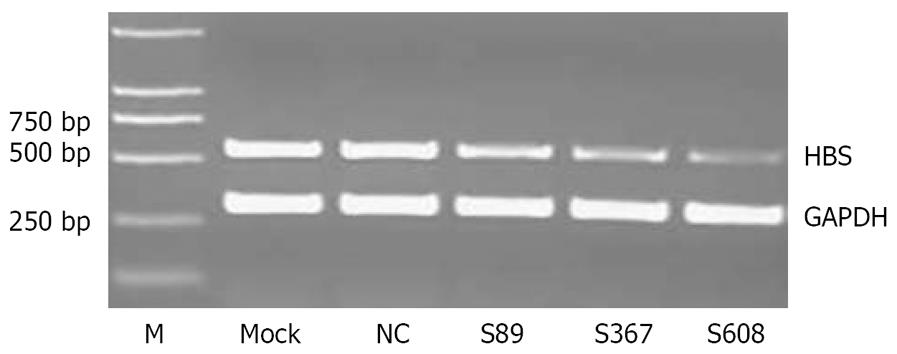
Figure 1 Effect of amiRNA-HBV with stable transfection on HBV S mRNA levels, compared with negative control, all three plasmids had significant inhibitory effect on HBV S mRNA (P = 0.
00094, 0.000047 and 0.000011, respectively).
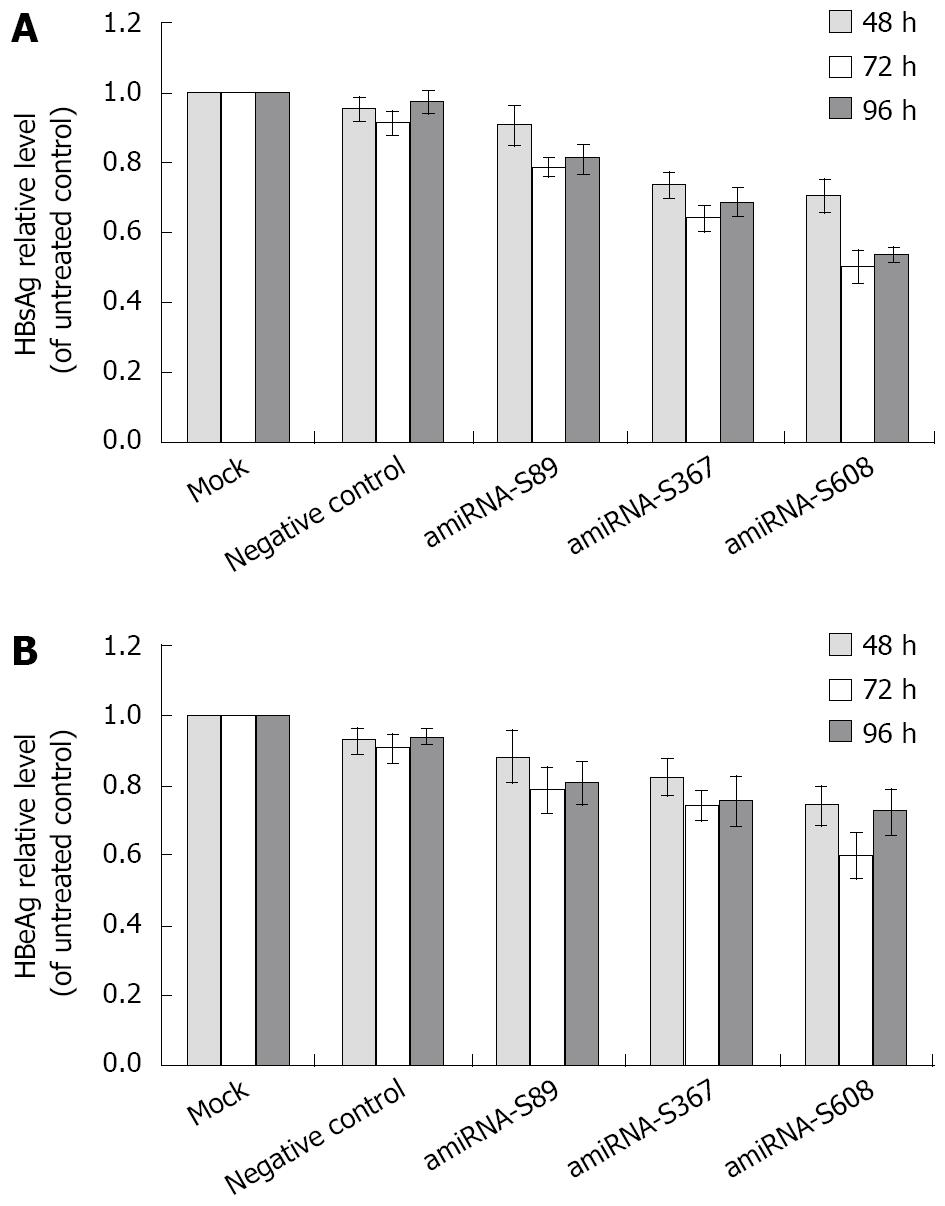
Figure 2 A: Effect of amiRNA-HBV on HBsAg levels; B: Effect of amiRNA-HBV on HBeAg levels.
HBsAg and HBeAg levels are expressed as mean ± SD. Compared with negative control, all three plasmids had significant inhibitory effect on HBsAg and HBeAg at 72 h and 96 h after transfection (HBsAg: P = 0.00039 and 0.0012 for S89 group, P = 0.000011 and 0.00021 for S367 group, P = 0.000016 and 0.000056 for S608 group; HBeAg: P = 0.02 and 0.035 for S89 group, P = 0.0093 and 0.0032 for S367 group, P = 0.007 and 0.0025 for S608 group).
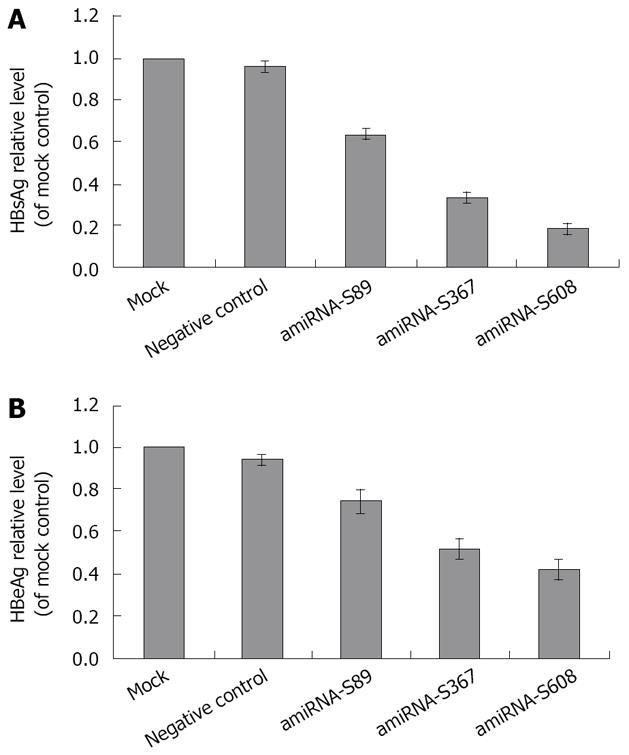
Figure 3 A: Effect of amiRNA-HBV with stable transfection on HBsAg levels; B: Effect of amiRNA-HBV with stable transfection on HBeAg levels.
HBsAg and HBeAg levels are expressed as mean ± SD. Compared with negative control, all three plasmids had significant inhibitory effect on HBsAg and HBeAg (HBsAg: P = 0.00019, 0.000035 and 0.000012, respectively; HBeAg: P = 0.003, 0.0002 and 0.000024, respectively).
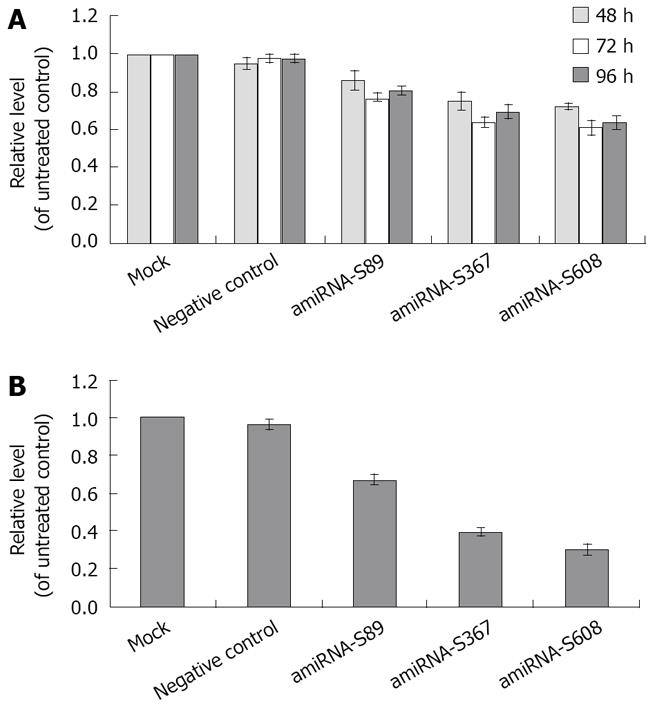
Figure 4 A: Effect of amiRNA-HBV with transient transfection on HBV DNA levels; B: Effect of amiRNA-HBV with stable transfection on HBV DNA levels, The amounts of HBV DNA are expressed as mean ± SD.
Compared with negative control, all three plasmids had significant inhibitory effect on HBsAg and HBeAg at 48 h, 72 h and 96 h after transfection (P = 0.049, 0.000021 and 0.0011 for S89 group; P = 0.0002, 0.000016 and 0.0012 for S367 group; P = 0.0003, 0.00006 and 0.00016 for S608 group). All three plasmids had significant inhibitory effect on HBV DNA in stably transfected groups, (P = 0.00009, 0.000007 and 0.000006, respectively).
- Citation: Gao YF, Yu L, Wei W, Li JB, Luo QL, Shen JL. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus gene expression and replication by artificial microRNA. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(29): 4684-4689
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i29/4684.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.4684