Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2008; 14(28): 4499-4504
Published online Jul 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4499
Published online Jul 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4499
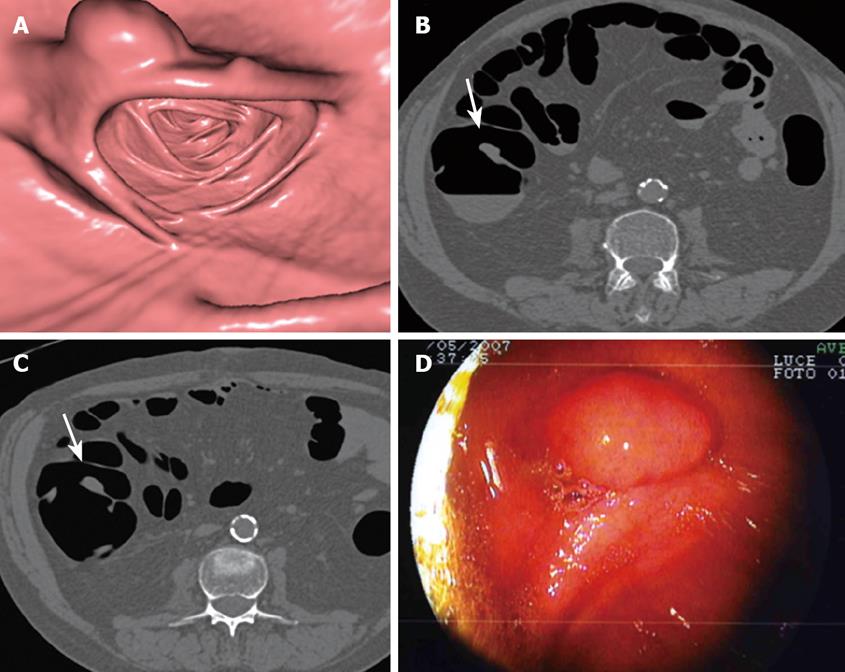
Figure 1 Adenomatous polyp of 13 mm of the ascending colon in a 61-year-old female with initial colonoscopy interrupted at the descending colon for severe discomfort.
A: Endoluminal CT image of the ascending colon shows 13 mm sessile polyp lying on a fold; B and C: Axial CT images acquired in supine and prone position show the polypoid lesion (arrow) on a fold; D: Sessile polyp of 13 mm of the ascending colon found at repeat colonoscopy. Histology evaluation revealed adenomatous polyp.
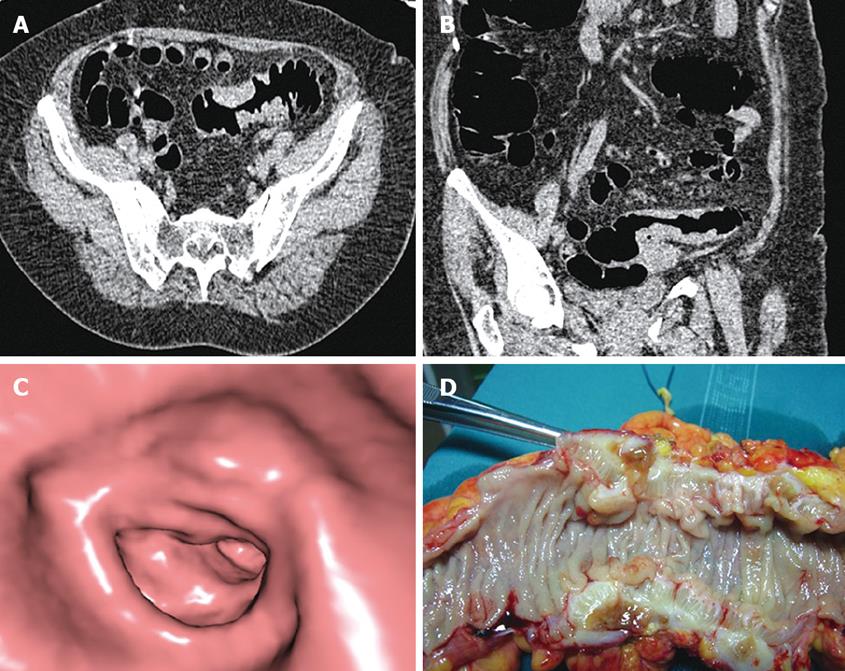
Figure 2 Stenosing mass of the proximal sigmoid colon in a 69-year-old female with initial colonoscopy interrupted at the distal sigmoid colon for diverticular disease.
A: Axial CT image acquired in prone decubitus shows a stenosing lesion of the proximal sigmoid colon with CT findings suspicious for malignancy: eccentric wall thickening, “shoulder sign”, absence of pericolonic fat stranding; B: Coronal oblique multiplanar reformation shows the lesion in the sigmoid colon; C: Endoluminal CT image shows the passage from the normal colonic wall to the stenosis; D: Surgical specimen from left hemicolectomy shows a stenosing lesion of about 5 cm in the proximal sigmoid colon with marked wall thickening due to advanced diverticular disease confirmed at histological evaluation.
- Citation: Sali L, Falchini M, Bonanomi AG, Castiglione G, Ciatto S, Mantellini P, Mungai F, Menchi I, Villari N, Mascalchi M. CT colonography after incomplete colonoscopy in subjects with positive faecal occult blood test. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(28): 4499-4504
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i28/4499.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.4499