Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2008; 14(24): 3872-3878
Published online Jun 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3872
Published online Jun 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3872
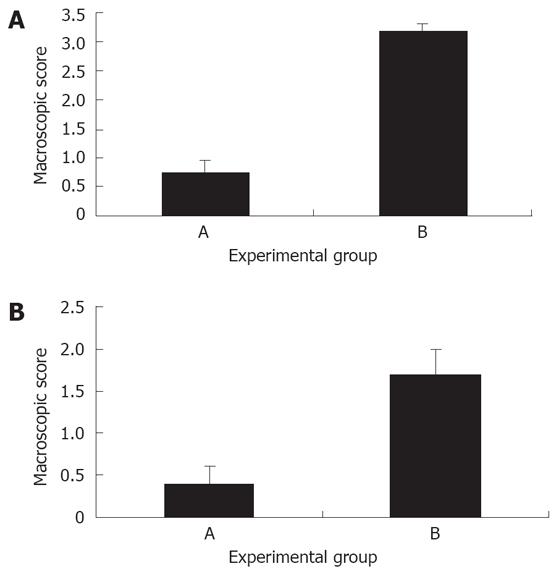
Figure 1 A: Effect of Shiitake administration on the macroscopic score of experimental colitis: Shiitake administration significantly alleviated the severity of colitis in group A mice compared with mice in control group B; B: Effect of Shiitake administration on the microscopic score of colitis: Shiitake administration alleviated the severity of colitis in group A mice compared with mice in control group B.
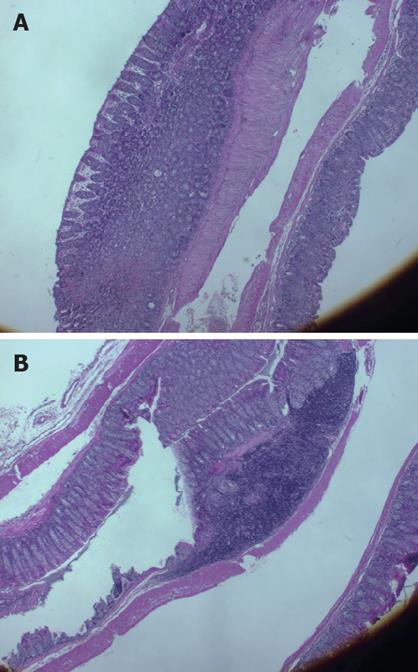
Figure 2 Histological evaluation of colonic tissues showed a marked reduction in the inflammatory response in Shiitake fed mice (A).
By contrast, severe colitis was observed in mice in group B, manifested by inflammatory infiltration of the mucosa, and patchy necrosis of the mucosa and submucosa, with purulent and fibrinoid material extending to the muscle layer (B).
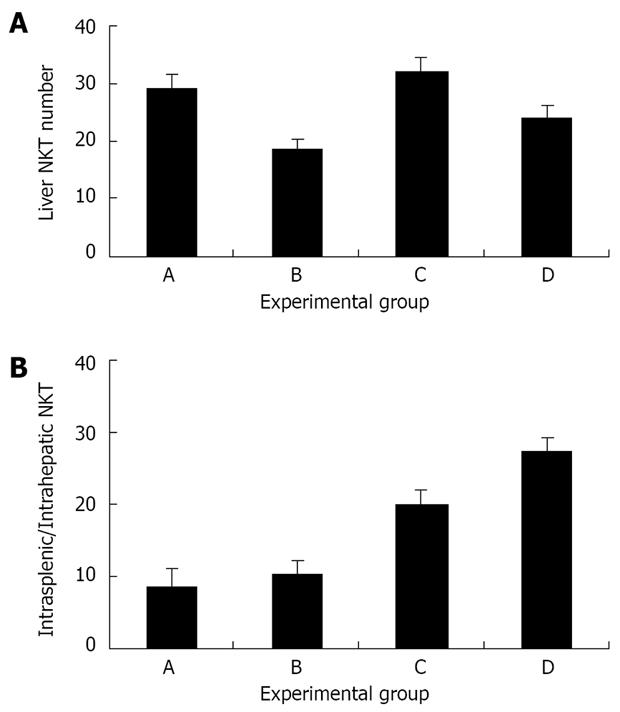
Figure 3 A: The effect of Shiitake administration on intrahepatic NKT cells.
Liver NKT cell numbers were increased in groups A and C (which received Shiitake), compared with mice in group B and in control group D; B: The effect of Shiitake administration on the intrasplenic/ intrahepatic NKT cell ratio.
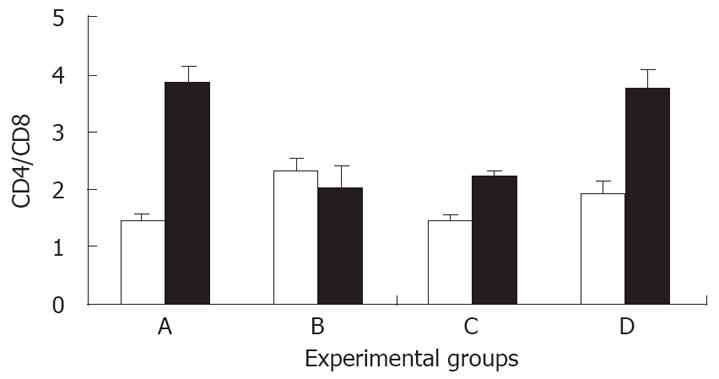
Figure 4 Effect of Shiitake administration on the intra-hepatic (open bars) and intrasplenic (black bars) CD4/CD8 ratio.
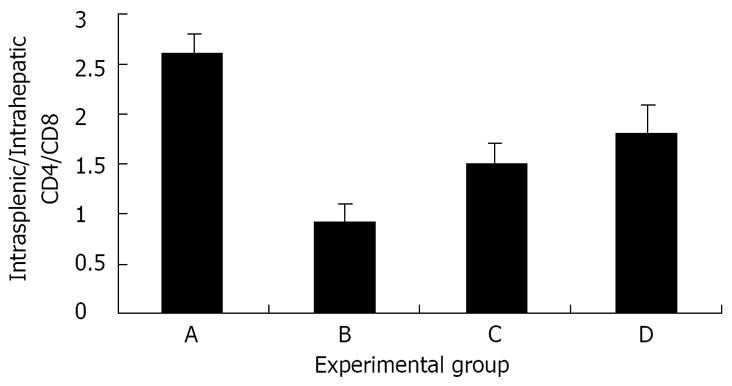
Figure 5 The effect of Shiitake administration on the intrasplenic/intrahepatic CD4/CD8 ratio: The peripheral (spleen)/intrahepatic (liver) CD4/CD8 ratio was markedly increased in groups A, C, and D.
By contrast, the ratio was markedly reduced in group B.
- Citation: Shuvy M, Hershcovici T, Lull-Noguera C, Wichers H, Danay O, Levanon D, Zolotarov L, Ilan Y. Intrahepatic CD8+ lymphocyte trapping during tolerance induction using mushroom derived formulations: A possible role for liver in tolerance induction. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(24): 3872-3878
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i24/3872.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.3872