Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2008; 14(25): 4054-4058
Published online Jul 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4054
Published online Jul 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4054
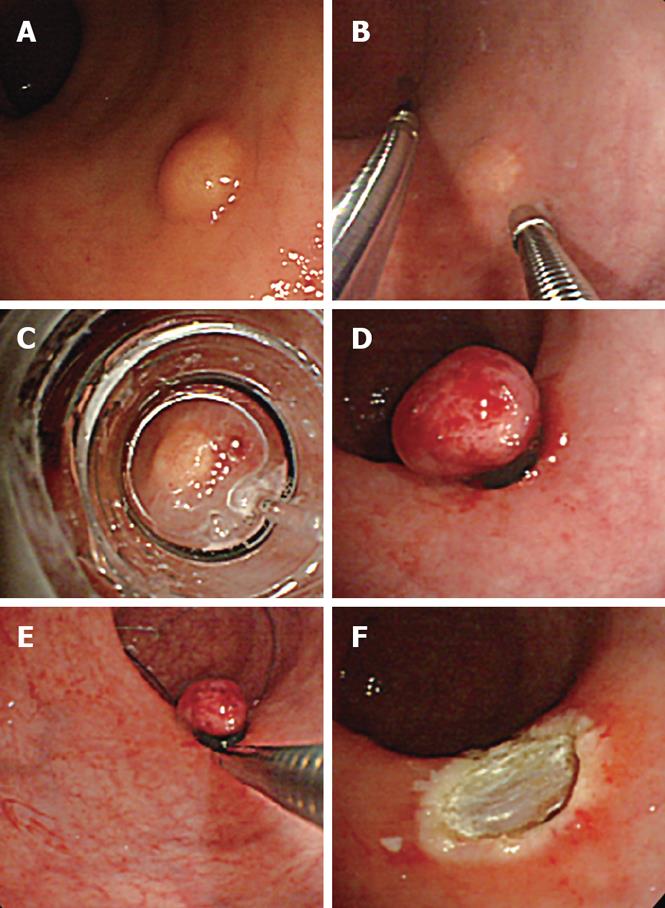
Figure 1 EMR-L combined with 3D-EUS using an ultrasonic probe.
A: Endoscopic view of rectal carcinoid; B: 3D-EUS was performed at the same time as saline injection into the submucosal layer; C: Aspiration of the tumor into the ligation device; D: Tumor ligated with the elastic band; E: Snaring below the elastic band; F: Ulcer after resection.
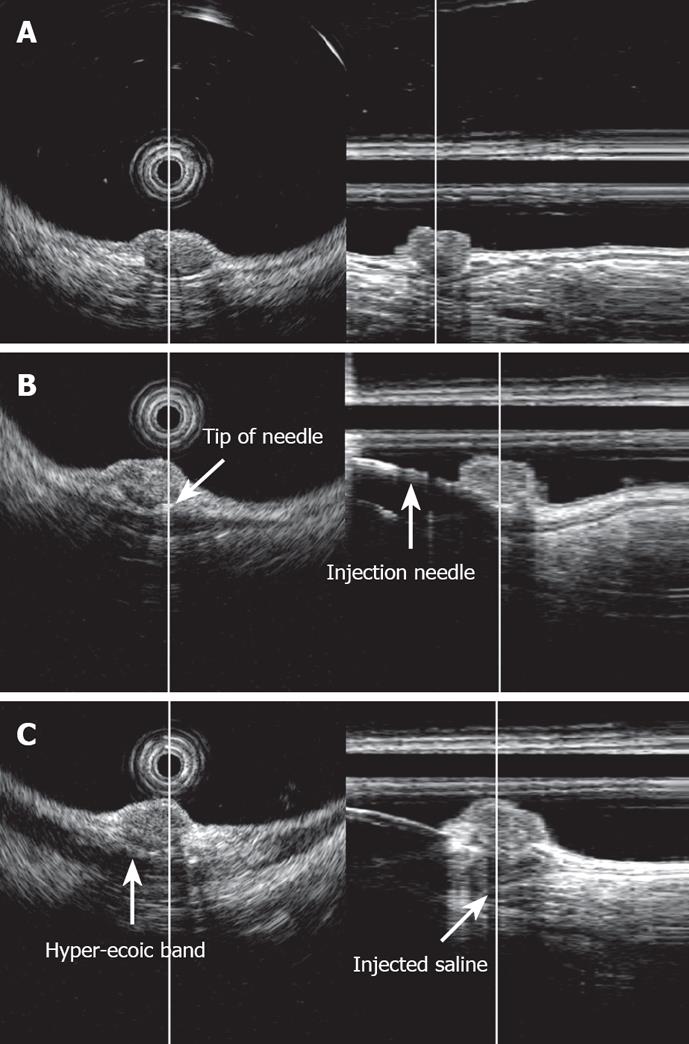
Figure 2 EUS image of rectal carcinoid (radial and linear image).
A: Carcinoid was imaged as a low-echoic region with a depth of invasion to the third layer, i.e. the submucosal layer; B: Image upon saline injection into the submucosal layer. The tip of the injection needle was located beneath the tumor in the submucosal layer; C: Image after saline injection into the submucosal layer. The injected saline was imaged as a low-echoic area beneath the tumor in the submucosal layer.
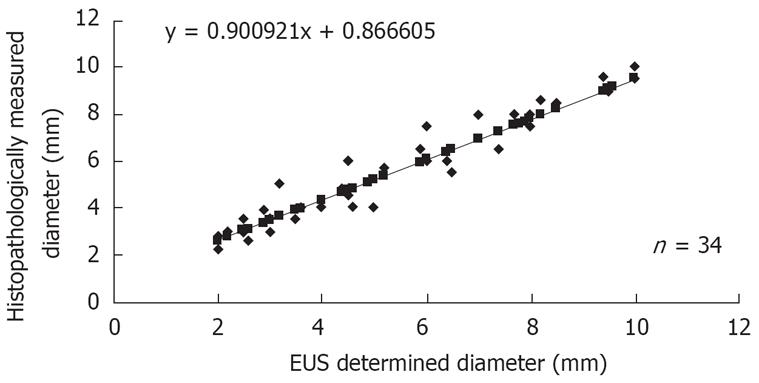
Figure 3 Comparison between EUS-determined and histopathologically measured tumor diameter.
- Citation: Abe T, Kakemura T, Fujinuma S, Maetani I. Successful outcomes of EMR-L with 3D-EUS for rectal carcinoids compared with historical controls. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(25): 4054-4058
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i25/4054.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.4054